Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oka, Toshitaka; Oshima, Akihiro*; Motohashi, Ryota*; Seto, Naoto*; Watanabe, Yuji*; Kobayashi, Ryoji*; Saito, Koki*; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Washio, Masakazu*; et al.
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 80(2), p.278 - 280, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:48.91(Chemistry, Physical)The chemical structures of various ion-beam irradiated isotactic-polypropylene samples were studied. Results of micro-Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy suggest not only the linear energy transfer, but also the fluence is effective in local transformation of the isotactic-polypropylene.
Ota, Yukihiro; Nakai, Noriyuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Inotani, Daisuke*; Ohashi, Yoji*; Koyama, Tomio*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review B, 81(21), p.214511_1 - 214511_6, 2010/06
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:75.43(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)An extension of the Ambegaokar-Baratoff relation to a superconductor-insulator-superconductor (SIS) Josephson junction with multiple tunneling channels is derived. Applying the resultant relation to a SIS Josephson junction formed by an iron-based (five-band) and a single-band Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer (BCS) type superconductors, a theoretical bound of the Josephson critical current (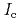 ) multiplied by the resistance of the junction (
) multiplied by the resistance of the junction (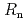 ) is given. We reveal that such a bound is useful for identifying the pairing symmetry of iron-pnictide superconductors. One finds that if a measured value of
) is given. We reveal that such a bound is useful for identifying the pairing symmetry of iron-pnictide superconductors. One finds that if a measured value of 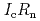 is smaller than the bound then the symmetry is
is smaller than the bound then the symmetry is 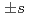 -wave, and otherwise
-wave, and otherwise  -wave without any sign changes. In addition, we stress that temperature dependence of
-wave without any sign changes. In addition, we stress that temperature dependence of 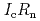 is sensitive to the difference of the gap functions from the BCS type gap formula in the above heterojunction.
is sensitive to the difference of the gap functions from the BCS type gap formula in the above heterojunction.
 -leg repulsive Hubbard ladders
-leg repulsive Hubbard laddersMachida, Masahiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Journal of Superconductivity and Novel Magnetism, 22(3), p.275 - 279, 2009/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.09(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Yamada, Susumu; Okumura, Masahiko; Machida, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physica C, 468(15-20), p.1237 - 1240, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.32(Physics, Applied)In order to study the vortex core electronic structure in high-T superconductors, we examine 1-D Hubbard model with trap potential by using the density matrix renormalization group method. Instead of directly treating the vortex, the approach mimics the carrier density depression inside the vortex core via the trap potential and exactly calculate strong correlation effects on the depressed region. Consequently, we find that the Mott state emerges in the central region and the metallic edge surrounds the Mott region. Furthermore, when adding spin imbalance, the calculations reveal that a local antiferromagnetic order covers the Mott state region, and moreover, the antiferromagnetic order modulates with a long periodicity. We expect that these results closely relate to the vortex core electronic structure while their calculation results can be directly compared with atomic Fermi gases loaded on an optical lattice.
superconductors, we examine 1-D Hubbard model with trap potential by using the density matrix renormalization group method. Instead of directly treating the vortex, the approach mimics the carrier density depression inside the vortex core via the trap potential and exactly calculate strong correlation effects on the depressed region. Consequently, we find that the Mott state emerges in the central region and the metallic edge surrounds the Mott region. Furthermore, when adding spin imbalance, the calculations reveal that a local antiferromagnetic order covers the Mott state region, and moreover, the antiferromagnetic order modulates with a long periodicity. We expect that these results closely relate to the vortex core electronic structure while their calculation results can be directly compared with atomic Fermi gases loaded on an optical lattice.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Okumura, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review A, 77(5), p.053614_1 - 053614_8, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:56.53(Optics)We investigate effects of optical lattice potential in one- and two-dimensional two-component trapped Fermi gases with population imbalances. Using the exact diagonalization and the density matrix renormalization group methods complementarily, we calculate the atom density profile from the groundstate many-body wavefunction as a function of attractive interaction strength for various population imbalances. The numerical results reveal that although a phase separation between the superfluid core and the shell cloud of excess atoms occurs as observed in experiments without the optical lattice, the population imbalance generally remains in the core region in contrast to the non-lattice cases. The essence of the numerical results in a strong attractive regime can be explained by an effective model composed of Cooper pairs and excess major fermions.
Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physica C, 463-465, p.103 - 106, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)In order to study an interplay between electronic inhomogeneity and superconductivity as seen in High-Tc cuprates as well as to predict effects of optical lattice in atomic Fermi gases, we numerically examine attractive Hubbard model in the absence of the translation symmetry. For the purpose, we systematically calculate the particle density profile for both 1-D and 2-D attractive Hubbard models with harmonic potential wells using the exact diagonalization and the density-matrix renormalization group methods. The numerical results reveal that fine inhomogeneous zigzag patterns universally emerge in the 1-D model case and the zig-zag structure becomes checkerboard type in the 2-D one. Moreover, it is numerically and theoretically found that such inhomogeneities are caused by double occupation component, i.e., pairs tightly bound on a site. These calculation results are universal for many-body Fermi-particle systems on lattice. We predict that the behavior described above is widely observable from atomic Fermi gas to strong coupled superconductors including High-Tc superconductors.
