Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oikawa, Kenichi; Harjo, S.; Pham, A. H.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Morito, Shigekazu*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Oba, Takuya*; Ito, Masakazu*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011062_1 - 011062_6, 2021/03
Oikawa, Kenichi; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Sato, Hirotaka*; Omae, Kazuma*; Pham, A.*; Watanabe, Kenichi*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Harjo, S.; et al.
Materials Research Proceedings, Vol.15, p.207 - 213, 2020/02
 -Fe
-Fe O
O solid solution thin films studied by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and ab initio multiplet calculations
solid solution thin films studied by soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism and ab initio multiplet calculationsHojo, Hajime*; Fujita, Koji*; Ikeno, Hidekazu*; Matoba, Tomohiko*; Mizoguchi, Teruyasu*; Tanaka, Isao*; Nakamura, Tetsuya*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Okane, Tetsuo; Tanaka, Katsuhisa*
Applied Physics Letters, 104(11), p.112408_1 - 112408_5, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:34.5(Physics, Applied)Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, S.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovsky, V. V.*; Skobelev, I.*; et al.
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.236 - 240, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.55(Physics, Applied)We irradiated the focusing soft X-ray laser pulses having a wavelength of 13.9 nm and the duration of 7 ps to aluminum surface. After the irradiation process, the irradiated surface was observed with a scanning electron microscope. The surface modifications caused by soft X-ray laser single pulse exposure were clearly seen. In addition, it was found that the conical structures having around 100 nm in diameters were formed in the shallow features. The nano-meter size modified surface structures on aluminum induced by the soft X-ray laser pulse is interesting as the newly surface structure. Hence, the soft X-ray laser beam would be a candidate for a tool of micromachining. We also provide a thermomechanical modeling of the soft X-ray laser interaction with aluminum briefly to explain the surface modification.
Norman, G.*; Starikov, S.*; Stegailov, V.*; Fortov, V.*; Skobelev, I.*; Pikuz, T.; Faenov, A.*; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Kato, Yoshiaki*; Ishino, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 112(1), p.013104_1 - 013104_8, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:82.23(Physics, Applied)Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A. Y.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, T.; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Kaihori, Takeshi; Kawachi, Tetsuya
Journal of Laser Micro/Nanoengineering, 7(2), p.147 - 151, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:27.93(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)We irradiated the soft X-ray laser (SXRL) pulses having a wavelength of 13.9 nm, the duration time of 7 ps to aluminum (Al), copper (Cu) and gold (Au) surfaces. After the irradiation processes of SXRL beam with laser flux of  14 mJ/cm
14 mJ/cm for Al case and of
for Al case and of  21 mJ/cm
21 mJ/cm for Cu and Au cases, the modified surfaces were observed with the visible microscope, the scanning electron microscope, and the atomic force microscope. The surface modifications caused by the SXRL irradiations were clearly seen on the surfaces, and it was found that the conical structures having around 100 nm in diameters were formed on the Al surface under a single pulse shot. The conical structures were formed in the features with the average depth of about 40 nm, and this value was in accordance with the attenuation length of the SXRL beam for Al. The modified structure on Al surface induced by SXRL pulse irradiations is different from those of Cu and Au surfaces. The modified structure formed on Al surface induced by the SXRL pulse exposure is interesting as the newly structure. Hence, the SXRL beam would be a candidate for a tool of micromachining, which enable to fabricate of three dimensional structures with nano-meter size on Al surface.
for Cu and Au cases, the modified surfaces were observed with the visible microscope, the scanning electron microscope, and the atomic force microscope. The surface modifications caused by the SXRL irradiations were clearly seen on the surfaces, and it was found that the conical structures having around 100 nm in diameters were formed on the Al surface under a single pulse shot. The conical structures were formed in the features with the average depth of about 40 nm, and this value was in accordance with the attenuation length of the SXRL beam for Al. The modified structure on Al surface induced by SXRL pulse irradiations is different from those of Cu and Au surfaces. The modified structure formed on Al surface induced by the SXRL pulse exposure is interesting as the newly structure. Hence, the SXRL beam would be a candidate for a tool of micromachining, which enable to fabricate of three dimensional structures with nano-meter size on Al surface.
