Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Negishi, Hitoshi; Kotake, Shoji; Niwa, Hajime
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 50(3), p.174 - 180, 2008/03
, 50(3), p.174 - 180, 2008/03
Based on the experience of R&D results, such as the developing the prototype FBR, "MONJU," and related fuel cycle, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency carried out the joint study "Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle Systems" with electric utilities, the Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry and manufacturers. This study has two objectives, presenting "an appropriate concept of the commercial FBR cycle system" and "the R&D programs for commercialization", toward 2015. The "Combined system of sodium-cooled reactor (MOX fuel), advanced aqueous reprocessing and simplified pelletizing fuel fabrication" was selected, as the concept to be developed mainly from now, because it has the greatest potential conformity to the development requirements and has the high technical feasibility because it uses the accumulated results of past R&D, and international cooperation in this is possible.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Fujita, Satoshi; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Sato, Ikken; Niwa, Hajime
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 238(1), p.66 - 73, 2008/01
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:86.96(Nuclear Science & Technology)For the transition phase analysis of core disruptive accidents, the development of a three-dimensional reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-IV, has been carried out based on the technology of the two-dimensional SIMMER-III code. The world first application of SIMMER-IV to a small-sized sodium-cooled fast reactor has also been attempted to clarify event progression in the early stage of the transition phase. This SIMMER-IV calculation is compared to the two-dimensional case calculated by SIMMER-III, neglecting the presence of control rod guide tubes. The present analysis with the three-dimensional representation suggests that the conventional scenario leading to rather early high-mobility fuel-pool formation is unrealistic and the degraded core tends to keep low mobility in the early stage of transition phase.
Niwa, Hajime; Aoto, Kazumi; Morishita, Masaki
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.62 - 70, 2007/09
Niwa, Hajime
Proceedings of 5th Korea-Japan Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS-5), p.29 - 31, 2006/11
The progress of a feasibility study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems in Japan is reported, followed by the introduction of innovative technologies in sodium-cooled MOX-fueled fast reactor selected as a principal concept in the phase 2 study. The roadmap toward commercialization are presented with highlighting the importance of international collaboration.
Nakabayashi, Hiroki; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Sato, Koji; Niwa, Hajime; Aoki, Kazuo*
JAEA-Technology 2006-027, 119 Pages, 2006/03
This report describes a study about the criticality safety design for the large-scale electrorefiner, which is designed in the activities of "The Design Study of Metal Fuel Recycle System (2002)", under the collaboration with Central Research Institute of Electric Power Industry, and the continuation of "A Study of the Criticality Safety Design for the Metal Fuel Recycle System", which was published at September 2003. The report includes a detail design and quantitative criticality parameter limits based on "the mass control supported with chemical form control" concept which is proposed in "A Study of the Criticality Safety Design for the Metal Fuel Recycle System". Furthermore procedures to determine these limits are presented in the report. Next we studied contingencies anticipated under the critical control and executed quantitative criticality safety analyses of models based on these abnormal conditions. The analytical result shows adequate safety margins are existed in the criticality safety design even if many of these contingencies could occur. Moreover we propose a concept of material transfer and production control system, we call it as "Operation by wire", which all equipment and handling machines are electrified and the control system provides completely automated process control and operation. The control system eliminates human errors and violations like over batching error or transfer error in the commercial scale metal fuel recycle system with complicated operation procedures.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Fujita, Satoshi; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Sato, Ikken; Niwa, Hajime
Proceedings of Technical Meeting on Severe Accident and Accident Management (CD-ROM), 12 Pages, 2006/03
For the transition phase analysis of core disruptive accidents, the development of a three-dimensional reactor safety analysis code, SIMMER-IV, has been carried out based on the technology of the two-dimensional SIMMER-III code. The world first application of SIMMER-IV to a small-sized sodium-cooled fast reactor was also attempted to clarify event progression in the early stage of the transition phase. This SIMMER-IV calculation was compared to the two-dimensional case calculated by SIMMER-III, neglecting the presence of control rod guide tubes. The present analysis with the three-dimensional representation suggested that the conventional scenario leading to rather early high-mobility fuel-pool formation is unrealistic and the degraded core tends to keep low mobility in the early stage of transition phase.
