Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Cheng, S.; 田上 浩孝; 山野 秀将; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春; 竹田 祥平*; 西 津平*; 錦戸 達也*; Zhang, B.*; 松元 達也*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 51(9), p.1096 - 1106, 2014/09
被引用回数:25 パーセンタイル:87.38(Nuclear Science & Technology)Studies on debris bed self-leveling behavior with non-spherical particles are crucial in the assessment of actual leveling behavior that could occur in core disruptive accident of sodium-cooled fast reactors. Although in our previous publications, a simple empirical model (based model), with its wide applicability confirmed over various experimental conditions, has been successfully advanced to predict the transient leveling behavior, up until now this model is restricted to calculations of debris bed of spherical particles. Focusing on this aspect, in this study a series of experiments using non-spherical particles was performed within a recently-developed comparatively larger-scale experimental facility. Based on the knowledge and data obtained, an extension scheme is suggested with the intention to extend the base model to cover the particle-shape influence. Through detailed analyses, it is found that by coupling this scheme, good agreement between experimental and predicted results can be achieved for both spherical and non-spherical particles given current range of experimental conditions.
Cheng, S.; 田上 浩孝; 山野 秀将; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春; 中村 裕也*; 竹田 祥平*; 西 津平*; Zhang, B.*; 松元 達也*; et al.
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 1(4), p.TEP0022_1 - TEP0022_16, 2014/08
To clarify the mechanisms underlying the debris-bed self-leveling behavior, several series of experiments were elaborately designed and conducted within a variety of conditions in recent years, under the collaboration between Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and Kyushu University. The current contribution, including knowledge from both experimental analyses and empirical model development, is focused on a recently developed comparatively larger-scale experimental facility using gas-injection to simulate the coolant boiling. Based on the experimental observation and quantitative data obtained, influence of various experimental parameters, including gas flow rate ( 300 L/min), water depth (180 mm and 400 mm), bed volume (3
300 L/min), water depth (180 mm and 400 mm), bed volume (3  7 L), particle size (1
7 L), particle size (1  6 mm), particle density (beads of alumina, zirconia and stainless steel) along with particle shape (spherical and irregularly-shaped) on the leveling is checked and compared. As for the empirical model development, aside from a base model which is restricted to calculations of spherical particles, the status of potential considerations on how to cover more realistic conditions (esp. debris beds formed with non-spherical particles), is also presented and discussed.
6 mm), particle density (beads of alumina, zirconia and stainless steel) along with particle shape (spherical and irregularly-shaped) on the leveling is checked and compared. As for the empirical model development, aside from a base model which is restricted to calculations of spherical particles, the status of potential considerations on how to cover more realistic conditions (esp. debris beds formed with non-spherical particles), is also presented and discussed.
Cheng, S.; 山野 秀将; 鈴木 徹; 飛田 吉春; 中村 裕也*; 竹田 祥平*; 西 津平*; Zhang, B.*; 松元 達也*; 守田 幸路*
Proceedings of 21st International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-21) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
To confirm the mechanisms of self-leveling behavior, several series of experiments were elaborately designed and performed in recent years under the constructive collaboration between Japan Atomic Energy Agency and Kyushu University. This paper summarizes the recent knowledge obtained from the newly developed large-scale experiments using gas-injection to simulate coolant boiling. Compared to previous investigations, it can cover a much wider range of gas velocities (presently up to a flow rate of around 300 L/min). The experiments were conducted in a cylindrical tank, in which water, nitrogen gas and different kinds of solid particles, simulate the coolant, vapor and fuel debris, respectively. Based on the quantitative data obtained, influence of various experimental parameters, including gas flow rate, water depth, particle size as well as particle density on the leveling was checked and compared. Moreover, with the help of dimensional analysis technique, a set of empirical correlations to predict the self-leveling development depending on particle size, particle density and gas injection velocity was proposed and validated over current conditions.
