Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Hirata, Yuho; Matsuya, Yusuke; Kai, Takeshi; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Norihiro; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 10, p.13_1 - 13_8, 2024/11
The latest updates on PHITS, a versatile radiation transport code, focusing specifically on track-structure models are presented. Track structure calculations are methods used to simulate the movement of charged particles while explicitly considering each atomic reaction. Initially developed for radiation biology, these calculation methods aimed to analyze the radiation-induced damage to DNA and chromosomes. Several track-structure calculation models, including PHITS-ETS, PHITS-ETS for Si, PHITS-KURBUC, ETSART, and ITSART, have been developed and implemented to PHITS. These models allow users to study the behavior of various particles at the nano-scale across a wide range of materials. Furthermore, potential applications of track-structure calculations have also been proposed so far. This collection of track-structure calculation models, which encompasses diverse conditions, opens up new avenues for research in the field of radiation effects.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuya, Yusuke; Matsuda, Norihiro; Hirata, Yuho; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 61(1), p.127 - 135, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:144 Percentile:99.97(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) is a general-purpose Monte Carlo radiation transport code that can simulate the behavior of most particle species with energies up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ions). Its new version, PHITS3.31, was recently developed and released to the public. In the new version, the compatibility with high-energy nuclear data libraries and the algorithm of the track-structure modes have been improved. In this paper, we summarize the upgraded features of PHITS3.31 with respect to the physics models, utility functions, and application software introduced since the release of PHITS3.02 in 2017.
 -ray spectrum in
-ray spectrum in  U(
U( )
)Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Orlandi, R.; L guillon, R.; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Soldner, T.*; K
guillon, R.; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Soldner, T.*; K ster, U.*; Pollitt, A.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; et al.
ster, U.*; Pollitt, A.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(4), p.044610_1 - 044610_7, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.31(Physics, Nuclear) -rays for low-energy neutron induced fission
-rays for low-energy neutron induced fissionMakii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Orlandi, R.; L guillon, R.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Soldner, T.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; A
guillon, R.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Soldner, T.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; A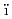 che, M.*; Astier, A.*; et al.
che, M.*; Astier, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 906, p.88 - 96, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed a new setup to measure prompt fission  -ray spectra in neutron induced fission up to energies sufficient to reveal the structure associated with giant dipole resonances of fission fragments. The setup consists of multi-wire proportional counters, to detect both fission fragments in coincidence, and two large volume (101.6 mm in diameter and 127.0 mm in length) LaBr
-ray spectra in neutron induced fission up to energies sufficient to reveal the structure associated with giant dipole resonances of fission fragments. The setup consists of multi-wire proportional counters, to detect both fission fragments in coincidence, and two large volume (101.6 mm in diameter and 127.0 mm in length) LaBr (Ce) scintillators, to measure the
(Ce) scintillators, to measure the  -rays. The setup was used to obtain the prompt fission
-rays. The setup was used to obtain the prompt fission  -ray spectrum for thermal neutron induced fission of
-ray spectrum for thermal neutron induced fission of  U at the PF1B cold-neutron beam facility of the Institut Laue-Langevin, Grenoble, France. We have successfully measured the
U at the PF1B cold-neutron beam facility of the Institut Laue-Langevin, Grenoble, France. We have successfully measured the  -ray spectrum up to energies of about 20 MeV, what extends the currently known
-ray spectrum up to energies of about 20 MeV, what extends the currently known  -ray spectrum limit to higher energies by approximately a factor of two.
-ray spectrum limit to higher energies by approximately a factor of two.
 -rays from neutron induced fission of U-235
-rays from neutron induced fission of U-235Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Orlandi, R.; L guillon, R.; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Soldner, T.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; Astier, A.*; Pollitt, A.*; et al.
guillon, R.; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Soldner, T.*; Hambsch, F.-J.*; Astier, A.*; Pollitt, A.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 146, p.04036_1 - 04036_4, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:88.62(Nuclear Science & Technology)The measurement of the prompt fission  -ray spectrum (PFGS) is quite important to study the de-excitation process of neutron-rich fission fragments as well as to generate data required to design a generation-IV reactors. The PFGS measured for spontaneous fission of
-ray spectrum (PFGS) is quite important to study the de-excitation process of neutron-rich fission fragments as well as to generate data required to design a generation-IV reactors. The PFGS measured for spontaneous fission of  Cf shows a broad hump at energies more than 8 MeV. This is interpreted as a giant dipole resonance (GDR) of the fragments centered around 15 MeV. To understand how the GDR is populated in the fission process, one needs to measure the PFGS for the reactions with the mass yields different from the spontaneous fission of
Cf shows a broad hump at energies more than 8 MeV. This is interpreted as a giant dipole resonance (GDR) of the fragments centered around 15 MeV. To understand how the GDR is populated in the fission process, one needs to measure the PFGS for the reactions with the mass yields different from the spontaneous fission of  Cf, such as (n,f). The measurements of the PFGS for (n,f), however, are limited less than 9 MeV even in the recent experiment. This prompts us to make a new measurement to extend the know PFGS up to 20 MeV. The measurement has been carried out at the PF1B beam line of Institut Laue-Langevin. In this contribution we will present the results obtained the measurement.