Niwa, Hajime; Fiorini, G.-L.*; Sim, Y.-S.*; Lennox, T.*; Cahalan, J. E.*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
None
Kuznetsov, I.*; Shvetsov, Y. E.*; Ashurko, Yu. M.*; Volkov, A. V.*; Kashcheev, M. V.*; Tsykunov, A. G.*; Kamanin, Y. L.*; Bakhmetyev, A. M.*; Zamyatin, V. A.*; Niwa, Hajime; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
None
Kubo, Shigenobu; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Yamano, Hidemasa; Niwa, Hajime
JNC TN9400 2005-025, 156 Pages, 2005/04
This study is dedicated to establish rational safety design concepts for the power plants and their related fuel cycle facilities in the feasibility study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. Major results of this study are as follows. *The principles of safety design and evaluation for the sodium-cooled reacter were formulated as well as the way to achives the equivalent safety level to LWRs,design requirements to eliminate necessity of the evacuation, and the contaiment performance requrement. As a result, the item for further investigation was clarified in the containment design. As for small scale sodium-cooled reacter with metallic fuel,state-of -the -arts of knowledge for the evaluation of GDA, the way for elimiration of re-critically and related design requirements for the reacter core were identifiled. *A preliminary evaluation shoed that the feasibility of molten fuel discharge capability of modified inner duct conceot forsodium-cooled MOX fuel reacters.The three dimentional effect in the course of the transition phase of CDA was investigated and foud that the cooling effect of the control rod guide tube is pronounced comparing with two dimensional case. * A preliminary evaluation showed that the occurrence probability of PLOHS can be reduced by more than one order with help of stome accident management measures such as steam spply to SGs, improvement of diversity for the air cooler dumper. * Concering the SG tube repture for the LBE-cooled reacter, it was found out that certain amoumt of steam can enter into the core in case of one tube rupture at the bottom of SG and that steam jet breaker should be installed in order to avoid massive ateam ingress. * A risk study on some typicals events in the facilities of the suoer-critical direct extraction reprocessing and the extraction chromatography method for MA recovery revealed that their risk levels are sufficiently low.
Kubo, Shigenobu; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kawada, Kenichi; Onoda, Yuichi; Sato, Ikkenn; Kamiyama, Kenji; Ueda, Nobuyuki*; Fujita, Satoshi; Niwa, Hajime
JNC TN9400 2004-041, 135 Pages, 2004/07
This report shows the results of the study on countermeasures for the elimination of re-criticality issue for the sodium cooled reactors, which was conducted in 2003 as a part of the feasibility study phase II for the commercialization of fast reactors. A sort of analytical studies related to the in-vessel retention capability under the unprotected loss of flow condition was conducted for the large scale and medium scale sodium cooled reactors, aiming at establishing some promising concepts to resolve the re-criticality issue keeping consistency with the basic concept of the core and plant design. Major conclusions are as follows. ABLE concept, which is proposed as a measure to enhance the fuel discharge capability in the early transition phase, needs much time to initiate fuel discharge than wrapper tube failure. Therefore it is currently concluded that it is difficult to show clear perspective. A modified version of FAIDUS which has less drawbacks on the core and cycle performance and related R&Ds than original FAIDUS was proposed for further study. In-place retention and cooling in the core region is important from view point of reduction of R&D loads conceming post accident material relocation and cooling at the bottom of the reactor vessel. A possibility of which the in-vessel retention can be achieved by quantitatively clarifying the effect of the superior cooling potential of sodium was shown. Based on the currently available information related to FAIDUS and ABLE, possible candidates of experimental studies were shown. An initiating phase analysis for the metallic fuel core with 550 C of core outlet temperature and 8
C of core outlet temperature and 8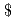 of sodium void worth resulted in mild consequence without prompt criticality. Although there is still large uncertainty in the early transition phase, it might be possible to avoid severe re-criticality. And it was shown that power excursion due to molten fuel sloshing might be milder than that of MOX fuel case.
of sodium void worth resulted in mild consequence without prompt criticality. Although there is still large uncertainty in the early transition phase, it might be possible to avoid severe re-criticality. And it was shown that power excursion due to molten fuel sloshing might be milder than that of MOX fuel case.
Konomura, Mamoru; Ogawa, Takashi; Okano, Yasushi; Yamaguchi, Hiroyuki; Murakami, Tsutomu; Takaki, Naoyuki; Nishiguchi, Youhei; Sugino, Kazuteru; Naganuma, Masayuki; Hishida, Masahiko; et al.
