Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O ) by mechanochemical treatment
) by mechanochemical treatment秋山 大輔*; 三島 大輝*; 岡本 芳浩; 桐島 陽*
High Temperature Materials and Processes, 42(1), p.20220268_1 - 20220268_9, 2023/04
UO とTiO
とTiO の混合粉末を、タングステンカーバイドバイアルとボールを粉砕媒体として、Ar雰囲気下、遊星ボールミルで1時間メカノケミカル処理した。このようなメカノケミカル(MC)処理により、UO
の混合粉末を、タングステンカーバイドバイアルとボールを粉砕媒体として、Ar雰囲気下、遊星ボールミルで1時間メカノケミカル処理した。このようなメカノケミカル(MC)処理により、UO とTiO
とTiO の結晶性が低下した。メカノケミカル処理した混合粉末をAr雰囲気下、973-1573Kで6時間加熱し、X線回折分析、走査型電子顕微鏡-エネルギー分散型X線分光分析、X線吸収微細構造分析を行った。1373K以下ではMC処理なしではUTi
の結晶性が低下した。メカノケミカル処理した混合粉末をAr雰囲気下、973-1573Kで6時間加熱し、X線回折分析、走査型電子顕微鏡-エネルギー分散型X線分光分析、X線吸収微細構造分析を行った。1373K以下ではMC処理なしではUTi O
O は生成せず、出発物質のみが観測された。1473Kと1573Kでは、それぞれ少量のUTi
は生成せず、出発物質のみが観測された。1473Kと1573Kでは、それぞれ少量のUTi O
O と同量のUTi
と同量のUTi O
O とUO
とUO が生成した。メカノケミカル処理した試料は、1173K以上で6時間加熱すると、少量のUO
が生成した。メカノケミカル処理した試料は、1173K以上で6時間加熱すると、少量のUO 不純物を含むほぼ純粋なUTi
不純物を含むほぼ純粋なUTi O
O が生成した。
が生成した。
末岡 茂; 岩野 英樹*; 檀原 徹*; 岡本 晃*; 田上 高広*
フィッション・トラックニュースレター, (35), p.1 - 4, 2022/12
沈み込み帯では、スラブからの脱水によりメルトが生成され火山弧が形成されることはよく知られている。一方で、西南日本前弧域などでは、メルトの生成を伴わないスラブ起源流体の活動が報告されている。このような流体活動は、前弧域における熱輸送・物質移動に関わるのみならず、内陸の地震活動や泥火山の噴出との関連が指摘されている。また、地熱資源の開発や地下重要施設の安全性評価などの社会的な側面からも、その性質の理解が望まれている。本講演では、過去のスラブ起源流体活動の痕跡と考えられる熱水変質帯を対象に、低温領域の熱年代学に基づいて、流体活動の熱的特徴(到達温度,継続期間など)の検討を試みた事例を紹介する。事例対象としたのは、紀伊半島本宮地域と有馬地域の2つで、いずれもスラブ起源流体の湧出が盛んな地域として知られている。本宮地域では、平治川の露頭において、熱水脈およびその近傍の母岩(四万十帯砂岩)を採取した。有馬地域では、白水峡付近の六甲断層露頭から、断層からの距離に応じて基盤岩(風化花崗岩)を採取した。これらの試料から分離したジルコンとアパタイトを対象に、FT法, U-Pb法, (U-Th)/He法による熱年代解析を実施した。しかし、いずれの試料,いずれの熱年代計においても、新しい時代の熱異常は検出できない結果となった。そこで、一次元熱伝導モデルとHeFTy ver. 1.9.3のフォワードモデルに基づいて、熱水活動に伴う冷却年代の空間分布を再現して検証を行った。その結果、熱水温度が150 Cの、1000年程度の加熱期間ではこれらの熱年代計では熱異常の検出は困難と推定された。一方、熱水温度が200-300
Cの、1000年程度の加熱期間ではこれらの熱年代計では熱異常の検出は困難と推定された。一方、熱水温度が200-300 Cの場合、1000年以下の加熱期間でも、アパタイトFT年代やジルコン(U-Th)/He年代の若返りが期待できる。スラブ起源流体の場合、火山性の熱水と異なり、地表付近で再加熱されないため、熱年代法で熱異常を検出するには、地表付近までどれだけ高温が維持されるかが鍵となる。スラブ起源流体の熱的特徴の把握と熱年代法によるアプローチの適用性のさらなる検証のためには、200-300
Cの場合、1000年以下の加熱期間でも、アパタイトFT年代やジルコン(U-Th)/He年代の若返りが期待できる。スラブ起源流体の場合、火山性の熱水と異なり、地表付近で再加熱されないため、熱年代法で熱異常を検出するには、地表付近までどれだけ高温が維持されるかが鍵となる。スラブ起源流体の熱的特徴の把握と熱年代法によるアプローチの適用性のさらなる検証のためには、200-300 Cの熱水活動が期待される地域における事例の蓄積が望まれる。