 Fe translocation in barley as monitored by a Positron-Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS); Evidence for the direct translocation of Fe from roots to young leaves via phloem
Fe translocation in barley as monitored by a Positron-Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS); Evidence for the direct translocation of Fe from roots to young leaves via phloem塚本 崇志*; 中西 啓仁*; 内田 博*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 森 敏*; 西澤 直子*
Plant & Cell Physiology, 50(1), p.48 - 57, 2009/01
被引用回数:88 パーセンタイル:90.06(Plant Sciences)The real-time translocation of iron (Fe) in barley ( L. cv. Ehimehadaka no.1) was visualized using the positron-emitting tracer
L. cv. Ehimehadaka no.1) was visualized using the positron-emitting tracer  Fe and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). PETIS allowed us to monitor Fe translocation in barley non-destructively under various conditions. In all cases,
Fe and a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS). PETIS allowed us to monitor Fe translocation in barley non-destructively under various conditions. In all cases,  Fe first accumulated at the basal part of the shoot. Fe-deficient barley showed greater translocation of
Fe first accumulated at the basal part of the shoot. Fe-deficient barley showed greater translocation of  Fe from roots to shoots than did Fe-sufficient barley. In the dark, translocation of
Fe from roots to shoots than did Fe-sufficient barley. In the dark, translocation of  Fe to the youngest leaf was equivalent to or higher than that under the light condition, while the translocation of
Fe to the youngest leaf was equivalent to or higher than that under the light condition, while the translocation of  Fe to the older leaves was decreased, in both Fe-deficient and Fe-sufficient barley. This suggests the possibility that the mechanism and/or pathway of Fe translocation to the youngest leaf may be different from that to the older leaves. When phloem transport in the leaf was blocked by steam treatment,
Fe to the older leaves was decreased, in both Fe-deficient and Fe-sufficient barley. This suggests the possibility that the mechanism and/or pathway of Fe translocation to the youngest leaf may be different from that to the older leaves. When phloem transport in the leaf was blocked by steam treatment,  Fe translocation from the roots to older leaves was not affected, while
Fe translocation from the roots to older leaves was not affected, while  Fe translocation to the youngest leaf was reduced. We propose a novel model in which root-absorbed Fe is translocated from the basal part of the shoots and/or roots to the youngest leaf via phloem in graminaceous plants.
Fe translocation to the youngest leaf was reduced. We propose a novel model in which root-absorbed Fe is translocated from the basal part of the shoots and/or roots to the youngest leaf via phloem in graminaceous plants.
鈴木 基史*; 塚本 崇志*; 井上 晴彦*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 高橋 美智子*; 中西 啓仁*; 森 敏*; 西澤 直子*
Plant Molecular Biology, 66(6), p.609 - 617, 2008/04
被引用回数:138 パーセンタイル:95.26(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)Rice secretes Deoxymugineic acid (DMA) in response to Fe deficiency to take up Fe in the form of Fe(III)-DMS complex. In contrast with barley, the roots of which secrete DMS in response to Zn deficiency, the amount of DMA secreted by rice roots was slightly decreased under conditions of low Zn supply. There was a concomitant increase in endogenous DMA in rice shoots, suggesting that DMA plays a role in the translocation of Zn within Zn-deficient rice plants. The expression of 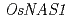 and
and 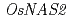 was not increased in Zn-deficient roots but that of
was not increased in Zn-deficient roots but that of 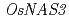 was increased in Zn-deficient roots and shoots. The expression of
was increased in Zn-deficient roots and shoots. The expression of 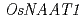 was also increased in Zn-deficient roots and dramatically increased in shoots; correspondingly, HPLC analysis was unable to detect nicotianamine in Zn-deficient shoots. The expression of
was also increased in Zn-deficient roots and dramatically increased in shoots; correspondingly, HPLC analysis was unable to detect nicotianamine in Zn-deficient shoots. The expression of 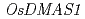 was increased in Zn-deficient shoots. Analyses using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) showed that Zn-deficient rice roots absorbed less
was increased in Zn-deficient shoots. Analyses using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS) showed that Zn-deficient rice roots absorbed less  Zn-DMA than
Zn-DMA than  Zn
Zn . Importantly, supply of
. Importantly, supply of  Zn-DMA rather than
Zn-DMA rather than  Zn
Zn increased the translocation of
increased the translocation of  Zn into the leaves of Zn-deficient plants. This was especially evident in the discrimination center (DC). These results suggest that DMA in Zn-deficient rice plants has an important role in the distribution of Zn within the plant rather than in the absorption of Zn from the soil.
