Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
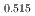 Gd
Gd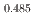 Mn
Mn O
O
Ishii, Yuta*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Lustikova, J.*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Wakabayashi, Yusuke*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*
Physical Review B, 110(18), p.184404_1 - 184404_7, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:96.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 ladder
ladderUeda, Hiroshi*; Onoda, Shigeki*; Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*; Yoshizawa, Daichi*; Morioka, Toshiaki*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Hagihara, Masato*; Soda, Minoru*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; et al.
Physical Review B, 101(14), p.140408_1 - 140408_6, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:25.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kaneko, Koji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tamura, Itaru; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; Munakata, Koji*; Moyoshi, Taketo*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 49(1), p.120 - 127, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:59 Percentile:96.22(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Oikawa, Kenichi; Kawasaki, Takuro; Ohara, Takashi; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Kaneko, Koji; Tamura, Itaru; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Harada, Masahide; Nakao, Akiko*; Hanashima, Takayasu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 1, p.014013_1 - 014013_5, 2014/03
A new single crystal time-of-flight neutron diffractometer has been installed at BL18 of the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility of J-PARC. The diffractometer "SENJU" was designed for precise crystal and magnetic structure analyses using a small crystal less than 1.0 mm under multiple extreme environments such as low-temperature and high-magnetic field. The first neutron beam was delivered to the sample position on March 5, 2012. Subsequently, the hardware and software of SENJU have been checked and confirmed that they worked fine. At the same time, diffraction experiments of several organic and inorganic crystals have been done using NaCl, C12A7, and so on. In these measurements, Bragg reflections in the high-Q region (d-spacing
under multiple extreme environments such as low-temperature and high-magnetic field. The first neutron beam was delivered to the sample position on March 5, 2012. Subsequently, the hardware and software of SENJU have been checked and confirmed that they worked fine. At the same time, diffraction experiments of several organic and inorganic crystals have been done using NaCl, C12A7, and so on. In these measurements, Bragg reflections in the high-Q region (d-spacing  0.5
0.5  ) were clearly observed and analyzed successfully. In this presentation, we will show the instrument design and performance evaluation of SENJU in detail.
) were clearly observed and analyzed successfully. In this presentation, we will show the instrument design and performance evaluation of SENJU in detail.
 O
O
Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Noda, Yukio*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
Physical Review B, 88(14), p.140403_1 - 140403_5, 2013/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:63.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Ti
Ti O
O
Chang, L.-J.*; Onoda, Shigeki*; Su, Y.*; Kao, Y.-J.*; Tsuei, K.-D.*; Yasui, Yukio*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Lees, M. R.*
Nature Communications (Internet), 3, p.992_1 - 992_7, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:172 Percentile:97.03(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Tamura, Itaru; Oikawa, Kenichi; Kawasaki, Takuro; Ohara, Takashi; Kaneko, Koji; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Takahashi, Miwako; Kiyotani, Tamiko*; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 340, p.012040_1 - 012040_4, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:94.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)Ogura, Koichi; Fukumi, Atsushi*; Li, Z.*; Orimo, Satoshi; Sagisaka, Akito; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Kado, Masataka; Mori, Michiaki; Yogo, Akifumi; Hayashi, Yukio; et al.
Journal of the Vacuum Society of Japan, 52(10), p.570 - 574, 2009/10
For accurate control of relativistic laser-plasma interaction under the repetitive operation, we have to measure and control the laser irradiation conditions such as laser parameters, the target shooting accuracy and so on as well as measuring proton parameter on each laser shot. The displacement of the laser shooting position on a tape target, that are used in the high energy proton generation using an ultra-short Ti:sapphire laser system, is measured by observing an X-ray image from laser plasma with an X-ray pinhole camera for each laser shot. The displacement of the shooting position on the target is about 20micron and the accuracy of the target positioning is within 20micron which is small enough for present laser focusing optics with an F number of 3.6 (f=179mm). The technique contributes to accurate control of a repetitive laser driven proton accelerators.
