Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS method
C-stainless steel composites using the improved MPS methodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Sharma, A.*; Kumar, R.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Pellegrini, M.*; Yokoyama, Ryo*; Okamoto, Koji*
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 250, p.127343_1 - 127343_17, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:0Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Okamoto, Koji
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 184, p.105710_1 - 105710_10, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Very recently, Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO) has been proposed as a scheme capable to inversely estimate radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms from air dose rate measurements together with the predicted lower bound of the measurement numbers for successful reconstructions. However, no one has ever analyzed how the uncertainty of input data including the measurement errors influences the accuracy of the inverse estimation results. In this paper, we therefore perform uncertainty analysis of the LASSO scheme and suggest an uncertainty estimation function derived based on the theory of Candes. We actually demonstrate in two types of numerical tests with different input uncertainties obtained by using Monte Carlo code, Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) that the calculated errors obey the proposed uncertainty estimation function. Thus, the LASSO scheme allows to successfully estimate radioactive distributions within the predicted uncertainty.
 C-SS eutectic melting and its relocation behaviour
C-SS eutectic melting and its relocation behaviourAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Okamoto, Koji*
Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 50(5), p.3361 - 3371, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2024-014, 54 Pages, 2025/02
XAFS measurements in the soft X-ray region are suitable for evaluating the chemical state of the surface layer of a measurement sample because the X-ray transmittance is low. In this study, the purpose of the study was to confirm the difference between the coagulated surface layer and the inside of the simulated waste glasses by measuring the K-edge of the glass constituent elements boron, oxygen, sodium, and silicon, and the L edge of the waste component cerium. As a result, the B K-edge XANES spectra showed that the proportion of B-O tetracoordinate sp
edge of the waste component cerium. As a result, the B K-edge XANES spectra showed that the proportion of B-O tetracoordinate sp structures (BO
structures (BO ) on the surface layer of the coagulated glass samples was higher than that on the cut surface inside the glass samples, which is expected to improve the water resistance of the coagulated surface. On the other hand, the O K-edge XANES spectra suggested that the O abundance in the coagulated surface layer was lower than that in the cut surface inside the glass samples, and that alkali metal elements may be concentrated in the coagulated surface layer. However, no difference was observed in the Na K-edge XANES spectra between the coagulated surface layer and the cut surface, and no difference was observed in the Si K-edge XANES spectra between the solidified surface and the inside of glass samples. In addition, the Ce L
) on the surface layer of the coagulated glass samples was higher than that on the cut surface inside the glass samples, which is expected to improve the water resistance of the coagulated surface. On the other hand, the O K-edge XANES spectra suggested that the O abundance in the coagulated surface layer was lower than that in the cut surface inside the glass samples, and that alkali metal elements may be concentrated in the coagulated surface layer. However, no difference was observed in the Na K-edge XANES spectra between the coagulated surface layer and the cut surface, and no difference was observed in the Si K-edge XANES spectra between the solidified surface and the inside of glass samples. In addition, the Ce L -edge XANES spectra confirmed that the Ce valence in the surface layer of coagulated glass samples were oxidized compared to the inside of glass samples.
-edge XANES spectra confirmed that the Ce valence in the surface layer of coagulated glass samples were oxidized compared to the inside of glass samples.
Aihara, Jun; Ueta, Shohei; Honda, Masaki*; Kasahara, Seiji; Okamoto, Koji*
JAEA-Research 2024-012, 98 Pages, 2025/02
Concept of Pu-burner high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) was proposed for the purpose of more safely reducing amount of recovered Pu. In Pu-burner HTGR concept, coated fuel particle (CFP), with ZrC coated yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) containing PuO (PuO
(PuO -YSZ) small particle and with tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coating, is employed for very high burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. ZrC layer is oxygen getter. In research project of Pu-burner HTGR carried out from fiscal year of 2014 to fiscal year of 2017, simulated CFPs were fabricated using Ce to simulate Pu. Moreover, simulated fuel compacts were fabricated using fabricated simulated CFPs. In this report, results of microstructural observation of CeO
-YSZ) small particle and with tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coating, is employed for very high burn-up and high nuclear proliferation resistance. ZrC layer is oxygen getter. In research project of Pu-burner HTGR carried out from fiscal year of 2014 to fiscal year of 2017, simulated CFPs were fabricated using Ce to simulate Pu. Moreover, simulated fuel compacts were fabricated using fabricated simulated CFPs. In this report, results of microstructural observation of CeO -YSZ and ZrC layer at each fabrication step are reported.
-YSZ and ZrC layer at each fabrication step are reported.