Zn into the leaves of Zn-deficient plants. This was especially evident in the discrimination center (DC). These results suggest that DMA in Zn-deficient rice plants has an important role in the distribution of Zn within the plant rather than in the absorption of Zn from the soil.
石丸 泰寛*; Kim, S.*; 塚本 崇志*; 大木 宏之*; 小林 高範*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 高橋 美智子*; 中西 啓仁*; 森 敏*; et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 104(18), p.7373 - 7378, 2007/05
被引用回数:130 パーセンタイル:93.37(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Fe deficiency is a worldwide agricultural problem on calcareous soils. Rice plants use a well documented phytosiderophore-based system to take up Fe from the soil. Rice plants are extremely susceptible to low-Fe supply, however, because of low phytosiderophore secretion and low Fe reduction activity. A yeast Fe
reduction activity. A yeast Fe chelate-reductase gene
chelate-reductase gene 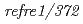 , selected for better performance at high pH, was fused to the promoter of the Fe-regulated transporter,
, selected for better performance at high pH, was fused to the promoter of the Fe-regulated transporter, 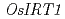 , and introduced into rice plants. The transgene was expressed in response to a low-Fe nutritional status in roots of transformants. Transgenic rice plants expressing the
, and introduced into rice plants. The transgene was expressed in response to a low-Fe nutritional status in roots of transformants. Transgenic rice plants expressing the 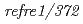 gene showed higher Fe
gene showed higher Fe chelate-reductase activity and a higher Fe-uptake rate than vector controls under Fe-deficient conditions. Consequently, transgenic rice plants exhibited an enhanced tolerance to low-Fe availability and 7.9x the grain yield of nontransformed plants in calcareous soils.
chelate-reductase activity and a higher Fe-uptake rate than vector controls under Fe-deficient conditions. Consequently, transgenic rice plants exhibited an enhanced tolerance to low-Fe availability and 7.9x the grain yield of nontransformed plants in calcareous soils.
 Fe translocation from the roots to the ear of rice using a Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS)
Fe translocation from the roots to the ear of rice using a Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS)塚本 崇志*; 中西 啓仁*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 西澤 直子*; 森 敏*
JAEA-Review 2006-042, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2005, P. 124, 2007/02
鉄は植物に必須な元素であるが、イネ中での移行、特に根で吸収された鉄の穂への移行については不明な点が多い。そこで、イネの穂への鉄の移行経路を明らかにするために、 Feを用いたポジトロンイメージング計測を試みた。開花から3週間の登熟期のイネの根から
Feを用いたポジトロンイメージング計測を試みた。開花から3週間の登熟期のイネの根から Feを吸収させ、植物内における動態をPETISにより計測したところ、
Feを吸収させ、植物内における動態をPETISにより計測したところ、 Fe投与後3.5時間で穂と止め葉に
Fe投与後3.5時間で穂と止め葉に Feが到達したことが明らかとなった。また、移行経路上にある節に
Feが到達したことが明らかとなった。また、移行経路上にある節に Feが集積していることがわかった。これらの結果から、鉄は導管から節において篩管へ移行した後、止め葉を経由せずに直接穂に輸送されることが示唆された。
Feが集積していることがわかった。これらの結果から、鉄は導管から節において篩管へ移行した後、止め葉を経由せずに直接穂に輸送されることが示唆された。
 Mn translocation in barley monitored using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system
Mn translocation in barley monitored using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system塚本 崇志*; 中西 啓仁*; 清宮 正一郎*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 西澤 直子*; 森 敏*
Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 52(6), p.717 - 725, 2006/12
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:63.02(Plant Sciences)Until now, the real-time uptake and movement of Mn, has not been documented in plants. In this study, the real-time translocation of Mn in barley was visualized using  Mn and PETIS. In all cases,
Mn and PETIS. In all cases,  Mn first accumulated in the discrimination center (DC), suggesting that this region may play an important role in Mn distribution in graminaceous plants. Mn deficient barley showed greater translocation of