 O
O (
( = Ho, Er)
= Ho, Er)Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Nishihata, Keisuke*; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Noda, Yukio*; Tokura, Yoshinori*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 404(17), p.2513 - 2516, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.63(Physics, Condensed Matter) O
O
Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Sakamoto, Yuma*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*; Abe, Nobuyuki*; Taniguchi, Koji*; Arima, Takahisa*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Takeda, Masayasu; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(7), p.077204_1 - 077204_4, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:52 Percentile:86.26(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Sb
Sb by single crystal neutron diffraction and maximum-entropy analysis
by single crystal neutron diffraction and maximum-entropy analysisKaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Kogi, Masafumi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(7), p.074710_1 - 074710_4, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:67.39(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In order to obtain a detailed picture of rattling in PrOs Sb
Sb , a single crystal neutron diffraction experiment and a maximum-entropy analysis were carried out. At room temperature, a widely distributed anisotropic Pr nuclear density in the Sb icosahedron cage was revealed. An unusual trapezoidal form in the cross-sectional density profile of Pr clearly demonstrates the presence of strong anharmonicity in the Pr potential, in which the
, a single crystal neutron diffraction experiment and a maximum-entropy analysis were carried out. At room temperature, a widely distributed anisotropic Pr nuclear density in the Sb icosahedron cage was revealed. An unusual trapezoidal form in the cross-sectional density profile of Pr clearly demonstrates the presence of strong anharmonicity in the Pr potential, in which the 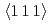 direction has the maximum spread. The highest density is found at an off-center position along the same direction. The Pr density distribution becomes isotropic and sharp by cooling down to 8 K. Moreover, the highest density of Pr at 8 K is found at the center of the cage. The obtained nuclear density distribution and its temperature variation indicate that the rattling in PrOs
direction has the maximum spread. The highest density is found at an off-center position along the same direction. The Pr density distribution becomes isotropic and sharp by cooling down to 8 K. Moreover, the highest density of Pr at 8 K is found at the center of the cage. The obtained nuclear density distribution and its temperature variation indicate that the rattling in PrOs Sb
Sb is a strong anharmonic thermal motion without an off-center potential minimum.
is a strong anharmonic thermal motion without an off-center potential minimum.
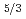 Sr
Sr NiO
NiO and La
and La (Ba,Sr)
(Ba,Sr) CuO
CuO superconducting compounds
superconducting compoundsWakimoto, Shuichi; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Ishii, Kenji; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko; Adachi, Tadashi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Koike, Yoji*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Noda, Yukio*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 102(15), p.157001_1 - 157001_4, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:74.10(Physics, Multidisciplinary) O
O
Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Fukunaga, Mamoru*; Noda, Yukio*; Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Kay, Kohn*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 78(3), p.034718_1 - 034718_5, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:36.47(Physics, Multidisciplinary) O
O
Kim, J.-H.*; Lee, S.-H.*; Park, S. I.*; Kenzelmann, M.*; Harris, A. B.*; Schefer, J.*; Chung, J.-H.*; Majkrzak, C. F.*; Takeda, Masayasu; Wakimoto, Shuichi; et al.
Physical Review B, 78(24), p.245115_1 - 245115_10, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:81.20(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fujii, Yasuhiko; Arai, Masatoshi; Kadono, Ryosuke*; Kanaya, Toshiji*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Niimura, Nobuo*; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*; Yagi, Takehiko*; Yamada, Kazuyoshi*
Kotai Butsuri, 43(7), p.441 - 450, 2008/07
no abstracts in English
 Sb
Sb
Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Kogi, Masafumi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 403(5-9), p.874 - 876, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.70(Physics, Condensed Matter)In order to clarify the detailed structure of PrOs Sb
Sb , single crystal neutron diffraction experiments were carried out and obtained data were analyzed by means of the maximum entropy method (MEM). A space- and time-averaged nuclear density distribution reflecting a thermal vibration can be obtained through the MEM analysis. The result unveils a widely spread Pr distribution in the Sb cage at room temperature. The Pr density has a almost flat distribution in the real space centered at the Sb cage, which reaches roughly 0.58
, single crystal neutron diffraction experiments were carried out and obtained data were analyzed by means of the maximum entropy method (MEM). A space- and time-averaged nuclear density distribution reflecting a thermal vibration can be obtained through the MEM analysis. The result unveils a widely spread Pr distribution in the Sb cage at room temperature. The Pr density has a almost flat distribution in the real space centered at the Sb cage, which reaches roughly 0.58 in the full width at half maximum (FWHM). These features are far from the simple harmonic model, namely, the present result suggests the strong anharmonicity of the Pr potential in the Sb cage.
in the full width at half maximum (FWHM). These features are far from the simple harmonic model, namely, the present result suggests the strong anharmonicity of the Pr potential in the Sb cage.