Cf, such as (n,f). The measurements of the PFGS for (n,f), however, are limited less than 9 MeV even in the recent experiment. This prompts us to make a new measurement to extend the know PFGS up to 20 MeV. The measurement has been carried out at the PF1B beam line of Institut Laue-Langevin. In this contribution we will present the results obtained the measurement.
Kido, Kentaro; Kasahara, Kento*; Yokogawa, Daisuke*; Sato, Hirofumi*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 143(1), p.014103_1 - 014103_9, 2015/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:17.55(Chemistry, Physical)Yamamoto, Masato*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Valo, M.*; Lambrecht, M.*; Viehrig, H.-W.*; Miura, Naoki*; Soneda, Naoki*
Small Specimen Test Techniques; 6th Volume (ASTM STP 1576), p.53 - 69, 2015/05
In order to ensure the robustness of the Master Curve technique, round-robin tests were performed using 0.16 inch-thick Mini-CT specimens by different investigators to see if consistent 
 values can be obtained. All the specimens used were machined and pre-cracked by one fabricator from unique Japanese RPV material. Seven institutes participated in this exercise, and obtained valid
values can be obtained. All the specimens used were machined and pre-cracked by one fabricator from unique Japanese RPV material. Seven institutes participated in this exercise, and obtained valid 
 values according to the ASTM E1921 standard. The scatter of
values according to the ASTM E1921 standard. The scatter of 
 values obtained was well within the uncertainty range defined in the standard, indicating the robustness of the Mini-CT specimen test technique. Throughout this activity, we could obtain 182
values obtained was well within the uncertainty range defined in the standard, indicating the robustness of the Mini-CT specimen test technique. Throughout this activity, we could obtain 182 
 for a single material. We investigated the statistics of this large database, and found that there is no remarkable difference not only in the
for a single material. We investigated the statistics of this large database, and found that there is no remarkable difference not only in the 
 values but also in the fracture toughness distribution between the Mini-CT specimen and the standard size 1T-C(T) specimen results.
values but also in the fracture toughness distribution between the Mini-CT specimen and the standard size 1T-C(T) specimen results.
Hayashi, Kentaro*; Kasahara, Seiji; Kurihara, Kohei*; Nakagaki, Takao*; Yan, X.; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Ogawa, Masuro
ISIJ International, 55(2), p.348 - 358, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:42.45(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Reducing coking coal consumption and CO emissions by application of iACRES (ironmaking system based on active carbon recycling energy system) was investigated using process flow modeling to show effectiveness of HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors) adoption to iACRES. Two systems were evaluated: a SOEC (solid oxide electrolysis cell) system using CO
emissions by application of iACRES (ironmaking system based on active carbon recycling energy system) was investigated using process flow modeling to show effectiveness of HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors) adoption to iACRES. Two systems were evaluated: a SOEC (solid oxide electrolysis cell) system using CO electrolysis and a RWGS (reverse water-gas shift reaction) system using RWGS reaction with H
electrolysis and a RWGS (reverse water-gas shift reaction) system using RWGS reaction with H produced by IS (iodine-sulfur) process. Both the effects on saving of the coking coal and reduction of CO
produced by IS (iodine-sulfur) process. Both the effects on saving of the coking coal and reduction of CO emissions were greater in the RWGS system. It was the reason of the result that excess H
emissions were greater in the RWGS system. It was the reason of the result that excess H which was not consumed in the RWGS reaction was used as reducing agent in the BF as well as CO. Heat balance in the HTGR, SOEC and RWGS modules were evaluated to clarify process components to be improved. Optimization of the SOEC temperature was desired to reduce Joule heat input for high efficiency operation of the SOEC system. Higher H
which was not consumed in the RWGS reaction was used as reducing agent in the BF as well as CO. Heat balance in the HTGR, SOEC and RWGS modules were evaluated to clarify process components to be improved. Optimization of the SOEC temperature was desired to reduce Joule heat input for high efficiency operation of the SOEC system. Higher H production thermal efficiency in the IS process for the RWGS system is effective for more efficient HTGR heat utilization. The SOEC system was able to utilize HTGR heat to reduce CO
production thermal efficiency in the IS process for the RWGS system is effective for more efficient HTGR heat utilization. The SOEC system was able to utilize HTGR heat to reduce CO emissions more efficiently by comparing CO
emissions more efficiently by comparing CO emissions reduction per unit heat of HTGR.
emissions reduction per unit heat of HTGR.
