Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishikawa, Satoru*; Ishimaru, Yasuhiro*; Igura, Masato*; Kuramata, Masato*; Abe, Tadashi*; Senoura, Takeshi*; Hase, Yoshihiro; Arao, Tomohito*; Nishizawa, Naoko*; Nakanishi, Hiromi*
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(47), p.19166 - 19171, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:349 Percentile:99.68(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Rice (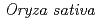 L.) is one of major sources of dietary intake of cadmium (Cd) for the human. However, the reliable technique to reduce substantially rice Cd contamination has not been offered so far. Here, we report the ion-beam irradiated rice mutants that do not nearly accumulate Cd in the grains and the mutant gene responsible for the Cd limitation. We found three mutants in which a favorable low-Cd trait is expressed by the different mutations on the same gene (
L.) is one of major sources of dietary intake of cadmium (Cd) for the human. However, the reliable technique to reduce substantially rice Cd contamination has not been offered so far. Here, we report the ion-beam irradiated rice mutants that do not nearly accumulate Cd in the grains and the mutant gene responsible for the Cd limitation. We found three mutants in which a favorable low-Cd trait is expressed by the different mutations on the same gene (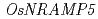 ), and the transporter encoded by the mutant gene
), and the transporter encoded by the mutant gene 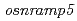 had a defective function of root Cd influx. The mutants adapted well in the Cd-polluted paddy fields by exhibiting nearly non-detectable Cd concentrations in their grains in accordance with no adverse economic traits. The DNA marker has been developed to breed new cultivars carrying
had a defective function of root Cd influx. The mutants adapted well in the Cd-polluted paddy fields by exhibiting nearly non-detectable Cd concentrations in their grains in accordance with no adverse economic traits. The DNA marker has been developed to breed new cultivars carrying 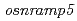 . Our findings would be useful for greatly reducing the Cd level of paddy rice.
. Our findings would be useful for greatly reducing the Cd level of paddy rice.
 I in the atmosphere emitted from nuclear fuel reprocessing plants
I in the atmosphere emitted from nuclear fuel reprocessing plantsNishizawa, Masato; Suzuki, Takashi; Nagai, Haruyasu; Togawa, Orihiko
Proceedings of Joint International Conference of 7th Supercomputing in Nuclear Application and 3rd Monte Carlo (SNA + MC 2010) (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2010/10
Suzuki et al. ( ,
,  , 268-275, 2008) estimated that more than 80% of Iodine-129 (
, 268-275, 2008) estimated that more than 80% of Iodine-129 ( I) in seawater in the Japan Sea came from nuclear fuel reprocessing plants. Considering the distance from the main nuclear reprocessing plants in Europe to the Japan Sea and the time scales of atmospheric and ocean circulations, large portion of
I) in seawater in the Japan Sea came from nuclear fuel reprocessing plants. Considering the distance from the main nuclear reprocessing plants in Europe to the Japan Sea and the time scales of atmospheric and ocean circulations, large portion of  I in the Japan Sea is presumed to be transported through the atmosphere. In the present study, a global chemical transport model, MOZART-4, is applied to investigate the behavior of
I in the Japan Sea is presumed to be transported through the atmosphere. In the present study, a global chemical transport model, MOZART-4, is applied to investigate the behavior of  I emitted from nuclear fuel reprocessing plants in Europe (Sellafield in the UK and La Hague in France) and to estimate the distribution in the atmosphere and deposition in remote sites. The result of numerical simulation for more than fifty-year period from the 1950s is validated by comparison with measurements of
I emitted from nuclear fuel reprocessing plants in Europe (Sellafield in the UK and La Hague in France) and to estimate the distribution in the atmosphere and deposition in remote sites. The result of numerical simulation for more than fifty-year period from the 1950s is validated by comparison with measurements of  I around the world and analyzed to clarify the characteristic of the distributions of concentration and deposition of
I around the world and analyzed to clarify the characteristic of the distributions of concentration and deposition of  I. The modeled concentrations of
I. The modeled concentrations of  I in precipitation in Europe and depositions in Japanese waters are in the same order as measurements. The emitted
I in precipitation in Europe and depositions in Japanese waters are in the same order as measurements. The emitted  I to the atmosphere is distributed and deposited all over the Northern Hemisphere due to the prevailing westerlies. The emission of
I to the atmosphere is distributed and deposited all over the Northern Hemisphere due to the prevailing westerlies. The emission of  I to the atmosphere is thus important in considering the transport and deposition of
I to the atmosphere is thus important in considering the transport and deposition of  I to remote sites.