Kobayashi, Tetsuya; Araki, Masaaki; Oba, Toshinobu; Torii, Yoshiya; Takeuchi, Masaki*
JAEA-Conf 2011-003, p.83 - 86, 2012/03
Nishikino, Masaharu; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Nagashima, Keisuke
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.93 - 98, 2011/12
The improvement of X-ray laser generation so as to have a high repetition rate will open up the possibility of new applications. In the last decade, progress in reducing the required pump energy for the X-ray lasing and raising the repetition rate has been achieved by new technologies, such as the Transient Collisional Excitation (TCE) scheme and Grazing Incidence Pumping (GRIP). Under this circumstance, the development of continuous pumping to the target system is an important issue for realizing an XRL with the high repetition rate. We have developed a 13.9 nm XRL using a silver tape target4 and demonstrated a highly coherent XRL with an oscillator-amplifier configuration5 using two tape target systems and the TOPAZ laser system6 with a 10-J and a 0.1-Hz repetition rate. The output energy is comparable to the X-ray laser generated with a silver-deposited slab target, and the pointing stability using the new tape target system is better than conventional slab target.
Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Kishimoto, Maki; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Momoko; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.15 - 24, 2011/12
This paper reviews recent improvement in the source development of laser-driven X-ray lasers and the applications in the research fields of material science, laser processing, X-ray imaging, and radiation damage in biological cells. In the application for material science, we have firstly observed temporal correlation between the domain structures of ferro-electric substance under the Curie temperature. In the laser processing, new X-ray laser interferometer reveals us the nano-scale surface distortion of substance pumped by a femto-second optical pulse. In the X-ray diffraction image, we have taken several static images of micro-structure of samples: now we are trying to extend the objective to nano-scale dynamics using pump and probe method. In the radiation damage of biological cells, we observed double strand break in DNA using X-ray laser exposure; this results are compared with the case using incoherent several KeV X-ray exposure.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Terakawa, Kota*; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Imazono, Takashi; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.353 - 358, 2011/12
The understanding of the dynamics of the initial process is important for the micro processing and welding by the ultra-short laser pulse. The X-ray laser is suitable for probing this initial process because it has short wavelength (Ni-like Ag, 13.9 nm) and short duration (7 ps). For this investigation, the origin of time of the pumping pulse is quite important. In this study, we used the scintillation plate and the plasma gate technique to realize the spatial and temporal synchronization of the pump and probe pulses. For the spatial alignment, a CsI scintillation plate that was set at the sample position was illuminated by both the X-ray laser pulse, and the fluorescence light were detected by the CCD camera. For the temporal synchronization, we set a thin foil at the sample position. We measured the transmission of the X-ray laser while changing a temporal delay of the pumping laser with respect to the time of X-ray laser pulse to obtain the origin of the irradiation time.
Starikov, S. V.*; Stegailov, V. V.*; Norman, G. E.*; Fortov, V. E.*; Ishino, Masahiko; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki*; Kaihori, Takeshi; et al.
JETP Letters, 93(11), p.642 - 647, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:75.48(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Tanaka, Momoko; Nakazato, Tomoharu*; Shimizu, Toshihiko*; Yamanoi, Kohei*; Sakai, Kohei*; Sarukura, Nobuhiko*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Ochi, Yoshihiro; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2011-001, p.126 - 128, 2011/03
The spatial resolution of hydrothermal method grown zinc oxide (ZnO) scintillator was evaluated using X-ray laser focused with Fresnel zone plate. The fluorescence image of the ZnO scintillator was measured to be less than 10um using CCD camera coupled with a Schbartzchild expander mirror. The availability of large size ZnO crystal up to 3-inch is quite attractive for future lithography and imaging applications.
Ishino, Masahiko; Faenov, A. Ya.*; Tanaka, Momoko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Pikuz, T. A.*; Inogamov, N. A.*; Zhakhovskii, V. V.*; Skobelev, I. Yu.*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 109(1), p.013504_1 - 013504_6, 2011/01
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:76.88(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Ishino, Masahiko; Kado, Masataka; Nishikino, Masaharu; Shinohara, Kunio*; Tamotsu, Satoshi*; Yasuda, Keiko*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kishimoto, Maki; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kawachi, Tetsuya
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.7589, p.75891B_1 - 75891B_8, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:72.69(Engineering, Biomedical)Soft X-ray microscopes operating in the water window are capable of imaging living hydrated biological specimens. Laser produced plasmas are attractive soft X-ray sources, because of their short duration time. Based on the minimum dose calculation, soft X-ray photons more than 10 photons/
photons/ m
m at the sample surface are needed to acquire an image of the biological specimens with spatial resolution up to 100 nm. The observations of soft X-ray emissions from laser produced plasmas using ultra thin film targets have been carried out. Au thin films were irradiated by a high contrast Nd:glass laser pulses. The spectral properties of emitted soft X-rays were monitored by an X-ray spectrograph from the rear side with respect to the surface of laser irradiation. The observed emission intensities had an obvious dependence on the film thickness, and the most intense emissions were obtained at the thickness of 28 nm. The experimental results have suggested that the most of the laser energy irradiated is absorbed by the film target, and it is resulted an efficient energy deposition from laser to X-rays.