Hayashi, Kentaro*; Kasahara, Seiji; Kurihara, Kohei*; Nakagaki, Takao*; Yan, X.; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Ogawa, Masuro
Tanso Junkan Seitetsu Kenkyukai Saika Hokokusho; Tanso Junkan Seitetsu No Tenkai, p.42 - 62, 2015/02
Reducing coking coal consumption and CO emissions by application of HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors) to iACRES (ironmaking system based on active carbon recycling energy system) was investigated using process flow modeling. Two systems were evaluated: a SOEC (solid oxide electrolysis cell) system using CO
emissions by application of HTGRs (high temperature gas-cooled reactors) to iACRES (ironmaking system based on active carbon recycling energy system) was investigated using process flow modeling. Two systems were evaluated: a SOEC (solid oxide electrolysis cell) system using CO electrolysis and a RWGS (reverse water-gas shift reaction) system using RWGS reaction with H
electrolysis and a RWGS (reverse water-gas shift reaction) system using RWGS reaction with H produced by IS (iodine-sulfur) process. Coking coal consumption was reduced from a conventional BF (blast furnace) steelmaking system by 4.3% in the SOEC system and 10.3% in the RWGS system. CO
produced by IS (iodine-sulfur) process. Coking coal consumption was reduced from a conventional BF (blast furnace) steelmaking system by 4.3% in the SOEC system and 10.3% in the RWGS system. CO emissions were decreased by 3.4% in the SOEC system and 8.2% in the RWGS system. Remaining H
emissions were decreased by 3.4% in the SOEC system and 8.2% in the RWGS system. Remaining H from the RWGS reactor was used as reducing agent in the BF in the RWGS system. This was the reason of the larger reduction of coking coal consumption and CO
from the RWGS reactor was used as reducing agent in the BF in the RWGS system. This was the reason of the larger reduction of coking coal consumption and CO emissions. Electricity generation for SOEC occupied most of HTGR heat usage in the SOEC system. H
emissions. Electricity generation for SOEC occupied most of HTGR heat usage in the SOEC system. H production in the IS process used most of the HTGR heat in the RWGS system. Optimization of the SOEC temperature for the SOEC system and higher H
production in the IS process used most of the HTGR heat in the RWGS system. Optimization of the SOEC temperature for the SOEC system and higher H production thermal efficiency in the IS process for the RWGS system will be useful for more efficient heat utilization. One typical-sized BF required 0.5 HTGRs and 2 HTGRs for in the SOEC system and RWGS system, respectively. CO
production thermal efficiency in the IS process for the RWGS system will be useful for more efficient heat utilization. One typical-sized BF required 0.5 HTGRs and 2 HTGRs for in the SOEC system and RWGS system, respectively. CO emissions reduction per unit heat input was larger in the SOEC system. Recycling H
emissions reduction per unit heat input was larger in the SOEC system. Recycling H to the RWGS will be useful for smaller emissions per unit heat in the RWGS system.
to the RWGS will be useful for smaller emissions per unit heat in the RWGS system.
 Sn explored with the long-lived isomer in
Sn explored with the long-lived isomer in  Pd
PdWatanabe, H.*; Lorusso, G.*; Nishimura, Shunji*; Otsuka, T.*; Ogawa, K.*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Sumikama, Toshiyuki*; S derstr
derstr m, P.-A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Li, Z.*; et al.
m, P.-A.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Li, Z.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 113(4), p.042502_1 - 042502_6, 2014/07
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:75.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)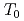 under various selections of temperature conditions
under various selections of temperature conditionsYamamoto, Masato*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Viehrig, H.-W.*; Miura, Naoki*; Soneda, Naoki*
Proceedings of 2014 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2014) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2014/07
The Master Curve (MC) approach for the fracture toughness reference temperature To is expected to be a powerful tool to ensure the reliability of long-term used RPV steels. In order to get sufficient number of data for the MC approach related to the present surveillance program for RPVs, the use of miniature specimens is important. The test technique for the miniature specimens (Mini-CT) of 4 mm thick had been verified the basic applicability of MC approach by means of Mini-CT for the determination of fracture toughness of typical Japanese RPV steels. A round robin (RR) program was organized to assure the robustness of the technique. As the third step of RR program, blinded tests were carried out. Precise material information was not provided to the participants. From the results obtained, the scatter range in 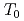 was within the acceptable scatter range specified in the testing standard. The selection of testing temperature seems to give limited effect like that in larger specimens.
was within the acceptable scatter range specified in the testing standard. The selection of testing temperature seems to give limited effect like that in larger specimens.