I to remote sites.
Nishizawa, Masato; Suzuki, Takashi; Nagai, Haruyasu; Togawa, Orihiko
JAEA-Conf 2010-001, p.105 - 108, 2010/03
no abstracts in English
 Rn and its decay products coupled with a mesoscale meteorological model, 2; Numerical analysis on the increase in
Rn and its decay products coupled with a mesoscale meteorological model, 2; Numerical analysis on the increase in  dose rate observed in the coastal area of Fukushima prefecture
dose rate observed in the coastal area of Fukushima prefectureNishizawa, Masato; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45(11), p.1129 - 1137, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)A three-dimensional Eulerian numerical model for  Rn and its decay products coupled with a mesoscale meteorological model, MM5-TMNR, is applied to investigate the mechanism of the naturally induced increase of
Rn and its decay products coupled with a mesoscale meteorological model, MM5-TMNR, is applied to investigate the mechanism of the naturally induced increase of  dose rate observed at the coastal area of Fukushima prefecture on October, 2002. The results obtained by MM5-TMNR are verified by the comparisons with observed wind, precipitation and
dose rate observed at the coastal area of Fukushima prefecture on October, 2002. The results obtained by MM5-TMNR are verified by the comparisons with observed wind, precipitation and  dose rate, and adequate to examine the mechanism. The unusual increase of
dose rate, and adequate to examine the mechanism. The unusual increase of  dose rate is occurred by the combination of the synoptic-scale transport of natural radionuclides due to inflow of cold air mass from the Asian Continent and the meso-
dose rate is occurred by the combination of the synoptic-scale transport of natural radionuclides due to inflow of cold air mass from the Asian Continent and the meso- -scale precipitation process within the coastal area of Fukushima prefecture. The contribution rate of natural radionuclides from the Asian Continent to the increase of
-scale precipitation process within the coastal area of Fukushima prefecture. The contribution rate of natural radionuclides from the Asian Continent to the increase of  dose rate is estimated to be more than 60%.
dose rate is estimated to be more than 60%.
 Rn and its decay products coupled with a mesoscale meteorological model, 1; Model description and validation
Rn and its decay products coupled with a mesoscale meteorological model, 1; Model description and validationNishizawa, Masato; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi; Moriizumi, Jun*; Yoshioka, Katsuhiro*; Okura, Takehisa; Yamazawa, Hiromi*; Iida, Takao*; Mukai, Hitoshi*; Tojima, Yasunori*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 44(11), p.1458 - 1466, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:37.19(Nuclear Science & Technology)A three-dimensional Eulerian numerical model for  Rn and its decay products coupled with a mesoscale meteorological model has been developed and applied to the reproduction of the daily and monthly variations of
Rn and its decay products coupled with a mesoscale meteorological model has been developed and applied to the reproduction of the daily and monthly variations of  Rn concentration, the monthly variation of
Rn concentration, the monthly variation of  Pb deposition in Japan and the temporal variation of
Pb deposition in Japan and the temporal variation of  dose rate after the cold front passage in the coastal area of the Japan Sea for the verification of model capability. The results are as follows: (1) The model reproduced the monthly variation of surface
dose rate after the cold front passage in the coastal area of the Japan Sea for the verification of model capability. The results are as follows: (1) The model reproduced the monthly variation of surface  Rn concentration in remote islands, but underestimated inland concentration due to coarse vertical resolution near the surface of the model. (2) The model reproduced the seasonal variation of the observed and the long-term yearly averaged
Rn concentration in remote islands, but underestimated inland concentration due to coarse vertical resolution near the surface of the model. (2) The model reproduced the seasonal variation of the observed and the long-term yearly averaged  Pb depositions as long as precipitations are predicted precisely. (3) The model reproduced the rise of
Pb depositions as long as precipitations are predicted precisely. (3) The model reproduced the rise of  dose rate in precipitation accompanied with the cold front passage. In particular,
dose rate in precipitation accompanied with the cold front passage. In particular,  Rn decay products in melted snow and graupel contributed the rise of
Rn decay products in melted snow and graupel contributed the rise of  dose rate.
dose rate.
