Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS method
C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS methodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Sharma, A.*; Kumar, R.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Pellegrini, M.*; Yokoyama, Ryo*; Okamoto, Koji*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 250, p.127343_1 - 127343_17, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:0Hartzell, S.*; Furutani, K. M.*; Parisi, A.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kase, Yuki*; Deglow, C.*; Friedrich, T.*; Beltran, C. J.*
Radiation (Internet), 5(2), p.21_1 - 21_24, 2025/06
Fablet, L.*; P drot, M.*; Choueikani, F.*; Kieffer, I.*; Proux, O.*; Pierson-Wickmann, A.-C.*; Cagniart, V.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Marsac, R.*
drot, M.*; Choueikani, F.*; Kieffer, I.*; Proux, O.*; Pierson-Wickmann, A.-C.*; Cagniart, V.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Marsac, R.*
Environmental Science; Nano, 12(5), p.2815 - 2827, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nickel is an omnipresent trace element in the environment. Due to its high affinity for iron oxide nanoparticles, its elimination from soils and water by these nanoparticles represents an interesting strategy, specially by magnetites, which is naturally present in the environment. However, the interactions between Ni and magnetite are poorly understood, because of the difficulty to control the stoichiometry (Fe(II)-to-Fe(III) ratio) of magnetite. The behavior of Ni in the presence of magnetite nanoparticles with different stoichiometries, in aqueous solution and inert atmosphere, are probed by adsorption experiments and X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy. This study helps predicting the interactions between Ni and magnetite in environmental conditions, which can be used for the development of efficient remediation strategies.
Hartzell, S.*; Parisi, A.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Beltran, C. J.*; Furutani, K. M.*
Physics in Medicine & Biology, 70(10), p.105010_1 - 105010_19, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Biomedical) crystals
crystalsTakatori, Sayuri*; Pimon, M.*; Pollitt, S.*; Bartokos, M.*; Beeks, K.*; Gr neis, A.*; Hiraki, Takahiro*; Homma, Tetsuo*; Hosseini, N.*; Leitner, A.*; et al.
neis, A.*; Hiraki, Takahiro*; Homma, Tetsuo*; Hosseini, N.*; Leitner, A.*; et al.
New Journal of Physics (Internet), 27(4), p.043024_1 - 043024_10, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Recent reports on laser excitation of the low-energy thorium-229 ( Th) nuclear isomeric state in calcium fluoride single crystals render this system a promising candidate for a solid-state nuclear clock. However, experimental characterization of the microscopic ion arrangement around the doped
Th) nuclear isomeric state in calcium fluoride single crystals render this system a promising candidate for a solid-state nuclear clock. However, experimental characterization of the microscopic ion arrangement around the doped  Th and its electronic charge state, crucial for the precise control of the clock transition and assessing the solid-state clock's performance, remains an unresolved task. This study uses X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy of
Th and its electronic charge state, crucial for the precise control of the clock transition and assessing the solid-state clock's performance, remains an unresolved task. This study uses X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy of  Th:CaF
Th:CaF to investigate the charge state and coordination environment of doped
to investigate the charge state and coordination environment of doped  Th. The results indicate that
Th. The results indicate that  Th is doped with a 4+ valence at the substitutional site of the Ca
Th is doped with a 4+ valence at the substitutional site of the Ca ion, with charge compensated provided by two F
ion, with charge compensated provided by two F ions located at interstitial sites adjacent to
ions located at interstitial sites adjacent to  Th.
Th.
 C-SS eutectic melting and its relocation behaviour
C-SS eutectic melting and its relocation behaviourAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Okamoto, Koji*
Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 50(5), p.3361 - 3371, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Scaria, J.*; P drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
drot, M.*; Fablet, L.*; Yomogida, Takumi; Nguyen, T. T.*; Sivry, Y.*; Catrouillet, C.*; Pradas del Real, A. E.*; Choueikani, F.*; Vantelon, D.*; et al.