Cの熱水活動が期待される地域における事例の蓄積が望まれる。
長田 充弘; 福田 将眞; 末岡 茂; 中嶋 徹; 梶田 侑弥*; 南 沙樹*; 岡本 晃*; 田上 高広*
フィッション・トラックニュースレター, (35), p.15 - 18, 2022/09
ジルコンを用いた年代測定の標準試料の探求の一環として、照来層群歌長流紋岩中のジルコンについて、U-Pb年代測定を実施した。歌長流紋岩からは、先行研究により約2.30-2.77Maのジルコンフィッション・トラック年代,ジルコン(U-Th)/He年代、および黒雲母K-Ar年代が報告されていた。ジルコンは短柱状から長柱状の自形を呈し、カソードルミネッセンス像観察では明瞭なコア・リム構造や累帯構造を示さない。レーザーアブレーション・マルチコレクター誘導結合プラズマ質量分析装置を用いてU-Pb同位体を測定した。2試料より得られたU-Pb年代は、いずれも2.5-3.0Maを示し、それぞれ2.65 0.16Maおよび2.66
0.16Maおよび2.66 0.15Maの
0.15Maの U-
U- Pb加重平均値を得た。得られた年代は、先行研究による閉鎖温度の異なる年代と整合的であるため、歌長流紋岩中のジルコンが標準試料として有効である可能性がある。今後、更なる各種年代、U, Th,希土類元素などの元素濃度の測定から標準試料として適切か検討する。
Pb加重平均値を得た。得られた年代は、先行研究による閉鎖温度の異なる年代と整合的であるため、歌長流紋岩中のジルコンが標準試料として有効である可能性がある。今後、更なる各種年代、U, Th,希土類元素などの元素濃度の測定から標準試料として適切か検討する。
 and CrUO
and CrUO
秋山 大輔*; 日下 良二; 熊谷 友多; 中田 正美; 渡邉 雅之; 岡本 芳浩; 永井 崇之; 佐藤 修彰*; 桐島 陽*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 568, p.153847_1 - 153847_10, 2022/09
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:68.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)ウラン酸鉄,ウラン酸クロム、およびその固溶体を合成し、これらのウラン酸塩が異なる熱的安定性を示すメカニズムを研究した。熱的安定性を評価するため、ウラン酸塩試料の熱重量分析を実施した結果、ウラン酸クロムの分解温度(約1250 C)に対してウラン酸鉄は低温(約800
C)に対してウラン酸鉄は低温(約800 C)で分解するが、クロムを含む固溶体では熱分解に対する安定性が高まることが分かった。この熱的安定性と結晶構造との関係性を調べるため、エックス線結晶構造解析,エックス線吸収微細構造測定,メスバウアー分光測定,ラマン分光分析による詳細な結晶構造と物性の評価を行ったが、本研究で用いたウラン酸塩試料の間に明瞭な差異は観測されなかった。そのため、熱的安定性の違いは結晶構造に起因するものではなく、鉄とクロムとの酸化還元特性の違いによるものと推定した。クロムは3価が極めて安定であるのに対して、鉄の原子価は2価と3価を取ることができる。このため、ウラン酸鉄の場合には結晶中でウランと鉄との酸化還元反応が起こり、低温での分解反応を誘起したものと考えられる。
C)で分解するが、クロムを含む固溶体では熱分解に対する安定性が高まることが分かった。この熱的安定性と結晶構造との関係性を調べるため、エックス線結晶構造解析,エックス線吸収微細構造測定,メスバウアー分光測定,ラマン分光分析による詳細な結晶構造と物性の評価を行ったが、本研究で用いたウラン酸塩試料の間に明瞭な差異は観測されなかった。そのため、熱的安定性の違いは結晶構造に起因するものではなく、鉄とクロムとの酸化還元特性の違いによるものと推定した。クロムは3価が極めて安定であるのに対して、鉄の原子価は2価と3価を取ることができる。このため、ウラン酸鉄の場合には結晶中でウランと鉄との酸化還元反応が起こり、低温での分解反応を誘起したものと考えられる。
桐島 陽*; 寺崎 万里子*; 宮川 和也; 岡本 芳浩; 秋山 大輔*
Chemosphere, 289, p.133181_1 - 133181_12, 2022/04
