Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mo hot atoms made by a neutron capture method from
Mo hot atoms made by a neutron capture method from  -MoO
-MoO to water
to waterQuach, N. M.*; Ngo, M. C.*; Yang, Y.*; Nguyen, T. B.*; Nguyen, V. T.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Do, T. M. D.*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(10), p.4057 - 4064, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:71.02(Chemistry, Analytical)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is the most widely used medical radioisotope in the world and is produced from molybdenum-99 (
Tc) is the most widely used medical radioisotope in the world and is produced from molybdenum-99 ( Mo). Production of
Mo). Production of  Mo via the neutron capture method draws attention as an alternative to fission-derived
Mo via the neutron capture method draws attention as an alternative to fission-derived  Mo due to non-proliferation issues, but the specific radioactivity of
Mo due to non-proliferation issues, but the specific radioactivity of  Mo is extremely low. In this work, a porous
Mo is extremely low. In this work, a porous  -MoO
-MoO wire was prepared as an irradiation target in order to improve the specific activity by extracting
wire was prepared as an irradiation target in order to improve the specific activity by extracting  Mo. Porous
Mo. Porous  -MoO
-MoO wire is synthesized from Mo metal wire by a two-step heating procedure. The hot atom effect of
wire is synthesized from Mo metal wire by a two-step heating procedure. The hot atom effect of  Mo was confirmed by activity and isotope measurements of the porous
Mo was confirmed by activity and isotope measurements of the porous  -MoO
-MoO wire after neutron irradiation and the water used for extraction. In term of the extraction effectiveness, the effectiveness of
wire after neutron irradiation and the water used for extraction. In term of the extraction effectiveness, the effectiveness of  Mo extraction in the porous
Mo extraction in the porous  -MoO
-MoO wire was comparable to that of commercial
wire was comparable to that of commercial  -MoO
-MoO powder.
powder.
 -MoO
-MoO whiskers in
whiskers in  Mo/
Mo/ Tc radioisotope production and
Tc radioisotope production and  Mo/
Mo/ Tc extraction using hot atoms
Tc extraction using hot atomsNgo, M. C.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Do, T. M. D.*; Seki, Misaki; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Niihara, Koichi*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(32), p.13140 - 13147, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:60.95(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.
Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.  Tc is a daughter product of the
Tc is a daughter product of the  Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce
Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n,
Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n, ) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n,
) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n, ) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,
) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,  -MoO
-MoO whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and
whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and  -MoO
-MoO particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce
particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the
Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc. As a result,
Tc. As a result,  -MoO
-MoO whisker yielded higher
whisker yielded higher  Mo extraction rate than that from
Mo extraction rate than that from  -MoO
-MoO . In addition, by comparing the dissolved
. In addition, by comparing the dissolved  Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of
Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of  -MoO
-MoO whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of
whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of  -MoO
-MoO being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,
being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,  -MoO
-MoO is considered a promising irradiation target for producing
is considered a promising irradiation target for producing  Mo/
Mo/ Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
 Mo/
Mo/ Tc generator by (n,
Tc generator by (n,  ) method, 4
) method, 4Fujita, Yoshitaka; Seki, Misaki; Ngo, M. C.*; Do, T. M. D.*; Hu, X.*; Yang, Y.*; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Nakano, Hiroko; Fujihara, Yasuyuki*; Yoshinaga, Hisao*; et al.
KURNS Progress Report 2021, P. 118, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
Burr, T.*; Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Howell, J.*; Jongo, C. E.*; Hamada, M. S.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 640(1), p.200 - 212, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.99(Instruments & Instrumentation)Process monitoring (PM) is increasingly important in nuclear safeguards as a complement to mass-balance based nuclear materials accounting (NMA). Typically, PM involves more frequent but lower quality measurements than NMA. While NMA estimates special nuclear material (SNM) mass balances and uncertainties, PM often tracks SNM attributes qualitatively or in the case of solution monitoring (SM) tracks bulk mass and volume. Automatic event marking is used in several nuclear safeguards PM systems. All methods are evaluated on both raw and smoothed data, and several smoothing options are compared, including standard filters, hybrid filters, and local kernel smoothing. The main finding is that for real and simulated examples considered, a two-step strategy is most effective. First, any reasonably effective initial smoother is used to provide a good initial guess at change point locations. Second, PLR is applied, looking for one change point at a time.
