Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tregoning, R.*; Wallace, J.*; Bouydo, A.*; Costa-Garrido, O.*; Dillstr m, P.*; Duan, X.*; Heckmann, K.*; Kim, Y.-B.*; Kim, Y.*; Kurth-Twombly, E.*; et al.
m, P.*; Duan, X.*; Heckmann, K.*; Kim, Y.-B.*; Kim, Y.*; Kurth-Twombly, E.*; et al.
Transactions of the 26th International Conference on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology (SMiRT-26) (Internet), 11 Pages, 2022/07
Fourteen organizations, representing eleven countries, participated in a leak-before-break (LBB) benchmark exercise that compared results from analyses among participating countries and identified the effects of weld residual stress (WRS) and crack morphology on crack opening displacement (COD), critical bending moment (CBM), and leak rate (LR) results. The participants determined whether the initial problem would meet their country's LBB acceptance criteria and then evaluated the effects of crack morphology and WRS for a prescribed crack size, geometry and loading. Six out of fourteen participants indicated that the initial problem met their LBB requirements. In the follow-on tasks, differences among the participant's CBM predictions were principally due to the material properties used in the analysis while the type of failure model chosen contributed much less. Most of the differences in the LR predictions were directly attributable to differences among the COD models, but a portion was attributable to the treatment of crack face pressure (CFP). The benchmark identified several aspects of an LBB analysis that could support a more realistic evaluation.
 ;
;  In NQR/NMR and
In NQR/NMR and  Co NMR study
Co NMR studySakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(8), p.085106_1 - 085106_12, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferromagnetism in a prototypical quantum critical metal CeCoIn is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn
is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn , an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn
, an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates
by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates  indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature
indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature  . At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature
. At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature  , and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
, and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
 Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Pu nuclear magnetic resonance in the candidate topological insulator PuB
Dioguardi, A. P.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi*; Thomas, S. M.*; Sakai, Hironori; Cary, S. K.*; Kozimor, S. A.*; Albrecht-Schmitt, T. E.*; Choi, H. C.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Thompson, J. D.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 99(3), p.035104_1 - 035104_6, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a detailed nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) study of  Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB
Pu in bulk and powdered single-crystal plutonium tetraboride (PuB ), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The
), which has recently been investigated as a potential correlated topological insulator. The  Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that
Pu NMR spectra are consistent with axial symmetry of the shift tensor showing for the first time that  Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the
Pu NMR can be observed in an anisotropic environment and up to room temperature. The temperature dependence of the  Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time (
Pu shift, combined with a relatively long spin-lattice relaxation time ( ), indicate that PuB
), indicate that PuB adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and
adopts a nonmagnetic state with gaplike behavior consistent with our density functional theory calculations. The temperature dependencies of the NMR Knight shift and 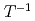 imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB
imply bulk gaplike behavior confirming that PuB is a good candidate topological insulator.
is a good candidate topological insulator.
Li, B.; Wang, H.*; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Zhang, Q.*; Feygenson, M.*; Yu, H. L.*; Wu, D.*; Ohara, Koji*; Kikuchi, Tatsuya*; Shibata, Kaoru; et al.
Nature Materials, 17(3), p.226 - 230, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:161 Percentile:97.18(Chemistry, Physical)Chadwick, M. B.*; Capote, R.*; Trkov, A.*; Herman, M. W.*; Brown, D. A.*; Hale, G. M.*; Kahler, A. C.*; Talou, P.*; Plompen, A. J.*; Schillebeeckx, P.*; et al.
Nuclear Data Sheets, 148, p.189 - 213, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:78 Percentile:98.03(Physics, Nuclear)The CIELO collaboration has studied neutron cross sections on nuclides that significantly impact criticality in nuclear facilities -  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Fe,
Fe,  O and
O and  H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
H - with the aim of improving the accuracy of the data and resolving previous discrepancies in our understanding. This multi-laboratory pilot project, coordinated via the OECD/NEA Working Party on Evaluation Cooperation (WPEC) Subgroup 40 with support also from the IAEA, has motivated experimental and theoretical work and led to suites of new evaluated libraries that accurately reflect measured data and also perform well in integral simulations of criticality. This report summarizes our results and outlines plans for the next phase of this collaboration.
Deng, Z.*; Zhao, K.*; Gu, B.; Han, W.*; Zhu, J. L.*; Wang, X. C.*; Li, X.*; Liu, Q. Q.*; Yu, R. C.*; Goko, Tatsuo*; et al.
Physical Review B, 88(8), p.081203_1 - 081203_5, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:77 Percentile:91.56(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Substitutions of In sites by Zn atoms in heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn is reported to induce an antiferromagnetic order by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki University. Near the critical region, non-Fermi-liquid behavior has been observed in magnetization and specific heat. We have performed NMR measurements to reveal the spin fluctuations near the critical region.
is reported to induce an antiferromagnetic order by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki University. Near the critical region, non-Fermi-liquid behavior has been observed in magnetization and specific heat. We have performed NMR measurements to reveal the spin fluctuations near the critical region.

Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; et al.
no journal, ,
In heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn , slight Zn substitutions for In atoms induce antiferromagnetism, while slight Ni substitutions for Co atoms suppress superconductivity. The both substituted CeCoIn
, slight Zn substitutions for In atoms induce antiferromagnetism, while slight Ni substitutions for Co atoms suppress superconductivity. The both substituted CeCoIn exhibit non- fermi-liquid behaviors near the phase boundaries which have been detected by magnetization and specific heat measurements. We have performed NMR experiments in these systems to investigate the microscopic effects by substituents. We will discuss about the spin fluctuations near the boundaries by NMR relaxation rates.
exhibit non- fermi-liquid behaviors near the phase boundaries which have been detected by magnetization and specific heat measurements. We have performed NMR experiments in these systems to investigate the microscopic effects by substituents. We will discuss about the spin fluctuations near the boundaries by NMR relaxation rates.