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:6.09(Environmental Sciences)令和2年度以降の幌延深地層研究計画において原子力機構が取り組んでいる課題の1つである「実際の地質環境における人工バリアの適用性確認」では、坑道周辺の掘削損傷領域において物質移行に関するデータの取得が必要である。これに資することが期待される基礎的知見として、深部地下水中のアクチニドの移行挙動をより良く理解するために、水質の異なる2種類の地下水試料にトレーサーを添加し、地下水中の溶存成分との相互作用を調べた。地下水試料は、幌延深地層研究センターの地下施設の250mおよび350m調査坑道のボーリング孔および、瑞浪超深地層研究所の地下施設の300mおよび500m坑道のボーリング孔から採取した。得られた地下水試料に対して、トレーサーとしてLa, Sm, Ho, Uを濃度10ppbまたは100ppbになるように添加した。その後、地下水試料を0.2 mフィルターと10kDaフィルターで順次濾過し、ろ液中のトレーサー濃度をICP-MSで分析し、ろ紙に捕獲されたトレーサー濃度をTOF-SIMSで分析し、化学形態をXAFSにより分析した。その結果、幌延の地下水中では、ランタニドの移行はリン酸塩により支配されていることが分かった。このことから、高レベル放射性廃棄物から海成堆積層の地下水中に溶出するマイナーアクチニドの溶解度は、リン酸塩により規定されることが示唆された。一方、瑞浪の地下水のように塩濃度が低くリン酸イオン濃度の低い地下水では、マイナーアクチニドの一部は水酸化物もしくはヒドロオキシ炭酸塩を形成することが示唆された。
mフィルターと10kDaフィルターで順次濾過し、ろ液中のトレーサー濃度をICP-MSで分析し、ろ紙に捕獲されたトレーサー濃度をTOF-SIMSで分析し、化学形態をXAFSにより分析した。その結果、幌延の地下水中では、ランタニドの移行はリン酸塩により支配されていることが分かった。このことから、高レベル放射性廃棄物から海成堆積層の地下水中に溶出するマイナーアクチニドの溶解度は、リン酸塩により規定されることが示唆された。一方、瑞浪の地下水のように塩濃度が低くリン酸イオン濃度の低い地下水では、マイナーアクチニドの一部は水酸化物もしくはヒドロオキシ炭酸塩を形成することが示唆された。
永井 崇之; 秋山 大輔*; 桐島 陽*; 佐藤 修彰*; 岡本 芳浩
2020年度「物質・デバイス領域共同研究拠点」および「人・環境と物質をつなぐイノベーション創出ダイナミック・アライアンス」研究成果・活動報告書(CD-ROM), 1 Pages, 2021/11
本研究は、ガラス組成や溶融条件を変えて作製したウラン(U)含有模擬廃棄物ガラスを放射光XAFS測定し、還元雰囲気で溶融作製したホウケイ酸ガラス中のUが4価状態で内包されることを確認した。
北里 宏平*; Milliken, R. E.*; 岩田 隆浩*; 安部 正真*; 大竹 真紀子*; 松浦 周二*; 高木 靖彦*; 中村 智樹*; 廣井 孝弘*; 松岡 萌*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
被引用回数:43 パーセンタイル:96.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics)2019年4月「はやぶさ2」ミッションは、地球に近い炭素質の小惑星(162173)リュウグウの人工衝撃実験を成功させた。これは露出した地下物質を調査し、放射加熱の潜在的な影響をテストする機会を提供した。はやぶさ2の近赤外線分光器(NIRS3)によるリュウグウの地下物質の観測結果を報告する。発掘された材料の反射スペクトルは、表面で観測されたものと比較して、わずかに強くピークがシフトした水酸基(OH)の吸収を示す。これは、宇宙風化や放射加熱が最上部の表面で微妙なスペクトル変化を引き起こしたことを示している。ただし、このOH吸収の強度と形状は、表面と同様に、地下物質が300 Cを超える加熱を経験したことを示している。一方、熱物理モデリングでは、軌道長半径が0.344AUに減少しても、推定される掘削深度1mでは放射加熱によって温度が200
Cを超える加熱を経験したことを示している。一方、熱物理モデリングでは、軌道長半径が0.344AUに減少しても、推定される掘削深度1mでは放射加熱によって温度が200 Cを超えて上昇しないことが示されている。これは、リュウグウ母天体が放射加熱と衝撃加熱のいずれか、もしくは両方により熱変化が発生したという仮説を裏付けている。
Cを超えて上昇しないことが示されている。これは、リュウグウ母天体が放射加熱と衝撃加熱のいずれか、もしくは両方により熱変化が発生したという仮説を裏付けている。
永井 崇之; 秋山 大輔*; 桐島 陽*; 佐藤 修彰*; 岡本 芳浩
2019年度「物質・デバイス領域共同研究拠点」および「人・環境と物質をつなぐイノベーション創出ダイナミック・アライアンス」研究成果・活動報告書(CD-ROM), P. 20191107_1, 2020/11
本研究は、ウラン(U)濃度を高めたホウケイ酸ガラス組成中のUの化学状態を把握するため、異なる原料ガラス組成を用いてU含有ガラスを作製し、放射光XAFS測定によりUの原子価等を評価した。ホウケイ酸ガラス組成へのU溶解度はUO 換算で15wt%以上であり、U含有ガラス中のUはガラス相に概ね6価状態で均一に存在する。