Nishizawa, Masato*; Chino, Masamichi
Taiki Kankyo Gakkai-Shi, 39(1), p.31 - 42, 2004/01
no abstracts in English
Nishizawa, Masato; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi; Sasaki, Hirotomo*; Kato, Kentaro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishizawa, Masato; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Terada, Hiroaki; Nishizawa, Masato; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi; Sasaki, Koichi*
no journal, ,
SPEEDI-MP has been developed for comprehensive prediction of migration of radionuclides in the atmosphere, ocean, and terrestrial region. In this study, we made attempt to distinguish the contributions to observed air dose rate between natural and artificial radionuclides from the reprocessing facility in Rokkasho, Aomori during the period when the increase of dose rate by precipitation was observed. For the purpose, two atmospheric dispersion models of SPEEDI-MP were applied, which were an Eulerian model for natural radionuclides and a Lagrangian particle model for artificial radionuclides. Simulation period is 10 September 2007. The data used for the model calculation and comparisons with the calculations are Grid Point Value (GPV), AMeDAS from Japan Meteorological Agency, and  Kr release amount, meteorological observations near the stack and environmental monitoring data around the facility from Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited (JNFL).
Kr release amount, meteorological observations near the stack and environmental monitoring data around the facility from Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited (JNFL).
Nishizawa, Masato; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Terada, Hiroaki; Nishizawa, Masato; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi; Sasaki, Koichi*
no journal, ,
SPEEDI-MP has been developed for comprehensive prediction of migration of radionuclides in the atmosphere, ocean, and terrestrial region. In this study, we made attempt to distinguish the contributions to observed air dose rate between natural and artificial radionuclides from the reprocessing facility in Rokkasho, Aomori. For the purpose, two atmospheric dispersion models of SPEEDI-MP were applied, which were an Eulerian model for natural radionuclides and a Lagrangian particle model for artificial radionuclides. During the period of 10 September 2007, the model prediction performance was improved by using the observation data at the height of 250 m and 300 m above ground in addition to those from the surface to 150 m level for data assimilation in meteorological prediction. We could also generally reproduce the monitoring results observed at the monitoring stations approximately 4 km distant from the main stack in 12 September 2007 with the same calculation method.
Furuno, Akiko; Nagai, Haruyasu; Terada, Hiroaki; Nishizawa, Masato; Katata, Genki; Togawa, Orihiko; Chino, Masamichi
no journal, ,
WSPEEDI is one of the basic model of the Numerical Environment Simulation System SPEEDI-MP, and it has almost completed. The next issue is to prepare WSPEEDI for the practical use. A conventional exercise "ConvEx" is useful for such issue. ConvEx is coordinated by IAEA, and it is a major exercise to test the response to a simulated accident at Mexico's Laguna Verde nuclear power plant. The purpose of the ConvEx is to identify shortcomings in the national and international emergency response systems that might disturbance the response to minimize the consequences of a nuclear accident. We carried out some test simulations by using the prepared calculation conditions. The simulations end promptly, and it was shown that WSPEEDI is useful as an actual emergency system.
Nagai, Haruyasu; Terada, Hiroaki; Nishizawa, Masato; Nakayama, Hiromasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Terada, Hiroaki; Nishizawa, Masato; Nagai, Haruyasu; Chino, Masamichi; Sasaki, Koichi*
no journal, ,
SPEEDI-MP has been developed for comprehensive prediction of migration of radionuclides in the atmosphere, ocean, and terrestrial region. In this study, we improved the atmospheric dispersion model in SPEEDI-MP and conducted its verification for the environmental assessment of the reprocessing facility in Rokkasho, Aomori. During the period of 00 - 24 JST 10 September 2007, the prediction performance of air dose rate was improved by introducing the Briggs's model for momentum jet rise process into the atmospheric particle dispersion model instead of fixed release height which is the sum of stack outlet height and mean plume rise height.
Nishizawa, Masato; Suzuki, Takashi; Nagai, Haruyasu; Togawa, Orihiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishizawa, Masato; Suzuki, Takashi; Nagai, Haruyasu; Togawa, Orihiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English