Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcement
Sn wires with and without Cu-Nb reinforcementNakamoto, Mio*; Sugano, Michinaka*; Ogitsu, Toru*; Sugimoto, Masahiro*; Taniguchi, Ryo*; Hirose, Kiyoshige*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Awaji, Satoshi*; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 34(5), p.8400806_1 - 8400806_6, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic) Sn cable-in-conduit conductors
Sn cable-in-conduit conductorsHemmi, Tsutomu; Harjo, S.; Ito, Takayoshi; Matsui, Kunihiro; Nunoya, Yoshihiko; Koizumi, Norikiyo; Takahashi, Yoshikazu; Nakajima, Hideo; Aizawa, Kazuya; Suzuki, Hiroshi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 21(3), p.2028 - 2031, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:48.78(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Residual strain in conductors is caused by the difference in the coefficient of expansion between Nb Sn strands and the jacket over a temperature range of 5 - 923 K. The superconducting properties of strands vary significantly, depending on the strain. It is important to clarify the residual strain as part of the evaluation of superconducting performance. However, the residual strain of strands in the conductor has not been measured so far because of their complicated configuration and their location in a jacket. The engineering materials diffractometer "Takumi" in J-PARC can measure residual strain with a relative accuracy of around 0.02%, using neutron diffraction. In this study, the Takumi was applied to the measurement of residual strain in strands for the ITER TF conductor. Results indicate that the residual strain of strands in the conductor can be determined, thereby clarifying the mechanism of residual strain and its relationship to superconducting performance.
Sn strands and the jacket over a temperature range of 5 - 923 K. The superconducting properties of strands vary significantly, depending on the strain. It is important to clarify the residual strain as part of the evaluation of superconducting performance. However, the residual strain of strands in the conductor has not been measured so far because of their complicated configuration and their location in a jacket. The engineering materials diffractometer "Takumi" in J-PARC can measure residual strain with a relative accuracy of around 0.02%, using neutron diffraction. In this study, the Takumi was applied to the measurement of residual strain in strands for the ITER TF conductor. Results indicate that the residual strain of strands in the conductor can be determined, thereby clarifying the mechanism of residual strain and its relationship to superconducting performance.
Ito, Takayoshi; Harjo, S.; Osamura, Kozo*; Hemmi, Tsutomu; Awaji, Satoshi*; Machiya, Shutaro*; Oguro, Hidetoshi*; Nishijima, Gen*; Takahashi, Koki*; Matsui, Kunihiro; et al.
Materials Science Forum, 681, p.209 - 214, 2011/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) YCu
YCu O
O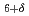 magnetic superconductor
magnetic superconductorMochiku, Takashi*; Hata, Yoshiaki*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Iwase, Kenji*; Sulistyanintyas, D.*; Oguro, Hidetoshi*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Igawa, Naoki; Tsuchiya, Yoshinori*; Iwai, Hideo*; et al.
no journal, ,
FeSr YCu
YCu O
O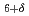 is expected to coexhibit superconductivity and magnetism, which has a tetragonal structure with the oxygen defect and the substitution between Cu and Fe. We have performed neutron powder diffraction of the FeSr
is expected to coexhibit superconductivity and magnetism, which has a tetragonal structure with the oxygen defect and the substitution between Cu and Fe. We have performed neutron powder diffraction of the FeSr YCu
YCu O
O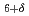 system to investigate the relation between the crystal structure and the physical properties.
system to investigate the relation between the crystal structure and the physical properties.