Environmental Science & Technology, 59(11), p.5747 - 5755, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Understanding and predicting the interaction mechanisms between chromium and magnetite is of particular interest to elucidate the biogeochemical behavior of Cr in the environment and to develop optimal soil remediation and water treatment strategies. However, while the elimination of the most toxic form of (Cr(VI)) by its reduction to Cr(III) has widely been documented, elucidating the exact mechanism involved in Cr(III) sorption to magnetite has attracted less attention. This study examined the interaction of Cr(III) solution with 10 nm-sized magnetites, whose stoichiometries were carefully defined and preserved in anaerobic conditions. This study reveals the joint effects of pH and magnetite stoichiometry on Cr(III) sorption mechanism, and that Cr(III)-(hydr)oxide precipitation is not necessarily the driving process of Cr(III) elimination from solutions. These results will help predict the fate and transport of chromium, as well as developing magnetite-based chromium remediation processes.
Yoshida, M.*; McDermott, R. M.*; Angioni, C.*; Camenen, Y.*; Citrin, J.*; Jakubowski, M.*; Hughes, J. W.*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Mantica, P.*; Mariani, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 65(3), p.033001_1 - 033001_132, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Progress in physics understanding and theoretical model development of plasma transport and confinement in the ITPA Transport and Confinement Topical Group since the publication of the ITER Physics Basis was summarized focusing on the contributions to ITER and burning plasma prediction and control. This paper provides a general and streamlined overview on the advances that were mainly led by the ITPA TC joint experiments and joint activities for the last 15 years. This paper starts with the scientific strategy and scope of the ITPA TC Topical group and overall picture of the major progress, followed by the progress of each research field: particle transport, impurity transport, ion and electron thermal turbulent transport, momentum transport, impact of 3D magnetic fields on transport, confinement mode transitions, global confinement, and reduced transport modeling.
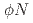 correlation function
correlation functionAbreu, L. M.*; Gubler, P.; Khemchandani, K. P.*; Mart nez Torres, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
nez Torres, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physics Letters B, 860, p.139175_1 - 139175_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:52.60(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Parisi, A.*; Furutani, K. M.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Beltran, C. J.*
Medical Physics, 51(10), p.7589 - 7605, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:70.65(Radiology, Nuclear Medicine & Medical Imaging)In this study, we have developed an approximate MKM (microdosimetric kinetic model) based on LET (dose-averaged linear energy transfer) to address the challenges of biological relative effectiveness (RBE) models for proton therapy. This is an attempt to apply the mechanism-based approach used in carbon ion therapy to proton beams. This LET-based MKM establishes a correlation between dose-averaged LET and microbiological indices and successfully models survival rates for multiple cell lines. This has resulted in a mathematical description of RBE based on physical quantities that can be readily used in proton therapy planning systems.
Sogabe, Joji; Ishida, Shinya; Tagami, Hirotaka; Okano, Yasushi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Onoda, Yuichi; Matsuba, Kenichi; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Kubota, Ryuzaburo*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In the frame of France-Japan collaboration, the calculational methodologies were defined and assessed, and the phenomenology and the severe accident consequences were investigated in a pool-type sodium-cooled fast reactor.
 H to
H to  U
UParisi, A.*; Furutani, K. M.*; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Beltran, C. J.*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(3), p.18_1 - 18_16, 2024/09
Endo, Shunsuke; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ino, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 60(8), p.166_1 - 166_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear) Se from combined conversion-electron and
Se from combined conversion-electron and  -ray spectroscopy
-ray spectroscopySmallcombe, J.; Garnsworthy, A. B.*; Korten, W.*; Singh, P.*; Muir, D.*; Pr chniak, L.*; Ali, F. A.*; Andreoiu, C.*; Ansari, S.*; Ball, G. C.*; et al.
