Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sogabe, Joji; Ishida, Shinya; Tagami, Hirotaka; Okano, Yasushi; Kamiyama, Kenji; Onoda, Yuichi; Matsuba, Kenichi; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Kubota, Ryuzaburo*; et al.
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Fuel Cycle (GLOBAL2024) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2024/10
In the frame of France-Japan collaboration, the calculational methodologies were defined and assessed, and the phenomenology and the severe accident consequences were investigated in a pool-type sodium-cooled fast reactor.
Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Muramatsu, Kazuo*; Sutani, Koichi*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Saruta, Koichi; Otake, Yoshie*
Journal of Neutron Research, 26(2-3), p.69 - 74, 2024/09
Slow neutrons, such as cold neutrons, are important non-destructive probes not only for basic physics but also for the structural genomics advancements in the life sciences and the battery technology advancements needed for the transition to a hydrogen society. Neutron-based science is also known as high-neutron-intensity-dependent science. A new unique method focusing on nanosized particle aggregation has been proposed to increase neutron intensity in that energy region. The method is based on intensity enhancement by multiple coherent scatterings with nanosized particle aggregation. The aggregation of nanosized particles matches the wavelength of below cold neutrons, causing a similar effect to coherent scattering, so-called Bragg scattering, leading to neutron intensity enhancement by several orders of magnitude. Nanodiamonds and magnesium hydride have recently been studied numerically and experimentally. The major challenge with nanodiamonds in practical applications is the molding method. Another carbon structure, graphene is focused on to find a solution to this problem. It is hypothesized that nanosized graphene could aid coherent neutron scattering under particle size conditions similar to nanodiamonds. We report the potential of nanosized graphene as a reflector material below cold neutrons, together with experimental results.
 O
OKondo, Yosuke*; Achouri, N. L.*; Al Falou, H.*; Atar, L.*; Aumann, T.*; Baba, Hidetada*; Boretzky, K.*; Caesar, C.*; Calvet, D.*; Chae, H.*; et al.
Nature, 620(7976), p.965 - 970, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:95.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)no abstracts in English
Teshigawara, Makoto; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Yan, M.*; Muramatsu, Kazuo*; Sutani, Koichi*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Saruta, Koichi; Otake, Yoshie*
Nanomaterials (Internet), 13(1), p.76_1 - 76_9, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:47.87(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)To enhance neutron intensity below cold neutrons, it is proposed that nanosized graphene aggregation could facilitate neutron coherent scattering under particle size conditions similar to nanodiamond. It might also be possible to use it in high neutron radiation conditions due to graphene's strong sp2 bonds. Using the RIKEN accelerator-driven compact neutron source and iMATERIA at J-PARC, we performed neutron measurement experiments, total neutron cross-section, and small-angle neutron scattering on nanosized graphene aggregation. The measured data revealed, for the first time, that nanosized graphene aggregation increased the total cross-sections and small-angle scattering in the cold neutron energy region, most likely due to coherent scattering, resulting in higher neutron intensities, similar to nanodiamond.
 )
)Komatsu, Kazuki*; Iwasaki, Tsugumi*; Murata, Kosuke*; Yamashiro, Hideaki*; Goh, V. S. T.*; Nakayama, Ryo*; Fujishima, Yohei*; Ono, Takumi*; Kino, Yasushi*; Shimizu, Yoshinaka*; et al.
Reproduction in Domestic Animals, 56(3), p.484 - 497, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:84.51(Agriculture, Dairy & Animal Science)We have established an archive system of livestock and wild animals from the surrounding ex-evacuation zone. Wildlife within the alert zone have been exposed to low-dose-rate (LDR) radiation for a long and continuous time. In this study, we analysed the morphological characteristics of the testes and in vitro fertilization (IVF) capacity of cryopreserved sperm of raccoons from the ex-evacuation zone of the FDNPP accident. This study revealed that the chronic and LDR radiation exposure associated with the FDNPP accident had no adverse effect on the reproductive characteristics and functions of male raccoons.
