Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Soba, A.*; Prudil, A.*; Zhang, J.*; Dethioux, A.*; Han, Z.*; Dostal, M.*; Matocha, V.*; Marelle, V.*; Lasnel-Payan, J.*; Kulacsy, K.*; et al.
Proceedings of TopFuel 2021 (Internet), 10 Pages, 2021/10
Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 59(6), p.062001_1 - 062001_6, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:38.75(Physics, Applied)Using a semiconductor microwave source and a coaxial cable for microwave transmission, a compact microwave-assisted, laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy system without a microwave cavity or waveguide was developed. Several types of electrode heads were tested, so that the emission intensity was 50 times larger than without microwave. The limit of the enhancement effect was also found.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2020-001, 142 Pages, 2020/03
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) method is an attractive technique because real-time, in-situ and remote elemental analysis is possible without any sample preparation. The LIBS technique can be applied for analyzing elemental composition of samples under severe environments such as the estimation of impurities in the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the detection of fuel debris in the post-accident nuclear core reactor of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. For applying LIBS to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is indispensable to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). In the present study, an echelle spectrometer with a resolving power of 50,000 was employed to identify spectra of plutonium of wavelength ranging from 350 to 670nm. The 465 atomic spectra and 341 ionic spectra can be identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength of spectra is consistent with published values.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Applied Physics A, 126(3), p.213_1 - 213_10, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:42.79(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in low pressure rare gas ambient was investigated with laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy for three refractory metals, i.e. titanium, zirconium and hafnium. A comparison of the plume expansion behaviors for the species of these elements revealed an atomic weight effect on the plume structure formation. A hemispherical thin layer and cavity structure reported previously for gadolinium were observed also for these elements. It was found that the plume size increases as well as the layer thickness decreases with increasing atomic weight. For ground state atoms of Ti, substantial amount of atoms were observed even at the center of the plume. Also, the persistence of the Ti atomic plume was as long as 300  s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
s, which was significantly longer than the other species studied. Furthermore, the mass-dependent elemental separation was observed in the ablation plume produced from a multielement sample. These results suggest that the observed plume structure arises from the ion-electron recombination process and the recoil of the ablated species during the multiple collisions with gas atoms.
 Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MS
Pd in Pd purified by selective precipitation from spent nuclear fuel by laser ablation ICP-MSAsai, Shiho; Ohata, Masaki*; Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Oba, Hironori*; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Horita, Takuma; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 411(5), p.973 - 983, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:58.34(Biochemical Research Methods)Determination of radiopalladium  Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of
Pd is required for ensuring the radiation safety of Pd extracted from spent nuclear fuel for recycling or disposal. We employed laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) to simplify an analytical procedure of  Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study,
Pd. Pd was separated through selective Pd precipitation reaction from spent nuclear fuel. Laser ablation allows direct measurement of the Pd precipitates, skipping the dissolution and dilution procedure. In this study, 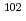 Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of
Pd in natural Pd standard solution was used as an internal standard, taking advantage of its absence in spent nuclear fuel. The Pd precipitate was uniformly embedded on the surface of the centrifugal filter, forming a microscopically thin flat surface of Pd. The resulting homogeneous Pd layer is suitable for obtaining a stable signal ratio of  Pd/
Pd/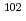 Pd. The amount of
Pd. The amount of  Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
Pd obtained by LA-ICP-MS corresponds to the values obtained by conventional solution nebulization measurement.
Sasaki, Hirokazu*; Nishikubo, Hideo*; Nishida, Shinsuke*; Yamazaki, Satoshi*; Nakasaki, Ryusuke*; Isomatsu, Takemi*; Minato, Ryuichiro*; Kinugawa, Kohei*; Imamura, Akihiro*; Otomo, Shinya*; et al.
