Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Kaihori, Takeshi; Morita, Toshimasa; Sasaki, Akira; Terakawa, Kota*; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2012; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.147, p.117 - 120, 2014/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We have developed the femto-second laser pump and soft X-ray laser probe system in order to observe the dynamical processes of the femto-second laser ablation. By using this system, we succeed to obtain the temporal evolution of the soft X-ray reflectivity from the laser induced Pt surface. The results lead that the rate of decrease in the reflectivity of the probe beam has a non-linear relation with the pump laser fluence.
Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Terakawa, Kota*; Minami, Yasuo*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 20(28), p.29329 - 29337, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:64.97(Optics)Pump and probe reflective imaging using a soft X-ray laser probe was applied to the observation of the early stage of femtosecond laser ablation process on platinum. In strongly excited area, drastic and fast reflectivity drop was observed. In moderately excited area, the decay of the reflectivity is slower than that in the strongly excited area, and the reflectivity reaches its minimum at t = 160 ps. In weakly excited area, laser-induced reflectivity change was not observed. These results give the critical information about the femtosecond laser ablation.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Terakawa, Kota*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Minami, Yasuo*; Tomita, Takuro*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Suemoto, Toru
AIP Conference Proceedings 1465, p.23 - 27, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.13(Physics, Applied)We have developed a soft X-ray laser (SXRL) interferometer capable of the single-shot imaging of nano-scaled structure dynamics. The depth and lateral resolutions of the interferometer were about 1 nm and 1.8 micron, respectively. We observed the initial stage ( 50 ps) of the ablation process of the Pt surface pumped by a 70 fs Ti:Sapphire laser pulse. The expansion speed of the Pt surface (34 nm/50 ps) indicated that the nano-bubble structures were formed in the initial stage of the ablation. In order to observe the detailed dynamics, the precision of temporal synchronization between the pump and probe pulses was improved to be 3 ps by adopting a portion of the SXRL and pump beams as the time fiducials.
50 ps) of the ablation process of the Pt surface pumped by a 70 fs Ti:Sapphire laser pulse. The expansion speed of the Pt surface (34 nm/50 ps) indicated that the nano-bubble structures were formed in the initial stage of the ablation. In order to observe the detailed dynamics, the precision of temporal synchronization between the pump and probe pulses was improved to be 3 ps by adopting a portion of the SXRL and pump beams as the time fiducials.
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Terakawa, Kota*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Tomita, Takuro*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Minami, Yasuo*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Imazono, Takashi; Ishino, Masahiko; et al.
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 51(1), p.016601_1 - 016601_3, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:40.61(Physics, Applied)We have developed a soft X-ray laser interferometer based on the double Lloyd's mirror and obtained a single shot interferogram by a 7-ps pulse at the wavelength of 13.9 nm. Micrometer grooves with 5-nm depth were successfully reconstructed from the interferogram. The lateral and depth resolutions were estimated to be 1.5  m and better than 1 nm, respectively. This interferometer will be an attractive diagnostic device for observing transiently changing nano-scale deviations on solid surfaces.
m and better than 1 nm, respectively. This interferometer will be an attractive diagnostic device for observing transiently changing nano-scale deviations on solid surfaces.
Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Kishimoto, Maki; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tanaka, Momoko; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.15 - 24, 2011/12
This paper reviews recent improvement in the source development of laser-driven X-ray lasers and the applications in the research fields of material science, laser processing, X-ray imaging, and radiation damage in biological cells. In the application for material science, we have firstly observed temporal correlation between the domain structures of ferro-electric substance under the Curie temperature. In the laser processing, new X-ray laser interferometer reveals us the nano-scale surface distortion of substance pumped by a femto-second optical pulse. In the X-ray diffraction image, we have taken several static images of micro-structure of samples: now we are trying to extend the objective to nano-scale dynamics using pump and probe method. In the radiation damage of biological cells, we observed double strand break in DNA using X-ray laser exposure; this results are compared with the case using incoherent several KeV X-ray exposure.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Terakawa, Kota*; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Imazono, Takashi; et al.