Sonoda, Tetsu*; Katayama, Ichiro*; Wada, Michiharu*; Iimura, Hideki; Sonnenschein, V.*; Iimura, Shun*; Takamine, Aiko*; Rosenbusch, M.*; Kojima, Takao*; Ahn, D. S.*; et al.
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2019(11), p.113D02_1 - 113D02_12, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.82(Physics, Multidisciplinary)An in-flight separator, BigRIPS, at RIBF in RIKEN provides each experiment with specific nuclides separated from many nuclides produced by projectile fragmentation or in-flight fission. In this process, nuclides other than separated ones are discarded on the slits in BigRIPS, although they include many nuclides interested from the view point of nuclear structure. In order to extract these nuclides for parasitic experiments, we are developing a method using laser ion-source (PALIS). A test experiment with  Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around
Se beam from RIBF has been performed by using a gas cell set in BigRIPS. Unstable nuclides around  Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
Se were stopped in the gas cell in accordance with a calculation using LISE code. The stopping efficiency has been estimated to be about 30%. As a next step, we will establish the technique for extracting reaction products from the gas cell.
 -butadiene) rubbers
-butadiene) rubbersYamaguchi, Daisuke; Yuasa, Takeshi*; Sone, Takuo*; Tominaga, Tetsuo*; Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Hashimoto, Takeji*
Macromolecules, 50(19), p.7739 - 7759, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:53.18(Polymer Science)We elucidated the spatial distribution of filler particles in cross-linked poly(styrene- -butadiene) rubbers (SBR) developed under a typical fillers/rubbers compounding process as one of dissipative structures formed under a stress field imposed on the given system. The dispersion state of the fillers in SBR was clarified on the basis of hierarchical structures consisting of five structure levels. More specifically, it has the following characteristics depending on the specific interactions: Small, compact clusters build up compact mass-fractal structures, while large, loose clusters build up open mass-fractal structures.
-butadiene) rubbers (SBR) developed under a typical fillers/rubbers compounding process as one of dissipative structures formed under a stress field imposed on the given system. The dispersion state of the fillers in SBR was clarified on the basis of hierarchical structures consisting of five structure levels. More specifically, it has the following characteristics depending on the specific interactions: Small, compact clusters build up compact mass-fractal structures, while large, loose clusters build up open mass-fractal structures.
Noda, Yohei*; Koizumi, Satoshi*; Masui, Tomomi*; Mashita, Ryo*; Kishimoto, Hiromichi*; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Kumada, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Junichi*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(6), p.2036 - 2045, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:76.98(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei; Ishikawa, Norito
Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 218, p.59 - 65, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:37.26(Biochemical Research Methods)We compared dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) behavior of electron-beam irradiated polyethylene (e-PE) with that of TEMPO-doped polystyrene (T-PS). Although both T-PS had a sharp maximum in nuclear polarization at the concentration of free radicals of 2 10
10 spins cm
spins cm , that of e-PE depend much less. Growth and decay rates of polarization of e-PE linearly increased with increasing the radical concentration, whereas those rates of T-PS increased with square of radical concentration. We concluded that, not a pair of unspecified radicals accidentally located nearby, but a pair of alkyl radicals produced by the dissociation of C-H bond by an electron irradiation and the subsequent hydrogen abstraction reaction play an important role on DNP of e-PE.
, that of e-PE depend much less. Growth and decay rates of polarization of e-PE linearly increased with increasing the radical concentration, whereas those rates of T-PS increased with square of radical concentration. We concluded that, not a pair of unspecified radicals accidentally located nearby, but a pair of alkyl radicals produced by the dissociation of C-H bond by an electron irradiation and the subsequent hydrogen abstraction reaction play an important role on DNP of e-PE.
