Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kada, Wataru*; Miura, Kenta*; Kato, Hijiri*; Saruya, Ryota*; Kubota, Atsushi*; Sato, Takahiro; Koka, Masashi; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 348, p.218 - 222, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:52.11(Instruments & Instrumentation)Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Udagawa, Makoto; Nakamura, Mitsuyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio
Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology, 135(5), p.051402_1 - 051402_9, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:71.44(Engineering, Mechanical)The residual stresses generated within the weld-overlay cladding and base material of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) steel was evaluated for as-welded and post-welded heat-treated conditions using thermo-elastic plastic creep analyses considering phase transformation. By comparing the analytical results with the experimentally determined values, we found a good agreement for the residual stress distribution within the cladding and the base material. It was shown that considering phase transformation during welding was important for improving the accuracy of residual stress analysis. Using the calculated residual stress distribution, we performed fracture mechanics analyses for an RPV during pressurized thermal shock events. We evaluated the effect of the weld residual stress on the structural integrity of an RPV. The results indicated that consideration of residual stress produced by weld-overlay cladding and PWHT is important for assessing the structural integrity of RPV.
Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Masaki, Koichi*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 12(3), p.211 - 221, 2013/09
Probabilistic fracture mechanics analysis code PASCAL3 has been developed at JAEA to support the validation of the codes and standards which provide the structural integrity assessment method of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs) during pressurized thermal shock. Previous version of PASCAL2 has many functions including the evaluation method for an embedded crack, PTS transient database, non-destructive inspection models. This code has been improved mainly focusing on cladding on the inner surface of RPV. Using the PASCAL3 code, effects of the initiation and growth model for a surface flaw have been analyzed to determine the standard condition of PASCAL3. Deterministic and probabilistic evaluation using PASCAL3 for current structural integrity assessment method for RPV has also been conducted. The results show that the consideration of warm pre-stress effect decreases the conditional probability
Tanabe, Yusuke*; Iwamoto, Takashi*; Takahashi, Junichi*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro
JAEA-Review 2012-046, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2011, P. 129, 2013/01
Omichi, Masaaki*; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Sato, Takahiro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Okubo, Takeru; Koka, Masashi; Kada, Wataru; Sugimoto, Masaki; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, 12, p.7401 - 7404, 2012/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:15.31(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Asano, Atsushi*; Maeyoshi, Yuta*; Marui, Hiromi*; Omichi, Masaaki*; Saeki, Akinori*; Seki, Shu*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; et al.
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 25(1), p.43 - 46, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:9.19(Polymer Science)Onizawa, Kunio; Masaki, Koichi; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Nishiyama, Yutaka
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-9-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.374 - 379, 2012/07
To assure the structural integrity of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) is known as one of the critical issues to maintain the safe long-term operation of a nuclear power plant. In Japan, the assessment methods for RPV integrity, stipulated in the codes and standards, have been endorsed by the regulatory body. Authors have initiated extensive research on the improvement of structural integrity assessment methods of RPVs. In this paper, we describe some research results obtained from the first-year activity. These include the study on revisiting the technical background of the methods, such as loading conditions, postulated crack definition, the other evaluation methods. In addition, studies on probabilistic methods for the applicability to the current rules and the standardization of the probabilistic analysis methods have been presented.
Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Asano, Atsushi*; Maeyoshi, Yuta*; Marui, Hiromi*; Omichi, Masaaki*; Saeki, Akinori*; Seki, Shu*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; et al.
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 37(2), p.237 - 240, 2012/06
Maeyoshi, Yuta*; Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Asano, Atsushi*; Marui, Hiromi*; Omichi, Masaaki*; Sato, Takahiro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Okubo, Takeru; Koka, Masashi; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 51(4R), p.045201_1 - 045201_4, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.17(Physics, Applied)Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Goto, Nobuhisa*; Suzuki, Hirokazu*; Katsuyama, Jinya; Onizawa, Kunio
Mizuho Joho Soken Giho (Internet), 4(1), 5 Pages, 2012/03
Stainless steel with 5 mm thickness is weld-overlay cladded on the inner surface reactor pressure vessels for protecting the vessel walls against the corrosion. Residual stress which corresponds to yield stress is generated near the cladding layer due to the weld-overlay cladding. However, there is no specific provision in the codes related to the cladding. Therefore, in order to confirm how the residual stress affects on the structural integrity of RPVs during pressurize thermal shock events, we evaluate the residual stress caused by the weld-overlay cladding and effects of the stress on the structural integrity. In this paper, the analysis method of welding residual stress of RPVs using finite element method and that of fracture mechanics considering postulated crack are introduced.