Furukawa Denko Jiho, (138), p.2 - 10, 2019/02
no abstracts in English
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
Jung, K.; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2017-008, 26 Pages, 2017/08
We are developing an analytical method using laser ablation absorption spectroscopy (LAAS) to analyze radioactive waste mixed with zirconium, uranium and so on. It is essential to evaluate the characteristics of the plume formed by the objective particles for LAAS analysis. Therefore, in this study, titanium and hafnium whose chemical properties are similar to those of Zr were chosen as analytical object. And the difference in expanding behavior of the plume due to the weight of the particles was investigated. As a result of changing the height of the probe beam and applying the optical time-of-flight method to the plume, it was found that the influence of the background gas is larger for Ti than Hf. The meaning of the resonance absorption signal of the waste sample mixed with nuclear fuel materials and nuclear reactor materials was understood by this study and basic knowledge to optimize experimental conditions were also obtained.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Jung, K.; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Kato, Masaaki; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Khumaeni, A.*; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 134, p.42 - 51, 2017/08
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:91.69(Spectroscopy)Spectroscopic properties of atomic species of plutonium were investigated by combining laser ablation and resonance absorption techniques for the analysis of a plutonium oxide sample. For 17 transitions of Pu atoms and ions, the absorbance, isotope shift, and hyperfine splitting were determined via Voigt profile fitting of the recorded absorption spectra. Three transitions were selected as candidates for analytical use. Using these transitions, we investigated the analytical performance that was attainable and determined a correlation coefficient R2 between the absorbance and plutonium concentration of 0.9999, a limit of detection of 30-130 ppm, and a relative standard deviation of approximately 6% for an abundance of  Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Pu of 2.4%. These results demonstrate that laser ablation absorption spectroscopy is applicable to the remote isotopic analysis of highly radioactive nuclear fuels and waste materials containing multiple actinide elements.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2016-005, 40 Pages, 2016/05
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) method is an attractive technique because real-time, in-situ and remote elemental analysis is possible without any sample preparation. The LIBS technique can be applied for analyzing elemental composition of samples under severe environments such as the estimation of impurities in the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the detection of fuel debris in the post-accident nuclear core reactor of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For applying LIBS to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is indispensable to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). In the present study, an echelle spectrometer with a resolving power of 50,000 was employed to identify spectra of natural uranium of wavelength ranging from 470 to 670 nm. The 173 atomic spectra and 119 ionic spectra can be identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 55(2), p.022401_1 - 022401_4, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.39(Physics, Applied)We used laser-induced fluorescence imaging with a varying beam focal point to observe ablation plumes from metal and oxide samples of gadolinium. The plumes expand vertically when the focal point is far from the sample surface. In contrast, the plume becomes hemispherical when the focal point is on the sample surface. In addition, the internal plume structure and the composition of the ablated atomic and ionic particles also vary significantly. The fluorescence intensity of a plume from a metal sample is greater than that from an oxide sample, which suggests that the number of monatomic species produced in each plume differs. For both the metal and oxide samples, the most intense fluorescence from atomic (ionic) species is observed with the beam focal point at 3-4 mm (2 mm) from the sample surface.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2015-012, 48 Pages, 2015/10
It is important to analyze the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the fuel debris generated at the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Therefore, the remote analysis for nuclear fuel materials using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) is studied. For applying Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is very important to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). Then, the high resolution spectra of natural uranium of wavelength region of 350-470 nm are measured using LIBS, 247 atomic spectra and 294 single ion spectra were identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Khumaeni, A.*; Kato, Masaaki; Wakaida, Ikuo
Spectrochimica Acta, Part B, 110, p.101 - 117, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:81.14(Spectroscopy)The dynamic behavior of an ablation plume in ambient gas has been investigated by laser-induced fluorescence imaging spectroscopy. The second harmonic beam from an Nd:YAG laser (0.5-6J/cm ) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
) was focused on a sintered oxide pellet or a metal chip of gadolinium. The produced plume was subsequently intersected with a sheet-shaped UV beam from a dye laser so that time-resolved fluorescence images were acquired with an intensified CCD camera at various delay times. The obtained cross-sectional images of the plume indicate that the ablated ground state atoms and ions of gadolinium accumulate in a hemispherical contact layer between the plume and the ambient gas, and a cavity containing a smaller density of ablated species is formed near the center of the plume. At earlier expansion stage, another luminous component also expands in the cavity so that it coalesces into the hemispherical layer. The splitting and coalescence for atomic plume occur later than those for ionic plume. Furthermore, the hemispherical layer of neutral atoms appears later than that of ions; however, the locations of the layers are nearly identical. This coincidence of the appearance locations of the layers strongly suggests that the neutral atoms in the hemispherical layer are produced as a consequence of three-body recombination of ions through collisions with gas atoms. The obtained knowledge regarding plume expansion dynamics and detailed plume structure is useful for optimizing the experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Hironori; Tampo, Motonobu; Wakaida, Ikuo
Applied Physics A, 112(1), p.87 - 92, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:74.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A uranium oxide sample was ablated by 2nd harmonic radiation from a Nd:YAG laser at a fluence of 0.5 J/cm . The temporal evolution of the ablation plume was investigated in vacuum and helium environments. In vacuum, the flow velocity perpendicular to the sample surface was determined to be 2.7 km/s for neutral atoms and 4.0 km/s for singly charged atoms. From the evolution of the plume in helium we found that an observation time of 3-5
. The temporal evolution of the ablation plume was investigated in vacuum and helium environments. In vacuum, the flow velocity perpendicular to the sample surface was determined to be 2.7 km/s for neutral atoms and 4.0 km/s for singly charged atoms. From the evolution of the plume in helium we found that an observation time of 3-5  s and an observation height of about 2.5 mm are most suited for obtaining higher sensitivity. Observation times less than 3
s and an observation height of about 2.5 mm are most suited for obtaining higher sensitivity. Observation times less than 3  s were unsuitable for precise isotope analysis since the spectral modifications arising from the Doppler splitting effect are different between the two uranium isotopes. Using the established conditions, we evaluated the calibration curve linearity, limit of detection, and precision for three samples having different abundances of
s were unsuitable for precise isotope analysis since the spectral modifications arising from the Doppler splitting effect are different between the two uranium isotopes. Using the established conditions, we evaluated the calibration curve linearity, limit of detection, and precision for three samples having different abundances of  U.