X-Ray Lasers 2010; Springer Proceedings in Physics, Vol.136, p.353 - 358, 2011/12
The understanding of the dynamics of the initial process is important for the micro processing and welding by the ultra-short laser pulse. The X-ray laser is suitable for probing this initial process because it has short wavelength (Ni-like Ag, 13.9 nm) and short duration (7 ps). For this investigation, the origin of time of the pumping pulse is quite important. In this study, we used the scintillation plate and the plasma gate technique to realize the spatial and temporal synchronization of the pump and probe pulses. For the spatial alignment, a CsI scintillation plate that was set at the sample position was illuminated by both the X-ray laser pulse, and the fluorescence light were detected by the CCD camera. For the temporal synchronization, we set a thin foil at the sample position. We measured the transmission of the X-ray laser while changing a temporal delay of the pumping laser with respect to the time of X-ray laser pulse to obtain the origin of the irradiation time.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Kaihori, Takeshi; Sasaki, Akira; Terakawa, Kota*; Minami, Yasuo*; et al.
Proceedings of SPIE, Vol.8140, p.81400G_1 - 81400G_8, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:82.2(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)We have developed a soft X-ray laser (SXRL) interferometer capable of the single-shot imaging of nano-scaled structure dynamics. The interferometer consisted of the reflection optics including double Lloyd's mirrors and focusing optics, and the interference fringes are produced on the detector surface. By using this interferometer, the initial stage ( 50 ps) of the ablation process of the Pt surface pumped by a 70 fs Ti:Sapphire laser pulse was observed. The expansion speed of the surface estimated from the result (34 nm/50 ps) indicated that the nano-bubble structures were formed in the initial stage of the ablation. In order to observe the detailed dynamics, the temporal synchronization between the pump and probe pulses was improved to be 3 ps by adopting a portion of the SXRL and pump beams as the time fiducials, to which the pump and probe timing was adjusted by using the X-ray streak camera.
50 ps) of the ablation process of the Pt surface pumped by a 70 fs Ti:Sapphire laser pulse was observed. The expansion speed of the surface estimated from the result (34 nm/50 ps) indicated that the nano-bubble structures were formed in the initial stage of the ablation. In order to observe the detailed dynamics, the temporal synchronization between the pump and probe pulses was improved to be 3 ps by adopting a portion of the SXRL and pump beams as the time fiducials, to which the pump and probe timing was adjusted by using the X-ray streak camera.
Yamamoto, Minoru; Hasegawa, Noboru; Terakawa, Kota*; Umeda, Yoshifumi*; Tomita, Takuro*; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Kaihori, Takeshi; et al.
Proceedings of 12th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication (LPM 2011) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2011/06
Femtosecond lasers have been used for material processing. However, the physical processes responsible for femtosecond laser ablation have not been understood completely. These processes involve melting, vaporization, re-solidification or ablation, which occur in a very short time from pico- to nano-seconds. To understand the physical processes, it is essential to reveal the dynamics of ultrafast surface morphological change after laser irradiation. At JAEA, the laser-driven plasma soft X-ray laser (SXRL) that has extremely high spatial and spectral purity was constructed. It delivers soft X-ray photons at 89.2 eV (13.9 nm) with a photon number of exceeding 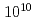 , which is sufficient to obtain a single shot interferogram. By using this system, the soft X-ray laser interferometer with the lateral resolution of 1.8
, which is sufficient to obtain a single shot interferogram. By using this system, the soft X-ray laser interferometer with the lateral resolution of 1.8  m and a depth resolution of 1 nm was developed. We report on demonstration of time-resolved measurement of femtosecond-laser ablation dynamics by using the soft X-ray laser interferometer.
m and a depth resolution of 1 nm was developed. We report on demonstration of time-resolved measurement of femtosecond-laser ablation dynamics by using the soft X-ray laser interferometer.
Suemoto, Toru; Terakawa, Kota*; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru; Hasegawa, Noboru; Deki, Manato*; Minami, Yasuo*; Kawachi, Tetsuya
Optics Express (Internet), 18(13), p.14114 - 14122, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:80.1(Optics)Using highly coherent radiation at a wavelength of 13.9 nm from a Ag-plasma soft X-ray laser, we constructed a pump-and-probe interferometer based on a double Lloyd's mirror system. The spatial resolutions are evaluated with a test pattern, showing 1.8 micrometers lateral resolution, and 1-nm depth sensitivity. This instrument enables a single-shot observation of the surface morphology with a 7-ps time-resolution. We succeeded in observing a nanometer scale surface dilation of Pt films at the early stage of the ablation process initiated by a 70 fs near infrared pump pulse.