Tanabe, Yusuke*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 163, 2012/01
Takano, Katsuyoshi*; Sato, Takahiro; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Okubo, Takeru; Koka, Masashi; Kada, Wataru; Sugimoto, Masaki; Seki, Shuhei*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*
JAEA-Review 2011-043, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2010, P. 162, 2012/01
 m band using focused proton beam
m band using focused proton beamMiura, Kenta*; Machida, Yuki*; Uehara, Masato*; Kiryu, Hiromu*; Ozawa, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Tomoyuki*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Koka, Masashi; et al.
Key Engineering Materials, 497, p.147 - 150, 2012/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:94.26(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) m band using focused proton beam
m band using focused proton beamMiura, Kenta*; Machida, Yuki*; Uehara, Masato*; Kiryu, Hiromu*; Ozawa, Yusuke*; Sasaki, Tomoyuki*; Hanaizumi, Osamu*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Koka, Masashi; et al.
Key Engineering Materials, 497, p.147 - 150, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:2.48Sasaki, Akira; Nishihara, Katsunobu*; Sunahara, Atsushi*; Furukawa, Hiroyuki*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Koike, Fumihiro*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6(Sp.1), p.2401145_1 - 2401145_4, 2011/12
Atomic processes and radiation from multiple charged ions in plasmas are of the interest in the investigation of plasma wall interaction and transport of impurity ions in the fusion devices. The emission from multiple charged ions is also investigated for the development of extreme ultra violet light (EUVL) sources at 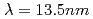 . Efficient emission through the 4d-4f + 4p-4d transition array is obtained from tin ions. An optimization of pumping conditions of laser produced plasma sources is carried out theoretically and experimentally. We also investigate an extension of the plasma light sources to short wavelength to
. Efficient emission through the 4d-4f + 4p-4d transition array is obtained from tin ions. An optimization of pumping conditions of laser produced plasma sources is carried out theoretically and experimentally. We also investigate an extension of the plasma light sources to short wavelength to 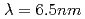 using Gd and Tb plasmas. We discuss requirements to the atomic structure, rate coefficient and collisional radiative codes to determine ion abundance and level population as a function of plasma temperature and density, to calculate the radiation intensity as well as emission spectrum.
using Gd and Tb plasmas. We discuss requirements to the atomic structure, rate coefficient and collisional radiative codes to determine ion abundance and level population as a function of plasma temperature and density, to calculate the radiation intensity as well as emission spectrum.
Kamiya, Tomihiro; Takano, Katsuyoshi; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Seki, Shu*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Okumura, Susumu; Fukuda, Mitsuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 269(20), p.2184 - 2188, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:80.90(Instruments & Instrumentation)Takano, Katsuyoshi; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Koka, Masashi; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Okubo, Takeru; Sugimoto, Masaki; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Seki, Shu*
Transactions of the Materials Research Society of Japan, 36(3), p.305 - 308, 2011/09
Tanabe, Yusuke*; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Seki, Yoshihiro*; Sato, Takahiro; Ishii, Yasuyuki; Kamiya, Tomihiro; Watanabe, Toru*; Sekiguchi, Atsushi*
Microelectronic Engineering, 88(8), p.2145 - 2148, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:46.25(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Masaki, Koichi; Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Osakabe, Kazuya*; Onizawa, Kunio
JAEA-Data/Code 2010-033, 350 Pages, 2011/03
The probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) analysis code PASCAL (PFM Analysis of Structural Components in Aging LWR) has been developed in JAEA. The PASCAL code evaluates the conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a reactor pressure vessel (RPV) under transient conditions such as pressurized thermal shock (PTS). Previous version of PASCAL (PASCAL ver.2) that was released in 2007 has many functions including the evaluation method for an embedded crack and conditional probabilities of crack initiation and fracture of a RPV, PTS transient database, inspection crack detection probability model and others. A generalized analysis method is available on the basis of the development of PASCAL ver.3 and sensitivity analysis results. Graphical user interface (GUI) including a generalized method and some functions of PFM have been also updated for PASCAL3. This report provides the user's manual, examples of analysis and theoretical background of PASCAL ver.3.
Nishikawa, Hiroyuki*; Onizawa, Kunio
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 10(1), p.12 - 23, 2011/03
Probabilistic fracture mechanics analysis code PASCAL2 has been developed in JAEA to support the validation of the codes and standards which provide the structural integrity assessment method of reactor pressure vessels during pressurized thermal shock. In this study, the evaluation methods of flaw initiation and growth considering weld-overlay cladding in PASCAL2 and non-destructive inspection models have been improved. Using the improved PASCAL2 code, effects of the initiation and growth models of a cladding flaw and the non-destructive inspection model on the failure probability have been analyzed. The analysis results, indicating the application of the improved initiation model decreases the conditional probability of failure, suggested the most feasible models. The results also showed that only maximum detection probability affected the failure probability among the parameter of the improved non-destructive inspection model.