Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Torigoe, Shuhei*; Hattori, Takayuki*; Kodama, Katsuaki; Honda, Takashi*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Abe, Hitoshi*; Murakawa, Hiroshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(13), p.134443_1 - 134443_7, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Hayashi, Koichi*; Oyama, Kenji*; Happo, Naohisa*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Hosokawa, Shinya*; Harada, Masahide; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Shishido, Toetsu*; Yubuta, Kunio*
Science Advances (Internet), 3(8), p.e1700294_1 - e1700294_7, 2017/08
Ito, Takanori*; Mori, Masashi*; Inukai, Manabu*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Yamamoto, Takashi*; Miyanaga, Takashi*; Igawa, Naoki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Ishida, Naoya*; Idemoto, Yasushi*
Photon Factory News, 33(1), p.18 - 24, 2015/05
The effect of the annealing on the crystal and local structures of doped zirconia was investigated by multi-probe technique using synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction, and first principles calculation. It was revealed that the annealing process enhances the periodic distortion of some zirconia compounds by Rietveld/ maximum entropy methods applied to the SR-X-ray and neutron diffractions. In addition, the combined X-ray absorption spectroscopy and first-principles calculations results showed the ZrO polyhedra in zirconia were distorted by the annealing. Those results indicate that the degradation of oxide ionic conductivity by the annealing was related to the periodic distortion in zirconia.
polyhedra in zirconia were distorted by the annealing. Those results indicate that the degradation of oxide ionic conductivity by the annealing was related to the periodic distortion in zirconia.
Ito, Takanori*; Mori, Masashi*; Inukai, Manabu*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Yamamoto, Takashi*; Miyanaga, Takashi*; Igawa, Naoki; Kitamura, Naoto*; Ishida, Naoya*; Idemoto, Yasushi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 119(16), p.8447 - 8458, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:52.46(Chemistry, Physical)The effects of the annealing process on the crystal and local structures of the doped zirconia were investigated by Rietveld refinements of synchrotron X-ray and neutron diffraction, maximum entropy method (MEM), X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and first principles calculation (FPC). This study reveals that the crystal structures of the sintered and annealed ((Zr Y
Y )O
)O and (Zr
and (Zr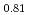 Sc
Sc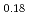 Ce
Ce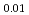 )O
)O ) are cubic with the space
) are cubic with the space 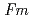 -3
-3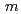 having large atomic displacement parameters (
having large atomic displacement parameters (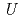 ). For the annealed (Zr
). For the annealed (Zr Y
Y )O
)O , the
, the 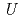 values reduce, and the electrons around the Zr/oxide ion sites gather at the center of each site. On the other hand, the annealed (Zr
values reduce, and the electrons around the Zr/oxide ion sites gather at the center of each site. On the other hand, the annealed (Zr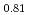 Sc
Sc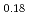 Ce
Ce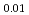 )O
)O shows the opposite tendency to that of the annealed (Zr
shows the opposite tendency to that of the annealed (Zr Y
Y )O
)O .
.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Denki Kagaku Oyobi Kogyo Butsuri Kagaku, 81(7), p.543 - 546, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:19.07(Electrochemistry)The molten state of simulated high-level waste glass and the behavior of ruthenium element in the melt were investigated by using synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. Melting, generating and moving of bubbles, condensation and sedimentation of ruthenium element were observed dynamically in continuous 12-bit gray-scale images from the CCD camera. X-ray intensity was obtained easily by digitizing gray-scale values in the image. The existence of ruthenium element is emphasized as a black color in the CCD image at X-ray energy higher than the Ru K-absorption edge. Position sensitive imaging X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement was also performed to clarify the chemical state of ruthenium element in the melt.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Proceedings of 4th Asian Conference on Molten Salt Chemistry and Technology & 44th Symposium on Molten Salt Chemistry, Japan, p.47 - 52, 2012/09
The molten state of the simulated high-level waste glass and the behavior of ruthenium element in the melt were investigated by using synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. Melting, generating and moving of bubbles, condensation and sedimentation of ruthenium element were observed dynamically in continuous 12-bit gray-scale images from the CCD camera. The existence of ruthenium in the X-ray CCD image was emphasized over the energy of Ru K-absorption edge. X-ray intensity was obtained easily by digitalizing gray-scale values in the image. Position sensitive imaging X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurement was performed to clarify the chemical state of ruthenium element in the melt.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 11(2), p.127 - 132, 2012/06
Distribution and the chemical state of Ru element in the simulated high-level waste glass were examined by using the synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. In this technique, a direct X-ray CCD camera is used in place of an ion chamber. Position sensitive X-ray absorption spectra were obtained by analyzing gray scale in images of the X-ray CCD camera. At first, we measured a test sample containing RuO and Ru metal powder. We successfully obtained information on the Ru distribution in the sample. In addition, the chemical state (oxide or metal ?) of each small Ru-rich spot was evaluated by the corresponding position sensitive XAFS spectrum. The imaging XAFS technique was applied to some simulated high-level waste glass samples. The Ru distribution of the glass sample and their chemical state were confirmed by image analyses. It can be seen that Ru element scattered in the glass sample exists as oxide RuO
and Ru metal powder. We successfully obtained information on the Ru distribution in the sample. In addition, the chemical state (oxide or metal ?) of each small Ru-rich spot was evaluated by the corresponding position sensitive XAFS spectrum. The imaging XAFS technique was applied to some simulated high-level waste glass samples. The Ru distribution of the glass sample and their chemical state were confirmed by image analyses. It can be seen that Ru element scattered in the glass sample exists as oxide RuO .