換算で15wt%以上であり、U含有ガラス中のUはガラス相に概ね6価状態で均一に存在する。
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*; et al.
Proceedings of 5th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '14) (Internet), p.28 - 33, 2014/07
Three-dimensional (3D) cooling of 40-keV  Mg
Mg ion beams with Doppler laser cooling and the coupling resonance has been demonstrated in the storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University toward the production of ultralow-emittance beams, in other words, ultracold beams and so-called crystalline beams. So far, the transverse temperatures of 6 K and 2 K have been experimentally attained in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, at a low beam intensity of about
ion beams with Doppler laser cooling and the coupling resonance has been demonstrated in the storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University toward the production of ultralow-emittance beams, in other words, ultracold beams and so-called crystalline beams. So far, the transverse temperatures of 6 K and 2 K have been experimentally attained in the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively, at a low beam intensity of about 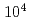 ions in the ring. These temperatures are the lowest ever attained by laser cooling of ion beams. Systematic molecular dynamics simulations predict the realization of further lower temperatures,
ions in the ring. These temperatures are the lowest ever attained by laser cooling of ion beams. Systematic molecular dynamics simulations predict the realization of further lower temperatures,  1 mK and
1 mK and  0.1 K in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, if the laser spot size and detuning are properly adjusted even with such a low laser power (
0.1 K in the longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively, if the laser spot size and detuning are properly adjusted even with such a low laser power ( 10 mW) as utilized in the experiments at S-LSR. A 3D ordered state of the beam with 3D laser cooling is also predicted. Recent experimental achievements and latest simulation results are presented.
