Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 copper nitrite reductase; Involvement of the unique N-terminal region in the interprotein electron transfer with its redox partner
copper nitrite reductase; Involvement of the unique N-terminal region in the interprotein electron transfer with its redox partnerFukuda, Yota*; Koteishi, Hiroyasu*; Yoneda, Ryohei*; Tamada, Taro; Takami, Hideto*; Inoue, Tsuyoshi*; Nojiri, Masaki
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta; Bioenergetics, 1837(3), p.396 - 405, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:47.19(Biochemistry & Molecular Biology)The crystal structures of copper-containing nitrite reductase (CuNiR) from the thermophilic Gram-positive bacterium  HTA426 and the amino (N)-terminal 68 residue-deleted mutant were determined at resolutions of 1.3
HTA426 and the amino (N)-terminal 68 residue-deleted mutant were determined at resolutions of 1.3 and 1.8
and 1.8 , respectively. Both structures show a striking resemblance with the overall structure of the well-known CuNiRs composed of two Greek key
, respectively. Both structures show a striking resemblance with the overall structure of the well-known CuNiRs composed of two Greek key  -barrel domains; however, a remarkable structural difference was found in the N-terminal region. The unique region has one
-barrel domains; however, a remarkable structural difference was found in the N-terminal region. The unique region has one  -strand and one
-strand and one  -helix extended to the northern surface of the type-1 copper site. The superposition of the
-helix extended to the northern surface of the type-1 copper site. The superposition of the  CuNiR model on the electron-transfer complex structure of CuNiR with the redox partner cytochrome
CuNiR model on the electron-transfer complex structure of CuNiR with the redox partner cytochrome  in other denitrifier system led us to infer that this region contributes to the transient binding with the partner protein during the interprotein electron transfer reaction in the
in other denitrifier system led us to infer that this region contributes to the transient binding with the partner protein during the interprotein electron transfer reaction in the  system. Furthermore, electron-transfer kinetics experiments using N-terminal residue-deleted mutant and the redox partner,
system. Furthermore, electron-transfer kinetics experiments using N-terminal residue-deleted mutant and the redox partner,  cytochrome
cytochrome  , were carried out. These structural and kinetics studies demonstrate that that region is directly involved in the specific partner recognition.
, were carried out. These structural and kinetics studies demonstrate that that region is directly involved in the specific partner recognition.
Fukuda, Yota*; Tamada, Taro; Takami, Hideto*; Suzuki, Shinichiro*; Inoue, Tsuyoshi*; Nojiri, Masaki
Acta Crystallographica Section F, 67(6), p.692 - 695, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:67.71(Biochemical Research Methods) structure of copper nitrite reductase from thermophilic denitrifer
structure of copper nitrite reductase from thermophilic denitriferFukuda, Yota*; Tamada, Taro; Takami, Hideto*; Inoue, Tsuyoshi*; Nojiri, Masaki
no journal, ,
Denitrification is known as anaerobic respiration in which nitrogenous compounds (NO
 or NO
or NO
 ) are used as terminal electron acceptors. Copper-containing nitrite reductase (CuNIR) catalyzes the one electron reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide (NO), which is the key step in the denitrification pathway. Here, we report the structure analysis of CuNIR from thermophilic
) are used as terminal electron acceptors. Copper-containing nitrite reductase (CuNIR) catalyzes the one electron reduction of nitrite to nitric oxide (NO), which is the key step in the denitrification pathway. Here, we report the structure analysis of CuNIR from thermophilic  HTA426(
HTA426(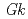 NIR) at 1.3
NIR) at 1.3  resolution.
resolution. 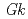 NIR folds a homo-trimeric structure, having two copper binding sites per a monomeric unit as well as other CuNIRs. There are main characteristics of
NIR folds a homo-trimeric structure, having two copper binding sites per a monomeric unit as well as other CuNIRs. There are main characteristics of 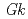 NIR in two loops (tower loop and extra loop regions) and the N-terminal region. The additional N-terminal
NIR in two loops (tower loop and extra loop regions) and the N-terminal region. The additional N-terminal  -helix is positioned in the vicinity of the tower loop. These characteristic structures found in
-helix is positioned in the vicinity of the tower loop. These characteristic structures found in 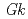 NIR structure suggest evolutionary diversity of CuNIR and play a key role in functioning in the particular environment where
NIR structure suggest evolutionary diversity of CuNIR and play a key role in functioning in the particular environment where  inhabits.
inhabits.
Oyama, Kenji*; Yokoo, Tetsuya*; Ito, Shinichi*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Sato, Taku*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Ino, Takashi*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
no journal, ,