chniak, L.*; Ali, F. A.*; Andreoiu, C.*; Ansari, S.*; Ball, G. C.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 110(2), p.024318_1 - 024318_16, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.60(Physics, Nuclear) C-stainless steel using the Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS) Method
C-stainless steel using the Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS) MethodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Okamoto, Koji*; Sharma, A.*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2024/08
The analysis show that once eutectic reaction occurs, the boron diffuses into the stainless steel (SS) wall. Melting initiates at the B C and SS interface, with melt flow following SS cladding penetration. Also, we observed that as temperature rises, a proportional increase in the boron concentration within the melt. The updated MPS method indicated a computational capability of the eutectic reaction model used to effectively analyze control rod eutectic reactions, simulating severe accidents, and its subsequent relocation to understand the effect of B
C and SS interface, with melt flow following SS cladding penetration. Also, we observed that as temperature rises, a proportional increase in the boron concentration within the melt. The updated MPS method indicated a computational capability of the eutectic reaction model used to effectively analyze control rod eutectic reactions, simulating severe accidents, and its subsequent relocation to understand the effect of B C ingress into the core.
C ingress into the core.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Takai, Toshihide; Emura, Yuki; Fukuyama, Hiroyuki*; Higashi, Hideo*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Morita, Koji*; Nakamura, Kinya*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2024/08
This paper describes the project overview and progress of experimental and analytical studies conducted until 2022. A specific result in this paper is to obtain first experimental data of B C-SS eutectic freezing.
C-SS eutectic freezing.
Costantini, J.-M.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(3), p.20_1 - 20_16, 2024/08
A novel Coulomb spike concept is applied to the radiation damage induced in LiF and SiO with about the same mass density (
with about the same mass density ( 2.65 g cm
2.65 g cm ) by
) by 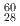 Ni and
Ni and 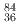 Kr ions of 1.0-MeV/u energy for about the same electronic energy loss (10 MeV/um). The distribution of ionizations and electrostatic energy gained in the electric field by the ionized atoms is computed with the PHITS code for both targets. Further, the atomic collision cascades induced by these low energy hot ions of about 500 eV are simulated with the SRIM2013 code. It is found that melting is reached in a small volume for SiO
Kr ions of 1.0-MeV/u energy for about the same electronic energy loss (10 MeV/um). The distribution of ionizations and electrostatic energy gained in the electric field by the ionized atoms is computed with the PHITS code for both targets. Further, the atomic collision cascades induced by these low energy hot ions of about 500 eV are simulated with the SRIM2013 code. It is found that melting is reached in a small volume for SiO due to the energy deposition in the subthreshold events of nuclear collisions induced by the Si and O ions. For LiF, the phonon contribution to the stopping power of the lighter Li and F ions is not sufficient to induce melting, even though the melting temperature is lower than for SiO
due to the energy deposition in the subthreshold events of nuclear collisions induced by the Si and O ions. For LiF, the phonon contribution to the stopping power of the lighter Li and F ions is not sufficient to induce melting, even though the melting temperature is lower than for SiO . The formation of amorphous domains in SiO
. The formation of amorphous domains in SiO is likely after fast quenching of the small molten pockets, whereas only point defects may be formed in LiF.
is likely after fast quenching of the small molten pockets, whereas only point defects may be formed in LiF.
 C powder and B
C powder and B C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steel
C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steelHong, Z.*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Erkan, N.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 171, p.105160_1 - 105160_13, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:91.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, it is found that the eutectic reaction between B C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B
C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B
C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
 C pellet-stainless steel under radiative heating
C pellet-stainless steel under radiative heatingAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kano, Sho*; Okamoto, Koji*
Ceramics International, 50(10), p.17665 - 17680, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:51.99(Materials Science, Ceramics)In this study, we identified two distinct failure mechanisms: the separation of stainless steel from the B C pellet, resulting in the formation of a later melting drop, and the fracture of the B
C pellet, resulting in the formation of a later melting drop, and the fracture of the B C pellet into multiple pieces, possibly due to thermal stress. The visualization technique and thermal interfacial resistance analysis precisely captured the eutectic temperature.
C pellet into multiple pieces, possibly due to thermal stress. The visualization technique and thermal interfacial resistance analysis precisely captured the eutectic temperature.
Baccou, J.*; Glantz, T.*; Ghione, A.*; Sargentini, L.*; Fillion, P.*; Damblin, G.*; Sueur, R.*; Iooss, B.*; Fang, J.*; Liu, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 421, p.113035_1 - 113035_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:96.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)