Mn first accumulated in the discrimination center (DC), suggesting that this region may play an important role in Mn distribution in graminaceous plants. Mn deficient barley showed greater translocation of  Mn from roots to shoots than did Mn-sufficient barley. In contrast, the translocation of
Mn from roots to shoots than did Mn-sufficient barley. In contrast, the translocation of  Mn from roots to shoots was suppressed in Mn-excess barley. In Mn-sufficient barley, the dark treatment did not suppress the translocation of
Mn from roots to shoots was suppressed in Mn-excess barley. In Mn-sufficient barley, the dark treatment did not suppress the translocation of  Mn to the youngest leaf, suggesting that the translocation of Mn to the youngest leaf is independent of the transpiration stream. Our results show that the translocation of Mn from the roots to the DC depends passively on water flow, but actively on the Mn transporter(s).
Mn to the youngest leaf, suggesting that the translocation of Mn to the youngest leaf is independent of the transpiration stream. Our results show that the translocation of Mn from the roots to the DC depends passively on water flow, but actively on the Mn transporter(s).
鈴木 基史*; 高橋 美智子*; 塚本 崇志*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 矢崎 潤史*; 岸本 直己*; 菊池 尚志*; 中西 啓仁*; 森 敏*; et al.
Plant Journal, 48(1), p.85 - 97, 2006/10
被引用回数:172 パーセンタイル:95.77(Plant Sciences)Mugineic acid family phytosiderophores (MAs) are metal chelators that are produced in graminaceous plants in response to Fe deficiency, but current evidence regarding secretion of MAs during Zn deficiency is contradictory. HPLC analysis showed that Zn deficiency induces the synthesis and secretion of MAs in barley plants. Studies of the genes involved in the methionine cycle using microarray analysis showed that the transcripts of these genes were increased in both Zn-deficient and Fe-deficient barley roots. Analysis using the PETIS confirmed that more  Zn(II)-MAs than
Zn(II)-MAs than  Zn
Zn were absorbed by the roots of Zn-deficient barley plants. These data suggest that the increased biosynthesis and secretion of MAs arising from a shortage of Zn are not due to an induced Fe deficiency, and that secreted MAs are effective in absorbing Zn from the soil.
were absorbed by the roots of Zn-deficient barley plants. These data suggest that the increased biosynthesis and secretion of MAs arising from a shortage of Zn are not due to an induced Fe deficiency, and that secreted MAs are effective in absorbing Zn from the soil.
 -phytosiderophore and as Fe
-phytosiderophore and as Fe
石丸 泰寛*; 鈴木 基史*; 塚本 崇志*; 鈴木 一正*; 中園 幹生*; 小林 高範*; 和田 泰明*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平; 高橋 美智子*; et al.
Plant Journal, 45(3), p.335 - 346, 2006/02
被引用回数:545 パーセンタイル:99.64(Plant Sciences)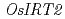 gean was isolated from rice, which is highly homologous to
gean was isolated from rice, which is highly homologous to 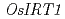 . Real-time PCR analysis revealed that
. Real-time PCR analysis revealed that 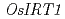 and
and 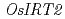 are expressed predominantly in roots, and these transporters are induced by low-Fe condition. Analysis using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system showed that rice plants are able to take up both an Fe
are expressed predominantly in roots, and these transporters are induced by low-Fe condition. Analysis using the positron-emitting tracer imaging system showed that rice plants are able to take up both an Fe -phytosiderophore and Fe
-phytosiderophore and Fe . This result indicates that, in addition to absorbing an Fe
. This result indicates that, in addition to absorbing an Fe -phytosiderophore, rice possesses a novel Fe-uptake system that directly absorbs the Fe
-phytosiderophore, rice possesses a novel Fe-uptake system that directly absorbs the Fe , a strategy that is advantageous for growth in submerged conditions.