.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Distribution and the chemical state of Ru element in the simulated high-level waste glass were examined by using the synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. In this technique, a direct X-ray CCD camera is used in place of an ion chamber. Position sensitive X-ray absorption spectra were obtained by analyzing gray scale in images of the X-ray CCD camera. It can be seen that Ru element scattered in the glass sample exists as oxide RuO .
.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Kawashima, Hidenori*; Komamine, Satoshi*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
The molten state of simulated high-level waste glass and the behavior of ruthenium element in the melt were investigated by using synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. Melting, generating and moving of bubbles, condensation and sedimentation of ruthenium element were observed dynamically in continuous 12-bit gray-scale images from the CCD camera. The imaging XAFS results of our experiment clearly show that the ruthenium in the high temperature glass melt exists as oxide.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
Chemical state analysis of Ru element scattered in an imitative glass matrix was performed by using the Imaging XAFS technique. Information on distribution of Ru element in the matrix was obtained from contrast values of CCD images before and after the Ru K-absorption edge. It is confirmed that the feature of the distributed element can be examined by getting XAFS spectra from the contrast information. We can get two kinds of XAFS spectra corresponding to Ru metal and oxide separately in the Imaging XAFS analysis.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
Distribution and the chemical state of fission product elements like Zr, Mo and Ru in the simulated high-level waste glass were examined by using the synchrotron radiation based X-ray imaging technique. We used the high resolution imaging system and the high-speed CCD camera for imaging XAFS measurement of the glass sample at molten state. Position sensitive X-ray absorption spectra were obtained by analyzing gray scale in images of the CCD camera.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Osugi, Takeshi; Akabori, Mitsuo; Nitani, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
The distribution and chemical state of cesium in soil/cray minerals and ash was investigated by using imaging XAFS technique. The imaging XAFS measurement of cesium element was carried out for L -edge at the BL-27B beamline and for K-edge at the NW10A beamline in KEK. In the imaging XAFS measurement for L
-edge at the BL-27B beamline and for K-edge at the NW10A beamline in KEK. In the imaging XAFS measurement for L -edge, chemical state of cesium was clarified from imaging XAFS spectrum. In the high-temperature imaging measurement for K-edge, behavior of cesium was observed visually from X-ray CCD camera.
-edge, chemical state of cesium was clarified from imaging XAFS spectrum. In the high-temperature imaging measurement for K-edge, behavior of cesium was observed visually from X-ray CCD camera.
Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Nakada, Masami; Akabori, Mitsuo; Komamine, Satoshi*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Ochi, Eiji*; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Nomura, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
The high level liquid waste (HLLW) generated in the reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels is disposed of as vitrified waste mixed with borosilicate glass. Chemical state of noble metals like Ru in simulated glasses was investigated by using the synchrotron based X-ray imaging analysis in the present work. The X-ray imaging measurement was performed at the NW10A of PF-AR and the BL-27B of PF, KEK. The imaging system is composed of the beam monitor (AA40 and AA50) and the CCD camera (high-speed type C9300-221 and high resolution type C11440-10C). X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spetcra of Ru K-edge for very small area were obtained from the imaging intensity data. It can be seen by comparing with standard materials that Ru in the small area exists as RuO .
.