 CuZn
CuZn P
P
May, A. F.*; Tabata, Chihiro; Okamoto, Satoshi*; Ortiz, B. R.*; Christianson, A. D.*; Yan, J.*; Kaneko, Koji; McGuire, M. A.*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_13, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Zhou, W.*; Miwa, Shuichiro*; Yamashita, Susumu; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 177, p.105441_1 - 105441_17, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Understanding air entrainment phenomena induced by plunging water jets is critical in the fields of nuclear and hydraulic engineering. Air entrainment is one of the key safety design parameters for nuclear systems. However, most existing studies rely on empirical correlations or curve-fitting models to estimate bubble penetration depth, and no agreed-upon calculation principle exists for varying jet conditions. To address these limitations, this research developed two advanced AI approaches: an improved YOLOv5 for segmenting air entrainment and the NSGA-III-BPNN method for predicting penetration depth. The improved YOLOv5 enables real-time segmentation and extraction of air entrainment motion and dynamics under diverse conditions, demonstrating high scalability and robustness. The penetration depth estimated using the improved YOLOv5 shows greater accuracy compared to conventional empirical correlations and is more efficient than traditional image post-processing techniques for classifying shape regimes based on dynamic air entrainment patterns. To overcome the limitations of object segmentation, which typically relies on video or image data, the NSGA-III-BPNN method predicts maximum penetration depths with greater accuracy than YOLOv5, offering a more effective prediction model for air entrainment penetration depth. By leveraging advanced AI techniques, the research not only provides valuable segmentation data for refining computational fluid dynamics (CFD) modeling but also paves the way for significant advancements in both nuclear and hydraulic engineering.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Tanaka, Satoshi*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Iwata, Ayako*; Aoki, Yuto; Aoki, Kazuhisa; Yanagisawa, Kenichi*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (70), p.3 - 22, 2024/09
Inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), there are many locations with high radiation levels due to contamination by radioactive materials that leaked from the reactor. These pose a significant obstacle to the smooth progress of decommissioning work. To help solve this issue, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), under a subsidy from the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry's decommissioning and contaminated water management project, is conducting research and development on digital technologies to improve the radiation environment inside the decommissioning site. This project, titled "Development of Technology to Improve the Environment Inside Reactor Buildings (Enhancing Digital Technology for Environment and Source Distribution to Reduce Radiation Exposure)," began in April of FY 2023. In this project, the aim is to develop three interconnected systems: FrontEnd, Pro, and BackEnd. The FrontEnd system, based on the previously developed 3D-ADRES-Indoor (prototype) from FY 2021-2022, will be upgraded to a high-speed digital twin technology usable on-site. The Pro system will carry out detailed analysis in rooms such as the new office building at 1F, while the BackEnd system will serve as a database to centrally manage the collected and analyzed data. This report focuses on the FrontEnd system, which will be used on-site. After point cloud measurement, the system will quickly create a 3D mesh model, estimate the radiation source from dose rate measurements, and refine the position and intensity of the estimated source using recalculation techniques (re-observation instructions and re-estimation). The results of verification tests conducted on Unit 5 are also presented. Furthermore, the report briefly discusses the future research and development plans for this project.
 C-stainless steel using the Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS) Method
C-stainless steel using the Moving Particle Semi-Implicit (MPS) MethodAhmed, Z.*; Wu, S.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Okamoto, Koji*; Sharma, A.*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 14th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics, Operation, and Safety (NTHOS-14) (Internet), 14 Pages, 2024/08
The analysis show that once eutectic reaction occurs, the boron diffuses into the stainless steel (SS) wall. Melting initiates at the B C and SS interface, with melt flow following SS cladding penetration. Also, we observed that as temperature rises, a proportional increase in the boron concentration within the melt. The updated MPS method indicated a computational capability of the eutectic reaction model used to effectively analyze control rod eutectic reactions, simulating severe accidents, and its subsequent relocation to understand the effect of B
C and SS interface, with melt flow following SS cladding penetration. Also, we observed that as temperature rises, a proportional increase in the boron concentration within the melt. The updated MPS method indicated a computational capability of the eutectic reaction model used to effectively analyze control rod eutectic reactions, simulating severe accidents, and its subsequent relocation to understand the effect of B C ingress into the core.
C ingress into the core.
 C powder and B
C powder and B C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steel
C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steelHong, Z.*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Erkan, N.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 171, p.105160_1 - 105160_13, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:91.70(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this study, it is found that the eutectic reaction between B C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B
C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B
C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
 C pellet-stainless steel under radiative heating
C pellet-stainless steel under radiative heatingAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kano, Sho*; Okamoto, Koji*
Ceramics International, 50(10), p.17665 - 17680, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:51.99(Materials Science, Ceramics)In this study, we identified two distinct failure mechanisms: the separation of stainless steel from the B C pellet, resulting in the formation of a later melting drop, and the fracture of the B
C pellet, resulting in the formation of a later melting drop, and the fracture of the B C pellet into multiple pieces, possibly due to thermal stress. The visualization technique and thermal interfacial resistance analysis precisely captured the eutectic temperature.