, a strategy that is advantageous for growth in submerged conditions.
 C]methionine translocation in barley in relation to mugineic acid phytosiderophore biosynthesis
C]methionine translocation in barley in relation to mugineic acid phytosiderophore biosynthesisBughio, N.*; 中西 啓仁*; 清宮 正一郎*; 松橋 信平; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 智; 内田 博*; 辻 淳憲*; 長 明彦; 久米 民和; et al.
Planta, 213(5), p.708 - 715, 2001/09
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:36.85(Plant Sciences)オオムギが土壌中の鉄を獲得するために分泌するムギネ酸の前駆体であるメチオニンが、植物体のどこに起源をもつかを明らかにするために、リアルタイムでの[ C]メチオニン転流をポジトロンイメージング法を中心とした計測により行なった。外部から供給した[
C]メチオニン転流をポジトロンイメージング法を中心とした計測により行なった。外部から供給した[ C]メチオニンが鉄欠乏オオムギの根に保持され、ムギネ酸生合成に使われたこと、地上部から根へのメチオニンの移行が見られなかったことなどから、ムギネ酸の前駆体であるメチオニンは植物体の根に起源をもつと結論した。
C]メチオニンが鉄欠乏オオムギの根に保持され、ムギネ酸生合成に使われたこと、地上部から根へのメチオニンの移行が見られなかったことなどから、ムギネ酸の前駆体であるメチオニンは植物体の根に起源をもつと結論した。
森 敏*; 中西 友子*; 林 浩昭*; 大山 卓爾*; 内田 博*; 松橋 信平; 関根 俊明
Radioisotopes, 50(9), p.408 - 418, 2001/09
原研が中心となり開発を進めてきた植物研究用ポジトロンイメージング装置(PETIS)とこれを用いて研究を行うためにこれまでに開発してきたポジトロン標識化合物について、開発経緯と現状を解説した。また、PETISを用いた原研・大学プロジェクト共同研究で得られた知見として、植物体を構成する主要元素である炭,窒素などの化合物,植物内での物質輸送に重要な役割を果たすと考えられる水,ミネラルとして重要な金属元素等の動態に関して、植物生理学的な立場から、これまでの研究手法ではえられなかった知見の新規性,重要性について解説した。
 F-labeled water movement in a cowpea plant by positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)
F-labeled water movement in a cowpea plant by positron emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)古川 純*; 横田 はる美*; 田野井 慶太朗*; 上岡 志ほり*; 松橋 信平; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 智; 内田 博*; 辻 淳憲*; 伊藤 岳人*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 249(2), p.495 - 498, 2001/08
被引用回数:16 パーセンタイル:73.21(Chemistry, Analytical)ポジトロン放出核種を利用したイメージング装置であるPETIS(Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System)を用いてササゲにおけるバナジウム(V )吸収をリアルタイムで測定した。バナジウム-48は、日本原子力研究所高崎研究所のAVFサイクロトロンを用い、Sc箔に50MeVの
)吸収をリアルタイムで測定した。バナジウム-48は、日本原子力研究所高崎研究所のAVFサイクロトロンを用い、Sc箔に50MeVの 粒子を照射することにより製造した。