Kawamura, Masato*; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hori, Toshihiko; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Sato, Fumiaki; Fukui, Yuji*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Yamazaki, Masayoshi*; Sagawa, Ryu*; Miyajima, Noriyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.605 - 607, 2014/06
This report describes the present status of the klystron power supply systems for the J-PARC linac. The systems for the 181 MeV linac were operated from September to May. A few breakdowns were occurred, and are described in this report. The new systems for the upgrade of the linac from 181MeV to 400 MeV have been installed until now, and the 3 HVDCPSs and the 3 anode modulators of the new systems have been operated. All the systems for 400 MeV linac will be operated in this autumn.
Kawamura, Masato*; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hori, Toshihiko; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Sato, Fumiaki; Fukui, Yuji*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Yamazaki, Masayoshi*; Sagawa, Ryu*; Yukitake, Mitsuteru*; et al.
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1243 - 1247, 2013/08
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Masato*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Mabuchi, Yasuhiro*; Miura, Naoki*
Proceedings of 2013 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2013) (DVD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2013/07
Master Curve (MC) approach for the fracture toughness evaluation is expected to be a powerful tool to assess the structural integrity of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In order to get sufficient number of reliable data by the MC approach from used specimens of surveillance tests for RPVs, the use of miniature specimens is necessary. For this purpose, a round robin test program on the miniature compact tension specimens (Mini-CT) of 4 mm thick for the MC approach was launched with the participation of academia, industries and a research institute in Japan. The program aims to verify the reliability of experimental data from Mini-CT, and to pick out technical issues to be solved. As the second step of this program, the effect of loading rate (d /d
/d ) was evaluated based on enlarged database. Despite of the difference in d
) was evaluated based on enlarged database. Despite of the difference in d /d
/d , no specific difference in scatter band of
, no specific difference in scatter band of 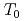 was found in d
was found in d /d
/d -
- 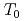 relationships. D
relationships. D /d
/d seems not to be sensitive on scatter band of To in the present results.
seems not to be sensitive on scatter band of To in the present results.
Matsuoka, Leo; Ogawa, Kenta*; Yokoyama, Keiichi
Proceedings of 10th Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Pacific Rim and 18th OptoElectronics and Communications Conference and Photonics in Switching 2013 (CLEO-PR & OECC/PS 2013) (USB Flash Drive), 2 Pages, 2013/06
Yamamoto, Masato*; Kimura, Akihiko*; Onizawa, Kunio; Yoshimoto, Kentaro*; Ogawa, Takuya*; Chiba, Atsushi*; Hirano, Takashi*; Sugihara, Takuji*; Sugiyama, Masanari*; Miura, Naoki*; et al.
Proceedings of 2012 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2012) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2012/07
Master curve (MC) approach for the fracture toughness evaluation is expected to be a powerful tool to assess the structural integrity of reactor pressure vessels (RPVs). In order to get sufficient number of reliable data for the MC approach from broken halves of surveillance test specimens for RPVs, the use of miniature specimens is necessary. For this purpose, a round robin test program on the miniature compact tension specimens (Mini-CT) of 4 mm thick for the MC approach of a Japanese RPV steel has been launched with the participation of academia, industries and a research institute in Japan. The program aims to verify the reliability of experimental data from Mini-CT, and to pick out further investigation items to be solved. As the first step of this program, four institutes carried out MC testing and evaluation using common test procedure and specimens. Valid reference temperature T was successfully obtained in each institute. However, the T
was successfully obtained in each institute. However, the T values showed large differences with maximum of 34
values showed large differences with maximum of 34 C. It was indicated on the reason of difference that there is a strong correlation between the T
C. It was indicated on the reason of difference that there is a strong correlation between the T values and loading rate, which was selected by each institute per test standard.
values and loading rate, which was selected by each institute per test standard.
Sugihara, Kenta; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Ogawa, Takemitsu; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
Proceedings of 20th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering and the ASME 2012 Power Conference (ICONE-20 & POWER 2012) (DVD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2012/07
Numerical simulation code, based on multi-phase thermohydraulics, has been being developed with a goal of a control and prediction for the laser cutting process. A thermohydraulic numerical simulation of the laser steel cutting was carried out to confirm an assist gas and sweep velocity effect to the cutting performance. The performance was evaluated, based on temperature profile and cutting front formation. Simulation results were as follows. If there was no effect of dross ejection by assist gas, a laser light was absorbed into molten steel stagnated in the kerf. Therefore, there was less laser heat input to a solid surface directly. Then, heat transport to the back side of steel plate got delayed. In the case of faster sweep velocity, delay of heat conduction and failure cut were confirmed at behind the cut starting position of the steel plate. Failure cut at the position was observed in our experiments. From these results, it was concluded that the thermohydraulics in the kerf takes important role for not only dross ejection but also promotion of heat input at solid surface.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
Sugihara, Kenta; Nakamura, Yasuyuki; Ogawa, Takemitsu; Yamada, Tomonori; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English