10 mW) as utilized in the experiments at S-LSR. A 3D ordered state of the beam with 3D laser cooling is also predicted. Recent experimental achievements and latest simulation results are presented.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 10th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.143 - 145, 2014/06
We have experimentally demonstrated transverse indirect laser cooling utilizing synchro-betatron resonance coupling in the ion accumulation cooler ring S-LSR. However, its efficiency was rather poor for relatively high beam intensity of 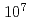 ions in the ring due to beam heating by intra-beam scattering and its cooling time was as long as 100 s. By application of beam scraping and optimization of laser detuning together with equilibrium deceleration with the use of an induction accelerator, we could reach the lowest transverse temperatures ever attained by laser cooling as 7.0 K and 2.1 K for the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The prospect of generating an ultra-low-temperature beam and realizing beam crystallization will be discussed on the basis of the present result.
ions in the ring due to beam heating by intra-beam scattering and its cooling time was as long as 100 s. By application of beam scraping and optimization of laser detuning together with equilibrium deceleration with the use of an induction accelerator, we could reach the lowest transverse temperatures ever attained by laser cooling as 7.0 K and 2.1 K for the horizontal and vertical directions, respectively. The prospect of generating an ultra-low-temperature beam and realizing beam crystallization will be discussed on the basis of the present result.
百合 庸介; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; He, Z.*; 想田 光*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '13) (Internet), p.162 - 165, 2013/11
Efficient transverse laser cooling of a low-intensity heavy-ion beam has been recently accomplished experimentally by means of the resonant coupling method at the cooler storage ring S-LSR of Kyoto University. In parallel with the experimental effort, multi-dimensional laser cooling of the ion beam has been studied also numerically with the molecular dynamics (MD) simulation code in which the stochastic interaction between ions and laser photons is incorporated in order to search optimum laser-cooling conditions and verify the results of the experiment. The present MD result demonstrates that, in spite of the limited experimental conditions of the cooling laser such as low power, fixed frequency, and short cooling section, a three-dimensionally low-temperature beam of 40-keV  Mg
Mg can be obtained through resonant coupling at a low intensity of
can be obtained through resonant coupling at a low intensity of 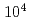 ions in the ring, which is consistent with the experimental result.
ions in the ring, which is consistent with the experimental result.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics (COOL '13) (Internet), p.157 - 161, 2013/11
We have tried to approach to the lowest attainable beam temperature with laser cooling of a 40-keV  Mg
Mg ion beam at a cooler storage ring S-LSR, which has a superperiodicity of six and is designed to be tough against resonant perturbation to the circulating beam. The capability of active indirect transverse laser cooling has been experimentally demonstrated with the use of the theoretically-proposed synchro-betatron resonance coupling scheme. For the reduction of beam heating due to intrabeam scattering, an additional scheme has been established to control the intensity of the circulating beam down to
ion beam at a cooler storage ring S-LSR, which has a superperiodicity of six and is designed to be tough against resonant perturbation to the circulating beam. The capability of active indirect transverse laser cooling has been experimentally demonstrated with the use of the theoretically-proposed synchro-betatron resonance coupling scheme. For the reduction of beam heating due to intrabeam scattering, an additional scheme has been established to control the intensity of the circulating beam down to 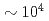 ions by scraping the outskirt of the beam with the use of a horizontally-moving scraper, which could cool the horizontal and vertical beam temperature down to
ions by scraping the outskirt of the beam with the use of a horizontally-moving scraper, which could cool the horizontal and vertical beam temperature down to 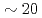 K and
K and 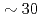 K, respectively, at an operation tune without horizontal-vertical (H-V) coupling. In the present paper, we would like to also present our recent results with H-V coupling in addition to longitudinal-horizontal coupling toward further reduction of the transverse beam temperature.