粒子を照射することにより製造した。 Vを水耕液に添加し、PETISによりリアルタイム計測を行った。また
Vを水耕液に添加し、PETISによりリアルタイム計測を行った。また V水溶液を添加してから3,6,20時間目の植物体を用いてバナジウム分布をラジオグラフィにより測定した。これらにより処理開始後20時間目には植物体全体にバナジウムが分布していることが明らかになった。植物に吸収されたバナジウムが及ぼす影響を見るために、同様にポジトロン放出核種であるフッ素-18で標識した水を用いてPETISによりササゲの水分吸収動態を測定した。計測前に20時時間バナジウムを吸収させると、標識水の吸収が極端に抑えられることが示された。これらの結果は植物体の地上部に移行したバナジウムが標識水の吸収を阻害する主な原因であることを示唆している。
V水溶液を添加してから3,6,20時間目の植物体を用いてバナジウム分布をラジオグラフィにより測定した。これらにより処理開始後20時間目には植物体全体にバナジウムが分布していることが明らかになった。植物に吸収されたバナジウムが及ぼす影響を見るために、同様にポジトロン放出核種であるフッ素-18で標識した水を用いてPETISによりササゲの水分吸収動態を測定した。計測前に20時時間バナジウムを吸収させると、標識水の吸収が極端に抑えられることが示された。これらの結果は植物体の地上部に移行したバナジウムが標識水の吸収を阻害する主な原因であることを示唆している。
 F used as tracer to study water uptake and transport imaging of a cowpea plant
F used as tracer to study water uptake and transport imaging of a cowpea plant中西 友子*; 田野井 慶太朗*; 横田 はる美*; Kang, D.-J.*; 石井 龍一*; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 智; 長 明彦; 関根 俊明; 松橋 信平; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 249(2), p.503 - 507, 2001/08
マメ科の植物の中できわめて乾燥に強いと考えられるササゲ( )を用いて水分吸収の計測を行った。ササゲは茎の下部に乾燥に耐えるための水分保持組織を発達させていると考えられている植物である。われわれは、中性子ラジオグラフィの手法を用いてこの組織が他の茎よりも水分量が多いことを確認した。またサイクロトロンによって製造された
)を用いて水分吸収の計測を行った。ササゲは茎の下部に乾燥に耐えるための水分保持組織を発達させていると考えられている植物である。われわれは、中性子ラジオグラフィの手法を用いてこの組織が他の茎よりも水分量が多いことを確認した。またサイクロトロンによって製造された F標識水を用いてPETIS法によりササゲの水分吸収動態を測定した。インゲンマメとササゲで水分吸収を比較すると、乾燥処理でもササゲのほうが高い水分吸収活性を維持していることが示され、より乾燥に強い性質を有していることが示唆された。
F標識水を用いてPETIS法によりササゲの水分吸収動態を測定した。インゲンマメとササゲで水分吸収を比較すると、乾燥処理でもササゲのほうが高い水分吸収活性を維持していることが示され、より乾燥に強い性質を有していることが示唆された。
 O-labeled and
O-labeled and  F-labeled water uptake in a soybean plant by PETIS (Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System)
F-labeled water uptake in a soybean plant by PETIS (Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System)中西 友子*; 横田 はる美*; 田野井 慶太朗*; 池上 奈通子*; 大國 曜子*; 古川 純*; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 智; 長 明彦; 関根 俊明; et al.