Noda, Yohei; Kumada, Takayuki; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 44(3), p.503 - 513, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.04(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We measured small angle neutron scattering (SANS) for dynamically polarized block copolymer sample, one phase of which were selectively doped with radical. Dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) caused the neutron scattering length of proton largely, as a result, the SANS intensity. By the analysis of the change of the SANS intensity, we found out the inhomogeneous distribution of the radical induced the inhomogeneous polarization (about 2% for the average polarization being 30%).
 He neutron spin filters on the small-angle neutron scattering spectrometer SANS-J-II
He neutron spin filters on the small-angle neutron scattering spectrometer SANS-J-IISakaguchi, Yoshifumi; Kira, Hiroshi; Oku, Takayuki; Shinohara, Takenao; Suzuki, Junichi; Sakai, Kenji; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; Noda, Yohei; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 294(1), p.012017_1 - 012017_7, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.29(Physics, Applied)Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei; Koizumi, Satoshi; Hashimoto, Takeji
Journal of Chemical Physics, 133(5), p.054504_1 - 054504_7, 2010/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:33.72(Chemistry, Physical)We carried out time-resolved small-angle neutron scattering studies of dynamically polarized high-density polyethylene (HDPE) doped with 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine 1-oxyl (TEMPO) persistent free radicals. We observed an enhancement of the scattering intensity by a factor of 100 in maximum after switching a microwave frequency. The enhancement was found to be due to concentration fluctuation of TEMPO, which generates heterogeneity of polarization with the length-scale of about 100 nm and scattering due to the heterogeneity. The length scale of the heterogeneity indicates that the TEMPO free radicals are localized more in non-fibrils but less in fibrils of HDPE.
Uchida, Yoshiaki*; Suzuki, Katsuaki*; Tamura, Rui*; Ikuma, Naohiko*; Shimono, Satoshi*; Noda, Yohei; Yamauchi, Jun*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 132(28), p.9746 - 9752, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:53 Percentile:75.31(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)An anisotropic and inhomogeneous magnetic interaction (the average spin-spin interaction constant, 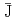
 0) was observed in the various liquid crystalline (LC) phases of racemic and nonracemic all-organic radical LC compounds. We discussed how the LC superstructures induced the magnetic interaction to operate in the LC phases in terms of spin-spin dipole and exchange interactions by means of VT-EPR spectroscopy. The magnitude of the magnetic interaction depended on the type of LC phase, or the superstructure. Furthermore, these radical LC droplets floating on water were commonly attracted to a permanent magnet and moved freely under the influence of this magnet, whereas the crystallized particles of the same compounds never responded to the magnet. The response of the LC droplets to the magnet also varied depending on the type of LC phase, that is, the extent of the magnetic interaction.
0) was observed in the various liquid crystalline (LC) phases of racemic and nonracemic all-organic radical LC compounds. We discussed how the LC superstructures induced the magnetic interaction to operate in the LC phases in terms of spin-spin dipole and exchange interactions by means of VT-EPR spectroscopy. The magnitude of the magnetic interaction depended on the type of LC phase, or the superstructure. Furthermore, these radical LC droplets floating on water were commonly attracted to a permanent magnet and moved freely under the influence of this magnet, whereas the crystallized particles of the same compounds never responded to the magnet. The response of the LC droplets to the magnet also varied depending on the type of LC phase, that is, the extent of the magnetic interaction.
Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 201(2), p.115 - 120, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.34(Biochemical Research Methods)We have carried out a dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) study of proton spins of UV-irradiated solid butanol containing phenol. By the aid of butyl free radicals produced by the photolysis, the butanol sample was dynamically polarized up to the polarization of 1.4% at 1.5 K and 1.2 T. Unlike persistent free radicals such as nitroxy and trityl free radicals commonly used for DNP, the butyl free radicals immediately decay by melting. We propose that free radicals produced by UV-photolysis are applicable to the DNP-enhanced hyperpolarized liquid-state NMR.
Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2637 - 2639, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:54.68(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have developed dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) system for SANS-J-II at the JRR-3 atomic research reactor at Japan Atomic Energy Agency. Our system is composed of superconducting magnet (3.3 Tesla), Gunn oscillator as a microwave source (94 GHz), and cryostat (1.2 K). We succeeded in polarizing polyethylene sample up to 0.32 and observing effects of polarization on SANS profile. We plan to use the DNP and SANS system in order to determine structure factors of multi-component systems.
Noda, Yohei; Kumada, Takayuki; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2572 - 2574, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:35.37(Physics, Condensed Matter)We polarized hydrogen nuclear spins of polyethylene samples, doped with organic radical (TEMPO), by use of a dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) technique, in which the sample was irradiated by microwave (94 GHz) at 3.3 Tesla and 1.4 K. For the samples under the DNP state, we conducted small-angle scattering experiments with polarized neutrons. For the sample with low crystallinity (polarization: 32%), the shift of the incoherent scattering level was observed. For the sample with high crystallinity (polarization: 23%), the enhancement of the coherent scattering due to the crystalline structure was observed.
Kumada, Takayuki; Noda, Yohei; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 606(3), p.669 - 674, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:60.62(Instruments & Instrumentation)We carried out a DNP study of high (HPE) and low (LPE) crystallinity polyethylene films, which were doped with TEMPO. The proton polarization of 32% was obtained for LPE and 23% for HPE at 3.35 T and 1.4 K. We found by ESR study that TEMPO did not incorporated into the crystalline part, and was localized only at the amorphous part. We suggest that the smaller nuclear polarization for HPE is related to the localization of TEMPO in the smaller amorphous regions.
Uchida, Yoshiaki*; Ikuma, Naohiko*; Tamura, Rui*; Shimono, Satoshi*; Noda, Yohei; Yamauchi, Jun*; Aoki, Yoshio*; Nohira, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Materials Chemistry, 18(25), p.2950 - 2952, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:76.24(Chemistry, Physical)We found out an unusual intermolecular magnetic interaction in the liquid-crystalline (LC) state of an all-organic radical compound on surface of water (73  C); the magnetic interaction actually allows the LC droplet on water to be attracted by a weak permanent magnet, whereas the crystalline phase did not respond to the magnet.
C); the magnetic interaction actually allows the LC droplet on water to be attracted by a weak permanent magnet, whereas the crystalline phase did not respond to the magnet.
 He detector to SANS-J-II
He detector to SANS-J-IINoda, Yohei; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Koizumi, Satoshi
no journal, ,
For focusing-geometry ultrasmall angle polarized neutron scattering spectrometer (SANS-J-II) at Japan Research Reactor-3 (JRR-3), there had been used a single-wire type detector, which composed of a pair of comb-shaped electrodes. However, the detector has a problem of mis-counting neutrons with a frequency of more than 10000 cps. We are going to carry out a project of increasing the incoming neutron flux by exchanging the Ni guide tubes for supermirror ones at upstream C3 beam line, through which neutrons pass from the reactor to SANS-J-II. For satisfying the required performance in neutron counting, we newly introduced a multi-wire type detector, which is composed of 80 one-dimensional  He detectors. In this presentation, we will report the design and performance of this newly introduced detector system.
He detectors. In this presentation, we will report the design and performance of this newly introduced detector system.
Noda, Yohei; Yamaguchi, Daisuke; Hashimoto, Takeji; Koizumi, Satoshi; Tominaga, Tetsuo*; Sone, Takuo*; Yuasa, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
For investigating the dispersion state of silica particles in styrene-butadiene rubber composites, we measured its small angle neutron scattering with polarizing its proton spins. By proton spin polarization, we can control the coherent scattering length for neutron beam. As a result, we succeeded in abstracting the scattering profile only from the silica particles.