K, respectively, at an operation tune without horizontal-vertical (H-V) coupling. In the present paper, we would like to also present our recent results with H-V coupling in addition to longitudinal-horizontal coupling toward further reduction of the transverse beam temperature.
He, Z.*; Wei, J.*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*
Proceedings of 25th North American Particle Accelerator Conference (NA-PAC '13) (Internet), p.1298 - 1300, 2013/09
The power of the cooling laser currently available in a compact ion cooler ring S-LSR, Kyoto University, is quite limited for generating ultralow-temperature ion beams. Therefore, parameters of laser cooling should be carefully determined in order to approach the lowest possible temperature in the experiment. This paper mainly concerns optimization of laser-cooling parameters and prediction of a possible lower limit of beam temperature in S-LSR, based on systematic molecular dynamics simulations. The adiabatic capture process of the ion beam was introduced to prevent the emittance from blowing up during bunching. The spot size of the laser was optimized with the total laser power limited. An optimum solenoid field strength was obtained for three-dimensional cooling. The lowest beam temperature achievable in S-LSR was predicted by choosing the parameters optimized.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; He, Z.*; Grieser, M.*; 野田 章*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 52(3), p.030202_1 - 030202_4, 2013/03
被引用回数:5 パーセンタイル:22.83(Physics, Applied)The efficiency of indirect transverse laser cooling of a heavy-ion beam using synchro-betatron resonant coupling (SBRC) was improved by the reduction of the beam intensity through scraping the tail part of the beam. In order to measure the beam size at low beam intensity, a new scheme was established where the beam profile was determined from the beam survival ratio by changing the insertion position of a beam scraper. At a beam intensity of 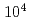 particles in the ring, the transverse cooling time of the beam was reduced to 1.2 s, and horizontal and vertical minimum beam sizes were 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm, corresponding to the beam temperatures of 20 K and 29 K, respectively. The cooling time was much improved compared with that of our previous experiment, 100 s at
particles in the ring, the transverse cooling time of the beam was reduced to 1.2 s, and horizontal and vertical minimum beam sizes were 0.2 mm and 0.6 mm, corresponding to the beam temperatures of 20 K and 29 K, respectively. The cooling time was much improved compared with that of our previous experiment, 100 s at 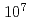 particles (Nakao et al.). The transverse temperature was comparable to that in other work (Madsen et al.), in spite of the limitation in the experimental conditions such as low laser power and short laser-cooling section. This suggests that the present SBRC scheme has a potential capacity for attaining a lower-temperature beam or even Coulomb crystallization.
particles (Nakao et al.). The transverse temperature was comparable to that in other work (Madsen et al.), in spite of the limitation in the experimental conditions such as low laser power and short laser-cooling section. This suggests that the present SBRC scheme has a potential capacity for attaining a lower-temperature beam or even Coulomb crystallization.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; Meshkov, I.*; Smirnov, A.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd Russian Particle Accelerator Conference (RuPAC 2012) (Internet), p.48 - 52, 2012/09
Various approaches to attaining low-temperature beams have been continued in the cooler storage ring S-LSR at Kyoto University. One-dimensional ordering of electron-cooled 7-MeV protons was realized with an abrupt longitudinal temperature jump from 2 K to 0.3 K at a particle number of around 2000. Laser cooling has been applied to 40-keV  Mg
Mg beams toward the realization of crystalline beams. For a coasting beam, the lowest longitudinal temperature of 3.6 K was attained at
beams toward the realization of crystalline beams. For a coasting beam, the lowest longitudinal temperature of 3.6 K was attained at 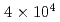 ions. The temperature was limited due to intra-beam scattering (IBS). On the other hand, the transverse temperature of the beam indirectly cooled through IBS was saturated at 500 K for
ions. The temperature was limited due to intra-beam scattering (IBS). On the other hand, the transverse temperature of the beam indirectly cooled through IBS was saturated at 500 K for 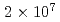 ions. In order to cool the transverse direction further, synchro-betatron resonance coupling has been applied to a bunched Mg beam. The transverse temperature has been reduced to the order of
ions. In order to cool the transverse direction further, synchro-betatron resonance coupling has been applied to a bunched Mg beam. The transverse temperature has been reduced to the order of 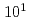 K at the beam intensity of
K at the beam intensity of 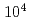 ions by the reduction of the beam intensity using a scraper.