Radioisotopes, 50(6), p.265 - 269, 2001/06
ダイズにおける O標識水と
O標識水と F標識水の吸収動態をPETIS(Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System)法を用いて比較検討した。
F標識水の吸収動態をPETIS(Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System)法を用いて比較検討した。 O標識水(半減期: 2分)はサイクロトロンを用いて
O標識水(半減期: 2分)はサイクロトロンを用いて N(d,n)
N(d,n) O反応により、また、
O反応により、また、 F標識水(半減期: 110分)は
F標識水(半減期: 110分)は O(
O( ,pn)
,pn) F反応により調製した。標識水の供給は、根を切り落としたダイズの茎の下部から行い、植物中の標識水から放出される
F反応により調製した。標識水の供給は、根を切り落としたダイズの茎の下部から行い、植物中の標識水から放出される 線をBGO検出器(5cm
線をBGO検出器(5cm 15cm)を用いてリアルタイム計測を行った。15秒ごとの計測の積算値からダイズの各茎における20分間の吸水動態を調べたところ、
15cm)を用いてリアルタイム計測を行った。15秒ごとの計測の積算値からダイズの各茎における20分間の吸水動態を調べたところ、 F標識水の方が
F標識水の方が O標識水より早く吸収されることがわかり、
O標識水より早く吸収されることがわかり、 F標識水ではフッ素は
F標識水ではフッ素は F
F イオンとなり、バルクの水とは異なる動態を示すことが示された。吸収された
イオンとなり、バルクの水とは異なる動態を示すことが示された。吸収された O標識水の静止画像を撮ったところ、10分間の吸収後においても初葉よりも上部に
O標識水の静止画像を撮ったところ、10分間の吸収後においても初葉よりも上部に O標識水の分布は見られなかった。
O標識水の分布は見られなかった。
 O-water flow in tomato and rice in the light and dark using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)
O-water flow in tomato and rice in the light and dark using a positron-emitting tracer imaging system (PETIS)森 敏*; 清宮 正一郎*; 中西 啓仁*; 石岡 典子; 渡辺 智; 長 明彦; 松橋 信平; 橋本 昭司; 関根 俊明; 内田 博*; et al.
Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 46(4), p.975 - 979, 2000/12
被引用回数:29 パーセンタイル:57.37(Plant Sciences)ポジトロン放出核種イメージングシステム(PETIS)を用いることによって植物中の水の流れの画像化に成功した。ポジトロン放出核種の O原子で構成される水分子(標識水)をトマトとイネに経根投与し、植物生体内の標識水の移行速度と分布を動的に画像化した。画像から
O原子で構成される水分子(標識水)をトマトとイネに経根投与し、植物生体内の標識水の移行速度と分布を動的に画像化した。画像から  O-水の生体内移行は光によって制御され、暗条件ではほぼ完全にその動きを停止することがわかった。トマトの茎とイネの新葉における水の移動速度は光の強度が500
O-水の生体内移行は光によって制御され、暗条件ではほぼ完全にその動きを停止することがわかった。トマトの茎とイネの新葉における水の移動速度は光の強度が500 mol m
mol m /sのとき、それぞれ1.9 cm/sと0.4 cm/sであった。イネの新葉の場合の速度はトマトの茎のそれの1/5であったが、光の強度を3倍にすると速度が1.7倍になることがわかった。
/sのとき、それぞれ1.9 cm/sと0.4 cm/sであった。イネの新葉の場合の速度はトマトの茎のそれの1/5であったが、光の強度を3倍にすると速度が1.7倍になることがわかった。
 C]methionine translocation in Fe-sufficient and Fe-deficient barley using a Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS)
C]methionine translocation in Fe-sufficient and Fe-deficient barley using a Positron Emitting Tracer Imaging System (PETIS)中西 啓仁*; N.Bughio*; 松橋 信平; 石岡 典子; 内田 博*; 辻 淳憲*; 長 明彦; 関根 俊明; 久米 民和; 森 敏*
Journal of Experimental Botany, 50(334), p.637 - 643, 1999/05
鉄欠乏時にオオムギの根より放出される三価鉄のキレーターであるムギ平酸は、メチオニンを出発材料として生合成される。そこで、 C-メチオニンを用いて、鉄欠乏時及び鉄供給時におけるオオムギ植物体内の移行をポジトロン・イメージング装置により計測した。
C-メチオニンを用いて、鉄欠乏時及び鉄供給時におけるオオムギ植物体内の移行をポジトロン・イメージング装置により計測した。 C-メチオニンは新葉及びクロロシスを呈した葉に1時間以内に移行したが、古い葉や根への移行はほとんど観察されなかった。葉と根の付け根部分への蓄積が15分後に始まり、他の葉への移行は25分後から認められた。このようなアミノ酸転流をリアルタイムで測定したのは世界で初めてである。
C-メチオニンは新葉及びクロロシスを呈した葉に1時間以内に移行したが、古い葉や根への移行はほとんど観察されなかった。葉と根の付け根部分への蓄積が15分後に始まり、他の葉への移行は25分後から認められた。このようなアミノ酸転流をリアルタイムで測定したのは世界で初めてである。
久米 民和; 松橋 信平; 伊藤 均; G.W.Roeb*; 石岡 典子; 長 明彦; 松岡 弘充; 関根 俊明; 内田 博*; 辻 淳憲*; et al.