Machida, Masahiko; Koyama, Tomio*; Ohashi, Yoji*
Physica C, 460-462(1), p.275 - 276, 2007/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.7(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Kano, Takuma; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*; Machida, Masahiko
Journal of the Earth Simulator, 7, p.23 - 35, 2007/06
In order to explore a possibility of superfluidity in confined strongly-correlated fermion systems, e.g., nano-scale cuprate High-Tc superconductors and atomic Fermi gases loaded on an optical lattice, we implement an exact diagonalization code for their mathematical model, i.e., a trapped Hubbard model on the Earth Simulator. We compare two diagonalization algorithms, the traditional Lanczos method and a new algorithm, the preconditioned conjugate gradient (PCG) method, and find that when using the PCG the total CPU time can be reduced to 1/3  1/5 compared to the former one since the convergence can be dramatically improved by choosing a good preconditioner and the communication overhead is much more efficiently concealed in the PCG method. Consequently, such a performance improvement enables us to do systematic studies for several parameters. Numerical simulation results reveal that an unconventional type of pairing specific to the confined system, which can cause superfluidity, develops under a strong repulsive interaction.
1/5 compared to the former one since the convergence can be dramatically improved by choosing a good preconditioner and the communication overhead is much more efficiently concealed in the PCG method. Consequently, such a performance improvement enables us to do systematic studies for several parameters. Numerical simulation results reveal that an unconventional type of pairing specific to the confined system, which can cause superfluidity, develops under a strong repulsive interaction.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review A, 74(5), p.053621_1 - 053621_6, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:68.38(Optics)In order to explore a universal feature of atomic Fermi gases loaded on optical lattices, we make a systematic study of the particle density profile for 1-D and 2-D attractive Hubbard models with harmonic potential wells. Using the exact diagonalization scheme and the density-matrix renormalization group technique, we show that fine inhomogeneous zigzag patterns universally emerge in the above models. Theoretical and numerical analyses suggest that these structures originate from an effective repulsive interaction between tightly-bound pairs and a breakdown of translational invariance. Furthermore, it is emphasized that the pattern obtained numerically in the 2-D model is the checkerboard type, which is very similar to results recently observed in a vortex core of High-T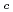 cuprate superconductor.
cuprate superconductor.
Machida, Masahiko; Koyama, Tomio*; Ohashi, Yoji*
Physica C, 445-448, p.194 - 197, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physica C, 445-448, p.90 - 93, 2006/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.58(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Koyama, Tomio*
Physical Review A, 74(2), p.023621_1 - 023621_5, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:31.73(Optics)no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Koyama, Tomio*; Ohashi, Yoji*
Physica C, 437-438, p.190 - 194, 2006/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.99(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review Letters, 95(21), P. 218902_1, 2005/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:78.36(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
Physical Review Letters, 93(20), p.200402_1 - 200402_4, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:74.91(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Koyama, Tomio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Ohashi, Yoji*; Koyama, Tomio*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nio, Daisuke; Ikekame, Yoshinori; Suwa, Masayuki; Isaka, Koji; Ouchi, Satoshi; Mineshima, Hiromi; Motohashi, Jun; Torii, Yoshiya; Kinase, Masami; Murayama, Yoji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Ohashi, Yoji*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 s-wave in iron-pnictide superconductors
s-wave in iron-pnictide superconductorsOta, Yukihiro; Nakai, Noriyuki; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Inotani, Daisuke*; Ohashi, Yoji*; Koyama, Tomio*; Matsumoto, Hideki*
no journal, ,
An enormous amount of studies has been devoted to the identification of the pairing symmetry in iron-based superconductors. In the paper, we focus on a heterotic (multiband) superconductor- insulator-(single-band)superconductor junction. First, we derive the Amgegaokar-Baratoff relation. We evaluate a theoretical lowerbound of 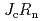 for s-wave without sign change, which may correspond to a upper bound for
for s-wave without sign change, which may correspond to a upper bound for  s-wave. Next, we discuss how a fluctuation of relative phases between multiple gaps and the pairing symmetry correct the Shapiro step, e.g., the step height and the step position. On the basis of these results, we propose a conventional and direct method to identify the
s-wave. Next, we discuss how a fluctuation of relative phases between multiple gaps and the pairing symmetry correct the Shapiro step, e.g., the step height and the step position. On the basis of these results, we propose a conventional and direct method to identify the  s-wave symmetry.
s-wave symmetry.