 O
O ; Understanding of the details of the Ising spin and the competitive interactions which made the devil's flower bloom
; Understanding of the details of the Ising spin and the competitive interactions which made the devil's flower bloomOwada, Kenji; Fujii, Yasuhiko; Muraoka, Jiro*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; Noda, Yukio*; Osumi, Hiroyuki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Isobe, Masahiko*; et al.
Hoshako, 21(2), p.87 - 96, 2008/03
Devil's flower has been found in a temperature-pressure phase diagram of NaV O
O , which shows a charge disproportionation (CD) at ambient pressure. By a complementary use of an X-ray structural analysis and a resonant X-ray diffraction, which is sensitive to CD, we have investigated the structural relationship between two ground states appeared in lower and higher pressure regions including the charge arrangements. It has been clarified that two equivalent types of charge arrangement in CD correspond to the Ising variable in NaV
, which shows a charge disproportionation (CD) at ambient pressure. By a complementary use of an X-ray structural analysis and a resonant X-ray diffraction, which is sensitive to CD, we have investigated the structural relationship between two ground states appeared in lower and higher pressure regions including the charge arrangements. It has been clarified that two equivalent types of charge arrangement in CD correspond to the Ising variable in NaV O
O . The atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. The results lead us to the conclusion that it is the first time that the devil's flower blooms in a charge-disproportionation system. The results also lead us to a hypothesis that the competitive interactions between a Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.
. The atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. The results lead us to the conclusion that it is the first time that the devil's flower blooms in a charge-disproportionation system. The results also lead us to a hypothesis that the competitive interactions between a Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.
Kaneko, Koji; Metoki, Naoto; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Kogi, Masafumi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 77(Suppl.A), p.245 - 247, 2008/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In filled skutterudite compounds, the importance of rattling is suggested in connection with the formation of heavy quasiparticles and superconductivity. A combination of the single crystal neutron diffraction and the maximum entropy method (MEM) offers an ability to unveil the thermal motion of Pr in PrOs Sb
Sb without any specific model. The result reveals the widely spread Pr nuclear density distribution at room temperature, which has a trapezoidal shape in the real space with the width of roughly 0.6
without any specific model. The result reveals the widely spread Pr nuclear density distribution at room temperature, which has a trapezoidal shape in the real space with the width of roughly 0.6  in the full width at half maximum. In contrast, the Pr distribution at 8 K has a sharp, isotropic gaussian shape, and the highest density locates at the center of the cage. These features indicate the strong anharmonicity of the Pr potential in the Sb cage.
in the full width at half maximum. In contrast, the Pr distribution at 8 K has a sharp, isotropic gaussian shape, and the highest density locates at the center of the cage. These features indicate the strong anharmonicity of the Pr potential in the Sb cage.
 O
O under high pressure; A Synchrotron X-ray diffraction study
under high pressure; A Synchrotron X-ray diffraction studyOwada, Kenji; Fujii, Yasuhiko; Muraoka, Jiro*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi; Noda, Yukio*; Osumi, Hiroyuki*; Ikeda, Naoshi*; Shobu, Takahisa; Isobe, Masahiko*; et al.
Physical Review B, 76(9), p.094113_1 - 094113_10, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:43.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Structural relations between two ground states of the ANNNI (Axial Next Nearest Neighbor Ising) compound NaV O
O , C
, C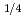 - and C
- and C -phases below and above the transition pressure
-phases below and above the transition pressure 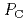 = 1 GPa, were investigated by X-ray diffraction and scattering techniques. The structure of the C
= 1 GPa, were investigated by X-ray diffraction and scattering techniques. The structure of the C -phase is well explained by the
-phase is well explained by the  (
(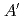 ) pattern which is one of four layers (
) pattern which is one of four layers (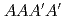 ) of the C
) of the C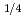 -phase, however, the amount of the atomic shifts under the conditions 1.6 GPa and 6 K is 27% that under ambient pressure. On the other hand, resonant X-ray scattering showed that the charges are disproportionated under high pressure. Based on these facts, it was concluded that charge disproportionation corresponds to the Ising variable in NaV
-phase, however, the amount of the atomic shifts under the conditions 1.6 GPa and 6 K is 27% that under ambient pressure. On the other hand, resonant X-ray scattering showed that the charges are disproportionated under high pressure. Based on these facts, it was concluded that charge disproportionation corresponds to the Ising variable in NaV O
O , where the atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. These results lead to the hypothesis that the competitive interactions between the Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.
, where the atomic shifts are regarded as linearly coupled to the Ising spins. These results lead to the hypothesis that the competitive interactions between the Ising spins may result from the Ising spin-phonon coupling.