JAERI-Review 97-015, p.51 - 53, 1997/11
植物の環境応答を非破壊で計測するための基礎として、ポジトロンイメージング装置を用いて植物の主要構成成分である炭素化物の転流について検討した。 CO
CO (半減期20分)を用いた計測では、葉に短時間で
(半減期20分)を用いた計測では、葉に短時間で CO
CO は吸収され、光合成産物の根への移行が観察された。そのコムギの根への
は吸収され、光合成産物の根への移行が観察された。そのコムギの根への CO化合物の移行は、特に新根で大きく、幼根の先端に多く蓄積することが認められた。また、光条件の影響を調べた結果では、新葉への
CO化合物の移行は、特に新根で大きく、幼根の先端に多く蓄積することが認められた。また、光条件の影響を調べた結果では、新葉への C化合物の移行は暗条件下で多いのに対し、穂への移行は逆に明条件の方が多かった。
C化合物の移行は暗条件下で多いのに対し、穂への移行は逆に明条件の方が多かった。 C-メチオニンを用いた実験では、Fe欠乏のオオムギの葉から根への移行が大きいと予測されたが、根には移行せずに新葉に転流していることが認められた。以上のように、ポジトロン放出核種を用いた計測は、植物のストレス応答を調べるのに有効な手段であると考えられた。
C-メチオニンを用いた実験では、Fe欠乏のオオムギの葉から根への移行が大きいと予測されたが、根には移行せずに新葉に転流していることが認められた。以上のように、ポジトロン放出核種を用いた計測は、植物のストレス応答を調べるのに有効な手段であると考えられた。
中西 啓仁*; 塚本 崇志*; 西澤 直子*; 森 敏*; 渡辺 智; 松橋 信平
no journal, ,
鉄と亜鉛は植物に必須な元素であるが、これらの植物体内における動態には未解明な部分が多く、特に、登熟期のイネにおける金属元素の移行を直接計測した報告はない。本研究では、PETISを用いたポジトロン放出金属元素の登熟期のイネ生体内における移行を計測し、新たな知見を得ることを目的とした。開花後3週間のイネに Fe
Fe -デオキシムギネ酸又は
-デオキシムギネ酸又は Zn
Zn を経根吸収させ、それぞれの移行をPETISにより計測した。その結果、
を経根吸収させ、それぞれの移行をPETISにより計測した。その結果、 Fe,
Fe,  Znのいずれについても複数存在する節への蓄積が観察された。それぞれの節における
Znのいずれについても複数存在する節への蓄積が観察された。それぞれの節における Fe及び
Fe及び Zn移行量の解析から、先端に近い上位の節ほど単位重量あたりの蓄積量が多いことがわかり、何らかの生理的な制御により上位の節に優先的に金属元素を蓄積する仕組みの存在が示唆された。
Zn移行量の解析から、先端に近い上位の節ほど単位重量あたりの蓄積量が多いことがわかり、何らかの生理的な制御により上位の節に優先的に金属元素を蓄積する仕組みの存在が示唆された。
中川 恭一*; 松浦 秀明*; 古賀 友稀*; 片山 一成*; 大塚 哲平*; 後藤 実; 濱本 真平; 石塚 悦男; 中川 繁昭; 飛田 健次*; et al.
no journal, ,
高温ガス炉用トリチウム(T)製造Liロッドに対しZrを用いたT閉じ込め方法を検討している。炉内に温度分布が存在することを考慮して、炉内の温度範囲でのZr水素吸収速度を測定し、T閉じ込め性能を評価した。