ions by the reduction of the beam intensity using a scraper.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 頓宮 拓*; 野田 章*; 神保 光一*; 大崎 一哉*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.388 - 390, 2012/08
京都大学化学研究所のイオン蓄積・冷却リングS-LSRでは、シンクロ・ベータトロン共鳴によって重イオンビームの運動の進行方向と水平方向の振動を結合させ、レーザー冷却によって横方向を間接的に冷却する実験を進めている。冷却の過程において、粒子数が多い場合Intra-beam散乱による自己加熱作用によって冷却が阻害されるため、スクレイパーによってビーム外縁部の粒子を除去することによって冷却効率を高めている。このとき、2枚のスクレイパーを用い、1枚目のスクレイパーで粒子数を減らした後、2枚目のスクレイパーの挿入距離を変えてビームの残存率を測定することで、ビーム中心からの距離とその内側にある粒子の割合が得られ、この関係から冷却後のビームサイズを測定した。その結果、40keV  Mg
Mg ビームについて、水平・鉛直ベータトロンチューン、及びシンクロトロンチューンがそれぞれ(2.074, 1.120, 0.072)、1枚目のスクレイパーをビーム中心から0.3mmまで挿入して粒子数を1
ビームについて、水平・鉛直ベータトロンチューン、及びシンクロトロンチューンがそれぞれ(2.074, 1.120, 0.072)、1枚目のスクレイパーをビーム中心から0.3mmまで挿入して粒子数を1 10
10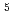 まで減少させた条件で、水平方向ビームサイズが0.3mm、温度に換算して52Kまで冷却されていることを観測した。この時、ビームサイズが1/eになるまでの冷却時間は1.25秒であった。
まで減少させた条件で、水平方向ビームサイズが0.3mm、温度に換算して52Kまで冷却されていることを観測した。この時、ビームサイズが1/eになるまでの冷却時間は1.25秒であった。
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 神保 光一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 9th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (インターネット), p.72 - 74, 2012/08
Laser cooling of 40-keV Mg ion has been performed at S-LSR. Indirect transverse laser cooling of a bunched beam with the use of synchro-betatron resonance coupling (SBRC) has been experimentally indicated. However, it is not so efficient due to heating by intra-beam scattering for the ion number of 10 . For attaining very low-temperature beam, it is inevitable to reduce the beam intensity without deterioration of beam detection signal. For this purpose, we have applied controlled scraping of a laser-cooled beam. After beam injection, the beam tail is cut off by a scraper moving in the horizontal direction and laser-cooled both in the longitudinal and horizontal directions with SBRC. Then, the horizontal beam size was measured with another scraper moving also in the horizontal direction. With this scheme, the beam intensity could be reduced from 10
. For attaining very low-temperature beam, it is inevitable to reduce the beam intensity without deterioration of beam detection signal. For this purpose, we have applied controlled scraping of a laser-cooled beam. After beam injection, the beam tail is cut off by a scraper moving in the horizontal direction and laser-cooled both in the longitudinal and horizontal directions with SBRC. Then, the horizontal beam size was measured with another scraper moving also in the horizontal direction. With this scheme, the beam intensity could be reduced from 10 to 10
to 10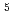 , which resulted in rather efficient indirect transverse laser cooling with the cooling time of about 1 sec.
, which resulted in rather efficient indirect transverse laser cooling with the cooling time of about 1 sec.