C pellet into multiple pieces, possibly due to thermal stress. The visualization technique and thermal interfacial resistance analysis precisely captured the eutectic temperature.
 C-SS and its relocation behavior
C-SS and its relocation behaviorAhmed, Z.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of Saudi International Conference On Nuclear Power Engineering (SCOPE2023) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2023/11
In this study, the eutectic behavior and subsequent melt structure of boron migration are observed by a quantitative and high-resolution visualization method using radiative heating. Experiments were conducted using B4C pellet and powder within SS tubes, replicating the actual control rod design in the temperature range of 1150 C to 1372
C to 1372 C to study long-duration melting and relocation behavior. The visualization technique accurately identified the time of eutectic melting onset and the related temperature, pointing out different values for the pellet and the powder cases.
C to study long-duration melting and relocation behavior. The visualization technique accurately identified the time of eutectic melting onset and the related temperature, pointing out different values for the pellet and the powder cases.
Nagai, Takayuki; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yamagishi, Hirona*; Shibata, Daisuke*; Kojima, Kazuo*; Hasegawa, Takehiko*; Sato, Seiichi*; Fukaya, Akane*; Hatakeyama, Kiyoshi*
JAEA-Research 2023-004, 45 Pages, 2023/09
The local structure of glass-forming elements and waste elements in borosilicate glasses varies with its chemical composition. In this study, simulated waste glass samples were prepared and the chemical state regarding boron (B), silicon (Si) and waste elements of iron (Fe), cesium (Cs) were estimated by using XAFS measurement in soft X-ray region. To understand the chemical stability of simulated waste glasses, XANES spectra of B K-edge, Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO
-edge were measured on the glass surface exposed to the leachate. As a result, it was found that the glass surface exposed to the leachate was changed and it was difficult to obtain a clear XANES spectrum. From the B K-edge XANES spectra on glass surfaces exposed to the leachate, an increase in three-coordination of B-O (BO ) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO
) and a decrease in four-coordination of B-O (BO ) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L
) were observed compared to the glass surfaces before immersion. The XANES spectra of Fe L , L
, L -edge, and Cs M
-edge, and Cs M , M
, M -edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na
-edge show that as the exposure time in the leachate increases, the Cs present on the glass surface dissolves into the leachate. The XANES spectra of Si K-edge were measured on simulated waste glass surfaces before immersion, and it was confirmed that the change in XANES spectra given by Na O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
O concentration had a larger effect than the waste component concentration.
Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Kim, M.; Okumura, Masahiko; Miyamura, Hiroko; Shikaze, Yoshiaki; Sato, Tomoki*; Numata, Yoshiaki*; Tobita, Yasuhiro*; Yamaguchi, Takashi; et al.
RIST News, (69), p.2 - 18, 2023/09
The contamination of radioactive materials leaked from the reactor has resulted in numerous hot spots in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F) building, posing obstacles to its decommissioning. In order to solve this problem, JAEA has conducted research and development of the digital technique for inverse estimation of radiation source distribution and countermeasures against the estimated source in virtual space for two years from 2021 based on the subsidy program "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management" performed by the funds from the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry. In this article, we introduce the results of the project and the plan of the renewal project started in April 2023. For the former project, we report the derivative method for LASSO method considering the complex structure inside the building and the character of the source and show the result of the inverse estimation using the method in the real reactor building. Moreover, we explain the platform software "3D-ADRES-Indoor" which integrates these achievements. Finally, we introduce the plan of the latter project.
Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 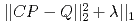 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
Li, C.-Y.; Wang, K.*; Uchibori, Akihiro; Okano, Yasushi; Pellegrini, M.*; Erkan, N.*; Takata, Takashi*; Okamoto, Koji*
Applied Sciences (Internet), 13(13), p.7705_1 - 7705_29, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:36.16(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Nanjo, Kotaro; Shiotsu, Hiroyuki; Maruyama, Yu; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(7), p.816 - 823, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Oba, Yojiro; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Kaneko, Koji; Nagai, Takayuki; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Shinohara, Takenao; Parker, J. D.*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.10071_1 - 10071_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 184, p.109686_1 - 109686_12, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:78.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)Okita, Shoichiro; Mizuta, Naoki; Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Goto, Minoru; Yoshida, Katsumi*; Nishimura, Yosuke*; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 30th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE30) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2023/05