U.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Hironori; Tampo, Motonobu; Wakaida, Ikuo
Hyperfine Interactions, 216(1-3), p.71 - 77, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:97.82(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)To determine experimental conditions suitable for isotope analysis, we studied the plume dynamics of uranium. A uranium oxide sample was ablated by 2nd harmonic radiation from a Nd:YAG laser at a fluence of 0.5 J/cm . The temporal evolution of the ablation plume was investigated in 800 Pa helium environment. It was found that the observation at 3-5
. The temporal evolution of the ablation plume was investigated in 800 Pa helium environment. It was found that the observation at 3-5 10
10 s after the ablation at the height of about 2.5 mm are most suited for obtaining higher sensitivity. Using the established conditions, we obtained the limit of detection of the isotope ratio (
s after the ablation at the height of about 2.5 mm are most suited for obtaining higher sensitivity. Using the established conditions, we obtained the limit of detection of the isotope ratio ( U/
U/ U) to be 0.01%. In addition, the limit of detection of elemental abundance of uranium in uranium glass was also evaluated.
U) to be 0.01%. In addition, the limit of detection of elemental abundance of uranium in uranium glass was also evaluated.
Oba, Masaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wakaida, Ikuo
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(4), p.042403_1 - 042403_3, 2013/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.36(Physics, Applied)We used nanosecond (ns) and femtosecond (fs) laser pulses to ablate gadolinium oxide samples and measured the ablated volume as a function of the laser pulse focal position. The defocusing effect of the ablated volume, which decreases as the ablation pulse focal position approaches the sample surface, was observed for both ns and fs pulses.
Miyabe, Masabumi; Oba, Masaki; Iimura, Hideki; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Oba, Hironori; Tampo, Motonobu; Wakaida, Ikuo
Journal of Applied Physics, 112(12), p.123303_1 - 123303_10, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:59.17(Physics, Applied)The temporal evolution of the ablation plume of cerium was investigated by absorption spectroscopy. Cerium oxide pellets were ablated in helium by 2nd harmonic radiation from a YAG laser. The lateral velocity of the plume was determined from the magnitude of the Doppler splitting of the absorption spectra. The velocities of neutral and ionized atoms were systematically investigated by varying several parameters. Temporal profiles of the transmittance signal were measured by detuning the probe laser frequency from the atomic resonant frequency in order to evaluate the temporal variation of the lateral velocity. On the basis of the drag force model, the slowing coefficients for atomic and ionic species in helium were evaluated along with the lateral velocity in a vacuum. This study may help in understanding the plume dynamics effect on deposited film properties as well as optimizing experimental conditions for ablation-based spectroscopic analysis.
Norman, G.*; Starikov, S.*; Stegailov, V.*; Fortov, V.*; Skobelev, I.*; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Kato, Yoshiaki*; Ishino, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 112(1), p.013104_1 - 013104_8, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:81.45(Physics, Applied)Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Araki, Masaaki; Oba, Toshinobu; Torii, Yoshiya; Takeuchi, Masaki*
JAEA-Conf 2011-003, p.83 - 86, 2012/03
Oba, Masaki; Maruyama, Yoichiro; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Wakaida, Ikuo
Applied Physics A, 101(3), p.545 - 549, 2010/11
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:72.89(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Emission characteristics of gadolinium (Gd) oxide are studied, using ns and fs laser pulses for ablation in double-pulse laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). In the current conditions of pulse energy and signal detection timing, emission intensity enhancement in the reheating mode is 25-fold, but the little effect can be observed in a pre-pulse mode. It is shown that the optimum focus position of the ablation pulse is about 5 mm apart from the sample surface in the reheating mode. Although little emission can be observed in single-pulse configuration with fs ablation pulses, the intense emission can be observed in the reheating mode in the double-pulse configuration.