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Terakawa, Kota*; Suemoto, Toru*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Deki, Manato*; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi
no journal, ,
We developed a soft X-ray laser interferometer dedicated to the solid state physics. The interferometer enabled us to observe dynamical changes on the solid surface such as the photo-induced phase transition with picoseconds temporal resolution and nanometer special resolution (in z-axis). We carried out a performance test using static test pattern and confirmed the performance.
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Terakawa, Kota*; Suemoto, Toru*; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Deki, Manato*; Tanaka, Momoko; Nishikino, Masaharu; et al.
no journal, ,
We have developed a chirped pulse amplification laser with zigzag slab Nd:glass power amplifiers which provides two synchronized beams with energy of  10 J and duration of a few ps at 0.1-Hz repetition-rate. Using this laser as a driver, fully spatial coherent X-ray laser at a wavelength of 13.9 nm is generated at 0.1 Hz. Typical energy, beam divergence and duration of the X-ray laser are
10 J and duration of a few ps at 0.1-Hz repetition-rate. Using this laser as a driver, fully spatial coherent X-ray laser at a wavelength of 13.9 nm is generated at 0.1 Hz. Typical energy, beam divergence and duration of the X-ray laser are  1
1  J, 0.5 mrad and 7 ps, respectively. Hence, a quite high peak brilliance is achieved. Using this X-ray laser, various application researches have been started.
J, 0.5 mrad and 7 ps, respectively. Hence, a quite high peak brilliance is achieved. Using this X-ray laser, various application researches have been started.
Kurihara, Arata; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Hayano, Akira; Hayakawa, Masashi; Tagami, Masahiko; Hodotsuka, Yasuyuki; Yuguchi, Takashi; Ochi, Minoru; Tokuyasu, Shingo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Terakawa, Kota*; Suemoto, Toru; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Deki, Manato*; Tanaka, Momoko; Nishikino, Masaharu; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Terakawa, Kota*; Suemoto, Toru*; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Deki, Manato*; Tomita, Takuro*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Hasegawa, Noboru; Nishikino, Masaharu; Tanaka, Momoko; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kishimoto, Maki; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Kaihori, Takeshi; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Terakawa, Kota*; Suemoto, Toru*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Deki, Manato*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Terakawa, Kota*; Suemoto, Toru*; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Tomita, Takuro*; Deki, Manato*; Hasegawa, Noboru
no journal, ,
Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Ochi, Minoru; Yuguchi, Takashi; Tagami, Masahiko; Kakamu, Kazuhiko; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; Nishimoto, Shoji*; Nishiyama, Tadao*; Nakamata, Kiminori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishikino, Masaharu; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Ishino, Masahiko; Imazono, Takashi; Tanaka, Momoko; Sato, Katsutoshi; Yamamoto, Minoru; Oba, Toshiyuki; et al.
no journal, ,
Recent Progress in the development of laser-driven plasma soft X-ray laser (XRL) and the applications are presented. In the source development, TOPAZ laser using Nd:glass zigzag slab amplifiers with 10 J, 0.1 Hz repetition-rate routinely provides the fully spatial coherent X-ray laser at 13.9 nm for the applications. The bright, coherent, and picoseconds X-ray pulse can be used in a variety of applications such as X-ray speckle measurement and interferometer for probing materials, diffraction imaging, nano-scale fabrication, radiation biology, and so on. In order to extend the use of XRLs, now we are constructing new XRL beam lines for the optical pump and XRL probe experiment.
Hasegawa, Noboru; Ochi, Yoshihiro; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Oba, Toshiyuki; Kaihori, Takeshi; Suemoto, Toru*; Terakawa, Kota*; Tomita, Takuro*; Yamamoto, Minoru*
no journal, ,
In this study, we developed the shingle-shot soft X-ray laser interferometer at the wavelength of 13.9 nm by use of the double Lloyd's mirror geometry to measure the dynamics of the laser ablation. The lateral resolution and depth sensitivity of this interferometer were measured to be less than 1.5 micron and 1 nm, respectively. We combined this interferometer with Ti;Sapphire laser for this experiment. After 50 ps from laser irradiation, 35 nm expansion of the platinum sample was measured. And the expansion speed of the ablation front was estimated to be 700 m/s. The result of it shows there is low density structure (like as bubble structure) under the ablation front.