JNC TN9400 2004-035, 2071 Pages, 2004/06
The attractive concepts for Sodium-, lead-bismuth-, helium- and water-cooled FBRs have been created through using typical plant features and employing advanced technologies. Efforts on evaluating technological prospects of feasibility have been paid for these concepts. Also, it was comfirmed if these concepts satisfy design requierments of capability and performance presumed in the feasibilty study on commertialization of Fast Breeder Reactor Systems. As results, it was concluded that the selection of sodium-cooled reactor was most rational for practical use of FBR technologies in 2015.
Ishida, Masayoshi; Kawada, Kenichi; Niwa, Hajime
JNC TN9400 2003-059, 74 Pages, 2003/07
Safety characteristics in core disruptive accidents (CDAs) of mid-sized MOX fueled liquid metal reactor core of high converter type have been examined by using the CDA initiating phase analysis code SAS4A. The design concept of high converter type reactor core has been studied as one of options in the category of sodium-cooled reactor in Phase II of Feasibility Study on Commercialized Fast Reactor Cycle System.An unprotected loss-of-flow accident (ULOF) has been selected as a representative CDA initiator for this study. A core concept of high converter type, which employed a large diameter fuel pin of 11.1mm with 1.2m core height to get a large fuel volume fraction in the core to achieve high internal conversion ratio was proposed in JFY2001. Each fuel subassembly of the core (abbreviated here as UPL120) was provided with an upper sodium plenum directly above the core to reduce the sodium void reactivity worth. Because of the large fuel pin diameter, average specific fuel power density (31 kW/kg-MOX) of UPL120 is about one half of those of conventional large MOX cores. The reactivity worth of sodium voiding is 6$ in the whole core, and -1$ in the all upper plenums. Initiating phase of ULOF accident in UPL120 under the conditions of nominal design and best estimate analysis resulted in a slightly super-prompt critical power burst. The causes of the super-prompt criticality have been identified twofold: (a) the low specific fuel power density of core reduced the effectiveness of prompt negative reactivity feedback of Doppler and axial fuel expansion effects upon increase in reactor power, and (b) the longer core height compared with conventional 1m cores brought, together with the lower specific power density, a remarkable delay in insertion of negative fuel dispersion reactivity after the onset of fuel disruption in sodium voided subassembly due to the lower linear heat rating in the top portion of the core. During the delay, burst-type fuel failures in sodium un-v
Niwa, Hajime; Pierre Lo Pinto*; Tobita, Yoshiharu; ; ; Kamiyama, Kenji
JNC TY9400 2002-021, 48 Pages, 2001/12
This is interim report describing the progress and the results of the collaborative research works between JNC snd CEA on the safety logic in future fast reactors under the title of "Establishment of Rationa- lizedSafety Assurance Logic Aiming at FBRs with Enhanced Social Acceptance" from 1999 to 2001. This contains JNC's contribution and common view of both partners. (1) Safety goals are proposed from JNC and CEA. Significant coherency is found such as to keep defence-in depth, mitigation measures against core melt are taken into account for containment design, "evacuation free" concept is pursued, quatitative safety target is also considered as well as deterministic approach, and improvement of social acceptance is considered from the development stage of the fuel cycle including nuclear power plants. (2) Safety characteristics of each candidate coolant were compared and discussed. Gascooled fast reactor is a common interest area. Discussions are focused
Niwa, Hajime
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 32(3-4), p.621 - 629, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:77.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)None
Tobita, Yoshiharu; Morita, Koji; Kawada, Kenichi; Niwa, Hajime; Nonaka, Nobuyuki
PNC TN9410 97-079, 106 Pages, 1997/09
The sequences of ULOF (unprotected loss-of-flow) event in the prototype FBR has been evaluated, as a part of the research and development (R&D) in the reactor safety research, reflecting the latest experimental and analytical knowledge on CDA (core disruptive accident) which has been accumulated at O-arai Engineering Center. In the R&D activity on the FBR reactor safety subject, we have accumulated the experimental knowledge of mitigation mechanism in the energy generating process in CDA, utilizing international in-pile safety experimental programs such as CABRI program, as well as the out-of-pile experiments in Japan and foreign countries. This knowledge has been reflected to the development and validation of the SAS and SIMMER code. The objectives of this study are to apply these new assessment techniques to the prototype FBR and to clarify quantitatively in detail the energy generation process of CDA. In this study, an emphasis is placed on the event sequence of the melt progression phase ("transition phase") which has been recognized as one of the important issues of CDA analysis. The major parameters to be considered in this phase are the change of the mobile molten fuel mass and the history of the fuel motion, and also the relation between these parameters and energy generation mechanism. The following methods and approaches have been taken into account in this evaluation study. (a)The SAS4A code is used for the analysis of the transient behavior in the first Phase driven by core voiding ("initiating phase"), and the SIMMER-III code is used for the latter phases with melt-progression (tansition phase) and also the energy conversion process from the thermal one to the mechanical one. These codes have been developed and validated under the collaboration among PNC, CEA and FZK. (b)The uncertainty band of the void reactivity worth and Doppler coeficient has been reduced through the re-evaluation of the critical experimental data in the neutron physics area. ...