at the sample surface are needed to acquire an image of the biological specimens with spatial resolution up to 100 nm. The observations of soft X-ray emissions from laser produced plasmas using ultra thin film targets have been carried out. Au thin films were irradiated by a high contrast Nd:glass laser pulses. The spectral properties of emitted soft X-rays were monitored by an X-ray spectrograph from the rear side with respect to the surface of laser irradiation. The observed emission intensities had an obvious dependence on the film thickness, and the most intense emissions were obtained at the thickness of 28 nm. The experimental results have suggested that the most of the laser energy irradiated is absorbed by the film target, and it is resulted an efficient energy deposition from laser to X-rays.
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Tanaka, Momoko; Kishimoto, Maki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Nagashima, Keisuke; Sugiyama, Akira
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 48(12), p.120212_1 - 120212_3, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:73.43(Physics, Applied)We have demonstrated the fully spatial coherent 13.9-nm laser with output energy of submicroJoule by means of the double target geometry by using new driver system. The power amplifiers providing tow beams with 10-J energy and picoseconds duration at the repetition rate of 0.1 Hz. The obtained 13.9-nm laser pulse with 10 coherent photons will enable us to make single-shot pump-probe observation of non-periodic ultrafast phenomena.
coherent photons will enable us to make single-shot pump-probe observation of non-periodic ultrafast phenomena.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Yamatani, Hiroshi*; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Nagashima, Keisuke
Review of Scientific Instruments, 80(1), p.116102_1 - 116102_3, 2009/11
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:54.68(Instruments & Instrumentation)A highly coherent 13.9 nm X-ray laser is generated under an oscillator-amplifier configuration using a new tape target system and a driver laser system with a 0.1 Hz repetition rate. The output energy is comparable to the X-ray laser generated with a silver-deposited slab target, and the pointing stability using the new tape target system is better than conventional slab targets.

Suzuki, Michiyo; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Yanase, Sumino*; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Oba, Hirofumi; Higashitani, Atsushi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Funayama, Tomoo; Fukamoto, Kana; Tsuji, Toshio*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 50(2), p.119 - 125, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:29.48(Biology)Ochi, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tanaka, Momoko; Kishimoto, Maki; Oba, Toshiyuki
X-Ray Lasers 2008; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.130, p.161 - 166, 2009/00

Miyazawa, Yutaka*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Negishi, Hiroshi*; Kobayashi, Akie*; Kaneyasu, Tomoko*; Oba, Atsushi*; Morohashi, Keita*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; et al.
Journal of Radiation Research, 49(4), p.373 - 379, 2008/07
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:63.75(Biology)We examined the role of root cap and elongation zone cells in root hydrotropism using heavy-ion and laser microbeam. Heavy-ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporary suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy-ion broad-beam irradiation suppressed 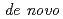 expression of
expression of 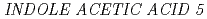 gene, but not
gene, but not 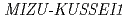 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that
gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that 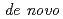 gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
 using heavy-ion microbeam
using heavy-ion microbeamMiyazawa, Yutaka*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Negishi, Hiroshi*; Kobayashi, Akie*; Kaneyasu, Tomoko*; Oba, Atsushi*; Morohashi, Keita*; Kakizaki, Takehiko*; Funayama, Tomoo; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; et al.
JAEA-Review 2007-060, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2006, P. 116, 2008/03
We examined the role of root cap and elongation zone cells in root hydrotropism of  using heavy ion and laser microbeam. Heavy ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporarily suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy ion broad beam irradiation suppressed de novo expression of INDOLE ACETIC ACID 5 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that de novo gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.
using heavy ion and laser microbeam. Heavy ion microbeam irradiation of the elongation zone, but not that of the columella cells, significantly and temporarily suppressed the development of hydrotropic curvature. However, laser ablation confirmed that columella cells are indispensable for hydrotropism. Systemic heavy ion broad beam irradiation suppressed de novo expression of INDOLE ACETIC ACID 5 gene. Our results indicate that both the root cap and elongation zone have indispensable and functionally distinct roles in root hydrotropism, and that de novo gene expression might be required for hydrotropism in the elongation zone, but not in columella cells.