Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yakushev, A.*; Gates, J. M.*; T rler, A.*; Sch
rler, A.*; Sch del, M.; D
del, M.; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Block, M.*; Br
llmann, Ch. E.*; Ackermann, D.*; Andersson, L.-L.*; Block, M.*; Br chle, W.*; Dvorak, J.*; et al.
chle, W.*; Dvorak, J.*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 53(3), p.1624 - 1629, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:113 Percentile:98.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We report on a gas-solid chromatography study of the adsorption of element 114 (flerovium, Fl) on a Au surface. Fl was produced in the nuclear fusion reaction  Pu(
Pu( Ca, 3-4n)
Ca, 3-4n)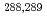 Fl and was isolated in-flight from the primary
Fl and was isolated in-flight from the primary  beam in a physical recoil separator. The adsorption behavior of Fl, its nuclear
beam in a physical recoil separator. The adsorption behavior of Fl, its nuclear  -decay product Cn, their lighter homologues in groups 14 and 12, i.e., Pb and Hg, and the noble gas Rn were studied simultaneously by isothermal gas chromatography and thermochromatography. Two Fl atoms were detected. They adsorbed on a Au surface at room temperature, but not as readily as Pb and Hg. The observed adsorption behavior of Fl points to a higher inertness compared to its nearest homologue in the group, Pb. However, the measured lower limit for the adsorption enthalpy of Fl on a Au surface points to the formation of a metal-metal bond of Fl with Au. Fl is the least reactive element in the group, but still a metal.
-decay product Cn, their lighter homologues in groups 14 and 12, i.e., Pb and Hg, and the noble gas Rn were studied simultaneously by isothermal gas chromatography and thermochromatography. Two Fl atoms were detected. They adsorbed on a Au surface at room temperature, but not as readily as Pb and Hg. The observed adsorption behavior of Fl points to a higher inertness compared to its nearest homologue in the group, Pb. However, the measured lower limit for the adsorption enthalpy of Fl on a Au surface points to the formation of a metal-metal bond of Fl with Au. Fl is the least reactive element in the group, but still a metal.
Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, C. E.*; Dvorak, J.*; Eichler, R.*; Gothe, O.*; Hild, D.*; J
llmann, C. E.*; Dvorak, J.*; Eichler, R.*; Gothe, O.*; Hild, D.*; J ger, E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kratz, J. V.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; Kratz, J. V.*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 51(12), p.6431 - 6433, 2012/06
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:82.09(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Carbonyl complexes of radioactive transition metals can be easily synthesized with high yields by stopping nuclear fission or fusion products in a gas volume containing CO. Here, we focus on Mo, W, and Os complexes. The reaction takes place at pressures of around 1 bar at room temperature, i.e., at conditions that are easy to accommodate. The formed complexes are highly volatile. They can thus be transported within a gas stream without major losses to setups for their further investigation or direct use. The rapid synthesis holds promise for radiochemical purposes and will be useful for studying, e.g., chemical properties of superheavy elements.