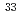 Mg sheds new light on the
Mg sheds new light on the  =20 island of inversion
=20 island of inversionKanungo, R.*; Nociforo, C.*; Prochazka, A.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Aumann, T.*; Boutin, D.*; Cortina-Gil, D.*; Davids, B.*; Diakaki, M.*; Farinon, F.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 685(4-5), p.253 - 257, 2010/05
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:86.47(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
 O as a new doubly magic nucleus
O as a new doubly magic nucleusKanungo, R.*; Nociforo, C.*; Prochazka, A.*; Aumann, T.*; Boutin, D.*; Cortina-Gil, D.*; Davids, B.*; Diakaki, M.*; Farinon, F.*; Geissel, H.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 102(15), p.152501_1 - 152501_4, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:96.80(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Be halo nucleus from
Be halo nucleus from  Bi at coulomb barrier
Bi at coulomb barrierMazzocco, M.*; Signorini, C.*; Romoli, M.*; De Francesco, A.*; Di Pietro, M.*; Vardaci, E.*; Yoshida, Koichi*; Yoshida, Atsushi*; Bonetti, R.*; De Rosa, A.*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 28(3), p.295 - 299, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:89.49(Physics, Nuclear)The scattering of the radioactive, weakly bound, halo nucleus  Be from
Be from  Bi has been studied at 40 MeV. The measurement performed with a low-intensity and a large-emittance secondary beam could be made using an extremely compact, large solid angle (
Bi has been studied at 40 MeV. The measurement performed with a low-intensity and a large-emittance secondary beam could be made using an extremely compact, large solid angle ( 2
2 sr) detecting set-up, based on 8 highly segmented Si telescopes. The
sr) detecting set-up, based on 8 highly segmented Si telescopes. The 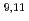 Be scattering angular distributions, as well as their relative reaction cross-sections, resulted to be rather similar. This may suggest that at Coulomb barrier energies the halo structure and the small weakly binding energy of the
Be scattering angular distributions, as well as their relative reaction cross-sections, resulted to be rather similar. This may suggest that at Coulomb barrier energies the halo structure and the small weakly binding energy of the  Be projectile have no big influence on the reaction dynamics.
Be projectile have no big influence on the reaction dynamics.
 targets; Contribution by vietnamese institutes, staffs and students
targets; Contribution by vietnamese institutes, staffs and studentsSuematsu, Hisayuki*; Ngo, M. C.*; Quach, N. M.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Do, T. M. D.*; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Nguyen, V. T.*; Niihara, Koichi*
no journal, ,
Radiopharmacies have been used in various medical diagnoses/therapies and their market has been growing by ten times in fifteen years. In particular,  Tc has been widely used in gamma ray diagnoses.
Tc has been widely used in gamma ray diagnoses.  Mo, the raw material for
Mo, the raw material for  Tc, is currently produced as a fission product by irradiating highly enriched uranium in nuclear reactors. Efforts are being made worldwide to reduce the use of uranium from the perspective of nuclear non-proliferation. A
Tc, is currently produced as a fission product by irradiating highly enriched uranium in nuclear reactors. Efforts are being made worldwide to reduce the use of uranium from the perspective of nuclear non-proliferation. A  Mo(n,
Mo(n, )
) Mo reaction in low enriched uranium reactors can be an alternative method. In this research, we revealed that
Mo reaction in low enriched uranium reactors can be an alternative method. In this research, we revealed that  -MoO
-MoO , a low-temperature phase of MoO
, a low-temperature phase of MoO , as a neutron irradiation target promotes the diffusion of
, as a neutron irradiation target promotes the diffusion of  Mo from the target to water due to the hot atom effect. Utilizing this phenomenon can contribute to the stable supply of
Mo from the target to water due to the hot atom effect. Utilizing this phenomenon can contribute to the stable supply of  Mo and
Mo and  Tc. The first nuclear reaction in/water dispersion experiments using an
Tc. The first nuclear reaction in/water dispersion experiments using an  -MoO
-MoO powder target was carried out in Dalat Nuclear Reactor, Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute to show the hot atom effect. Then, the water recovery efficiency was dramatically improved using a novel
powder target was carried out in Dalat Nuclear Reactor, Vietnam Atomic Energy Institute to show the hot atom effect. Then, the water recovery efficiency was dramatically improved using a novel  -MoO
-MoO whisker target by Vietnamese students and staffs. Their contributions to this research will be explained in the presentation.
whisker target by Vietnamese students and staffs. Their contributions to this research will be explained in the presentation.
Broughton, D.*; Suzuki, Risa; Nagatani, Taketeru; Okada, Toyofumi; Henzlova, D.*; Longo, J.*; Mendez, J.*; Rael, C.*; Swinhoe, M. T.*
no journal, ,
This presentation will discuss issues and potential improvements in the measurement of nuclear material generated from ongoing decommissioning activities at JAEA facilities. This material is subject to safeguards requirements, but its high impurity content makes it difficult to measure using standard deployed NDA systems.