Niwa, Hajime; Kawata, Norio; Ieda, Yoshiaki; Sato, Ikken; Ohno, Shuji; Uto, Nariaki; Miyahara, Shinya; Kondo, Satoru; Kamide, Hideki; Yamaguchi, Akira; et al.
PNC TN9410 94-154, 317 Pages, 1995/03
None
Niwa, Hajime; Ieda, Yoshiaki
PNC TN9410 93-297, 82 Pages, 1993/11
This is an interim report of a study on requested roles of the Safety Engineering Reactor for Accident Phenomenology (SERAPH) project which has been performed by the working group organized under the FBR safety research specialist committee. In this working group, the future requirements for SERAPH has been studied as follows: (1)Considering that the safety level of future FBRs would be much more improved from the present concept of sodium cooled mixed-oxide fueled large scale FBR, prevention and mitigation measures could be introduced or much more enhanced. Therefore currently proposed design measures have been widely reviewed and some were newly proposed, then the information was presented to the working group. An investigation was conducted by means of "questionnaire" to the working group members asking their effectiveness and technical feasibility. (2)Based on the results of the questionnaire and discussions in the working group, "risk reduction" has been selected as an index which should be pursued of through long-term safety research where SERAPH is expected to play an important role. The presented measures were analyzed and evaluated from the viewpoint of preventing and/or mitigating important phenomena in CDA (for example, recriticality) because CDA is a risk dominant event in FBRs. (3)R&D plans of each measure were drafted and needs of in-pile and reactor-scale experiments were examined including new experimental facilities. Based on this study, new R&D themes were preliminarily selected as future requirements for the SERAPH project. The final report will be presented at the end of the FY1993. This will include the results of the additional study reflecting the comments from the members of the FBR safety research specialist committee.
Niwa, Hajime
PNC TN9410 93-231, 104 Pages, 1993/11
The SAS4A, an FBR safety analysis code, has a material motion model for analysis of post fuel failure accident progression. This model, named LEVITATE, is a three-velocity field model, and the third velocity field is assigned for solid chunk fuel component. In the initiating phase of the ATWS accident of FBR's, which is the subject of the SAS4A, solid fuel chunks generated at the disruption-type fuel pin failure play an important role in the flow, freezing and jamming of the molten fuel. Therefore, the chunk model has been improved in this study. Models improved are as follows: hydraulics related models; (1)friction model between chunks and structure wall, (2)drag term between chunks and gas mixture dependent on flow regime, jamming related models; (3)jamming due to increased volume fraction of chunks, (4)jamming of large chunks at contraction point, (5)jamming due to arch formation at contraction point, and (6)break up of jamming due to pressure gradient. These models have been validated through experimental analyses of CABRI E13. These models have also been applied to reactor cases, and their validity has been confirmed, then problems to be solved in the future have been pointed out. This model decreases the uncertainty of the boundary conditions to the succeeding transition phase, thus adoptability of SAS4A to the reactor cases has been very much improved. Furthermore, the improved SAS4A allows us to investigate the early termination scenario of the accident which could be highly expected in future FBRs with decreased boid reactivity. It was agreed upon among PNC, KfK, and CEA to include this model into their next unified version of SAS4A, which will be called as "SAS4A.REF94".
Mukai, Kazuo; Niwa, Hajime; Sagayama, Yutaka; Ono, Katsumi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Niwa, Hajime; Kurisaka, Kenichi; Sato, Ikken; Tobita, Yoshiharu; Kamiyama, Kenji; Yamano, Hidemasa; Miyahara, Shinya; Ohno, Shuji; Seino, Hiroshi; Ishikawa, Hiroyasu; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to develop the core damage evaluation technology (level 2 PSA) for sodium-cooled fast reactors, we develop the new analysis codes of post accident material relocation phase and of ex-vessel events, and we develop the technical bases that is necessary for level 2 PSA. In this presentation, summary and scope of the entire study is introduced as a part of the 4 series presentations.