Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from 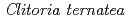
Hiromoto, Takeshi; Honjo, Eijiro*; Noda, Hisanobu*; Tamada, Taro; Kazuma, Kohei*; Suzuki, Masahiko*; Blaber, M.; Kuroki, Ryota
Protein Science, 24(3), p.395 - 407, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:72 Percentile:89.80(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)UDP-glucose: anthocyanidin 3- -glucosyltransferase (UGT78K6) from
-glucosyltransferase (UGT78K6) from 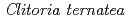 catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin. To understand the acceptor-recognition scheme of UGT78K6, the crystal structure of UGT78K6 and its complex forms with anthocyanidin delphinidin and petunidin, and flavonol kaempferol were determined to resolutions of 1.85
catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin. To understand the acceptor-recognition scheme of UGT78K6, the crystal structure of UGT78K6 and its complex forms with anthocyanidin delphinidin and petunidin, and flavonol kaempferol were determined to resolutions of 1.85  , 2.55
, 2.55  , 2.70
, 2.70  and 1.75
and 1.75  respectively. The anthocyanidin- and flavonol-acceptor binding details are almost identical in each complex structure, although the glucosylation activities against each acceptor were significantly different. The acceptor substrates in UGT78K6 are reversely bound to its binding site by a 180
respectively. The anthocyanidin- and flavonol-acceptor binding details are almost identical in each complex structure, although the glucosylation activities against each acceptor were significantly different. The acceptor substrates in UGT78K6 are reversely bound to its binding site by a 180 rotation about the O1-O3 axis of the flavonoid backbones observed in
rotation about the O1-O3 axis of the flavonoid backbones observed in  GT1 and UGT78G1. These substrate recognition schemes suggest the potential for controlled synthesis of natural pigments.
GT1 and UGT78G1. These substrate recognition schemes suggest the potential for controlled synthesis of natural pigments.
 -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from 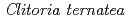
Hiromoto, Takeshi; Honjo, Eijiro*; Tamada, Taro; Noda, Hisanobu*; Kazuma, Kohei*; Suzuki, Masahiko*; Kuroki, Ryota
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 20(6), p.894 - 898, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:42 Percentile:86.61(Instruments & Instrumentation)Flowers of the butterfly pea ( ) accumulate a group of polyacylated anthocyanins, named ternatins, in their petals. The first step in ternatin biosynthesis is the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin, a reaction catalyzed in
) accumulate a group of polyacylated anthocyanins, named ternatins, in their petals. The first step in ternatin biosynthesis is the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin, a reaction catalyzed in  by UDP-glucose:anthocyanidin 3-
by UDP-glucose:anthocyanidin 3- -glucosyltransferase (
-glucosyltransferase ( 3GT-A; AB185904). To elucidate the structure-function relationship of
3GT-A; AB185904). To elucidate the structure-function relationship of  3GT-A, recombinant
3GT-A, recombinant  3GT-A was expressed in
3GT-A was expressed in  and its tertiary structure was determined to 1.85
and its tertiary structure was determined to 1.85  , resolution by using X-ray crystallography. The structure of
, resolution by using X-ray crystallography. The structure of  3GT-A shows a common folding topology, the GT-B fold, comprised of two Rossmann-like
3GT-A shows a common folding topology, the GT-B fold, comprised of two Rossmann-like  /
/ /
/ domains and a cleft located between the N- and C-domains containing two cavities that are used as binding sites for the donor (UDP-Glc) and acceptor substrates. By comparing the structure of
domains and a cleft located between the N- and C-domains containing two cavities that are used as binding sites for the donor (UDP-Glc) and acceptor substrates. By comparing the structure of  3GT-A with that of the flavonoid glycosyltransferase
3GT-A with that of the flavonoid glycosyltransferase 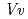 GT1 from red grape (
GT1 from red grape ( ) in complex with UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose and kaempferol, locations of the catalytic His-Asp dyad and the residues involved in recognizing UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose were essentially identical in
) in complex with UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose and kaempferol, locations of the catalytic His-Asp dyad and the residues involved in recognizing UDP-2-deoxy-2-fluoro glucose were essentially identical in  3GT-A, but certain residues of
3GT-A, but certain residues of 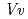 GT1 involved in binding kaempferol were found to be substituted in
GT1 involved in binding kaempferol were found to be substituted in  3GT-A. These findings are important for understanding the differentiation of acceptor-substrate recognition in these two enzymes.
3GT-A. These findings are important for understanding the differentiation of acceptor-substrate recognition in these two enzymes.
 -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from 
Hiromoto, Takeshi; Honjo, Eijiro*; Tamada, Taro; Kuroki, Ryota; Noda, Hisanobu*; Kazuma, Kohei*; Suzuki, Masahiko*
no journal, ,
UDP-glucose: anthocyanidin 3- -glucosyltransferase from
-glucosyltransferase from  (
( 3GT-A) catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin. The glucosylation of delphinidin at the 3-hydroxyl group has been proposed as an initial glucosylation step toward the biosynthesis of ternatins, which are blue anthocyanins found in the petals of
3GT-A) catalyzes the transfer of glucose from UDP-glucose to anthocyanidins such as delphinidin. The glucosylation of delphinidin at the 3-hydroxyl group has been proposed as an initial glucosylation step toward the biosynthesis of ternatins, which are blue anthocyanins found in the petals of  . Although the crystal structures of several flavonoid glycosyltransferases (UGTs) were determined, the acceptor-substrate complexes were limited to the flavonol-bound forms. Here, in order to understand the acceptor-recognition scheme of
. Although the crystal structures of several flavonoid glycosyltransferases (UGTs) were determined, the acceptor-substrate complexes were limited to the flavonol-bound forms. Here, in order to understand the acceptor-recognition scheme of  3GT-A, the crystal structures in complex with anthocyanidin delphinidin and petunidin, and flavonol kaempferol were determined to resolutions of 2.6
3GT-A, the crystal structures in complex with anthocyanidin delphinidin and petunidin, and flavonol kaempferol were determined to resolutions of 2.6  , 2.7
, 2.7  , and 1.8
, and 1.8  respectively. The enzyme recognition of unstable anthocyanidins was firstly observed in this structural determination; nevertheless, the molecular orientations of these three acceptors in the binding site are different from those of the known flavonoid UGTs,
respectively. The enzyme recognition of unstable anthocyanidins was firstly observed in this structural determination; nevertheless, the molecular orientations of these three acceptors in the binding site are different from those of the known flavonoid UGTs, 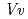 GT1 and UGT78G1. The crystal structures of
GT1 and UGT78G1. The crystal structures of  3GT-A provide insight not only into anthocyanidin configurations in enzyme, but also into a different binding scheme for acceptor-substrate recognition compared with the known UGTs.
3GT-A provide insight not only into anthocyanidin configurations in enzyme, but also into a different binding scheme for acceptor-substrate recognition compared with the known UGTs.