想田 光*; 中尾 政夫*; 野田 章*; 頓宮 拓*; 伊藤 清一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; He, Z.*
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.397 - 399, 2012/05
The longitudinal temperature of 40 keV  Mg
Mg beams was measured through bunch length measurement during laser cooling at S-LSR. The bunch length was measured as time-domain signals from a pair of parallel-plate electrostatic pickups. Injected non-cooled beams gave a bunch length of 2.5 m and cooled beams had two components of broad and sharp distributions. The broad distribution had a longitudinal length of 2.2 m, which is close to that of the initial beam. The length of the sharp distribution shrunk to 0.25 m and is expected as a cooled part. The capture efficiency of cooling, which represents the ratio of particle numbers of the cooled part and the total particle number, varied with laser detuning. With a scanning range of 2 GHz, it was improved from 66% to 92%, while the bunch became longer by 10% with scanning. A new scheme for improving the capture efficiency will be applied to attain a strong signal from a low-current low-temperature beam.
beams was measured through bunch length measurement during laser cooling at S-LSR. The bunch length was measured as time-domain signals from a pair of parallel-plate electrostatic pickups. Injected non-cooled beams gave a bunch length of 2.5 m and cooled beams had two components of broad and sharp distributions. The broad distribution had a longitudinal length of 2.2 m, which is close to that of the initial beam. The length of the sharp distribution shrunk to 0.25 m and is expected as a cooled part. The capture efficiency of cooling, which represents the ratio of particle numbers of the cooled part and the total particle number, varied with laser detuning. With a scanning range of 2 GHz, it was improved from 66% to 92%, while the bunch became longer by 10% with scanning. A new scheme for improving the capture efficiency will be applied to attain a strong signal from a low-current low-temperature beam.
野田 章*; 中尾 政夫*; 想田 光*; 頓宮 拓*; 伊藤 清一*; 岡本 宏巳*; 大崎 一哉*; 百合 庸介; 神保 光一*; Grieser, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.394 - 396, 2012/05
Mg ion beams have been successfully laser-cooled both in longitudinal and transverse directions at S-LSR in ICR, Kyoto University. The cooling rate, however, is not strong enough to realize a crystalline beam due to heating from intra-beam scattering (IBS). Reduction of the beam intensity is inevitable to suppress this IBS effect, which, however, had resulted in poor S/N ratio for observation of the transverse beam size. We, therefore, describe a new beam-scraping scheme: The scheme selects out ions in the distribution tail of the transverse phase space, keeping the beam density in the core part by simultaneous application of multi-dimensional laser cooling and beam scraping. The strategy to realize the scheme effectively has been searched by combination of the beam experiments and computer simulations.
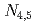 absorption edges
absorption edges岡根 哲夫; 竹田 幸治; 岡本 淳*; 間宮 一敏*; 大河内 拓雄; 藤森 伸一; 斎藤 祐児; 山上 浩志; 藤森 淳; 落合 明*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 77(2), p.024706_1 - 024706_6, 2008/02
被引用回数:15 パーセンタイル:64.38(Physics, Multidisciplinary)X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) was measured for the ferromagnetic uranium monochalcogenides US and USe at U 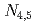 absorption edges in the soft X-ray region. The obtained
absorption edges in the soft X-ray region. The obtained 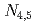 XMCD signal of US was comparable to the
XMCD signal of US was comparable to the 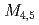 XMCD signal obtained in previous studies. From the sum-rule analysis of XMCD data, it was shown that the estimated ratios of orbital magnetic moment to spin magnetic moment were almost the same for US and USe. The analysis of the XAS branching ratio indicated an increase in 5
XMCD signal obtained in previous studies. From the sum-rule analysis of XMCD data, it was shown that the estimated ratios of orbital magnetic moment to spin magnetic moment were almost the same for US and USe. The analysis of the XAS branching ratio indicated an increase in 5 electron occupation number from US to USe.
electron occupation number from US to USe.