Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Yoshikawa, Masahito; Tanaka, Shigeru; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ito, Masayoshi*
Journal of Materials Science, 42(1), p.130 - 135, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:14.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have synthesized minute SiC products from polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid organosilicon polymer, with radiation curing. Since there is a close relationship between the properties of obtained SiC products and pyrolysis condition, it is important to investigate the ceramization process of PVS in order to find out the optimum pyrolysis condition. In this paper, the ceramization process of the PVS cured by  -ray irradiation at room temperature was investigated by gas analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, density measurement, and so on. It was found that the ceramization of
-ray irradiation at room temperature was investigated by gas analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, density measurement, and so on. It was found that the ceramization of  -ray cured PVS starts above 500K, and that drastic organic-inorganic conversion occurs in the temperature range of 700-1100K. According to the results of the changes of mass and density, it was found that the volume shrinkage of PVS during the curing and pyrolysis processes is 80%. The SiC obtained by pyrolysis at 1573K showed the density of 2.50g/cm
-ray cured PVS starts above 500K, and that drastic organic-inorganic conversion occurs in the temperature range of 700-1100K. According to the results of the changes of mass and density, it was found that the volume shrinkage of PVS during the curing and pyrolysis processes is 80%. The SiC obtained by pyrolysis at 1573K showed the density of 2.50g/cm and microvickers hardness of 31.6GPa.
and microvickers hardness of 31.6GPa.
Okamura, Kiyohito*; Shimoo, Toshio*; Suzuya, Kentaro; Suzuki, Kenji*
Nihon Seramikkusu Kyokai Gakujutsu Rombunshi, 114(1330), p.445 - 454, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:56 Percentile:78.79(Materials Science, Ceramics)Several types of Si-based ceramic fibers have been prepared using an organic-to-inorganic conversion process. In this article, the preparation, microstructure, and high-temperature stability of SiC-based ceramic fibers prepared from polycarbosilane of an organosilicon polymer are reviewed. The first fiber produced was an amorphous Si-C-O fiber, next was a low-oxygen content Si-C fiber, and finally, a nearly stoichiometric SiC fiber was developed. These fibers are continuous fine fibers that have high tensile strength with high heat resistance. The pyrolytic behavior and active-passive oxidation of these fibers at high temperatures are described here. The heat resistance of these fibers increases in the order of the Si-C-O fiber, the Si-C fiber, and the SiC fiber. The high-temperature properties are dependent on the atomic arrangement and the quantity of amorphous SiC O
O and glassy carbon in the fibers.
and glassy carbon in the fibers.
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Tanaka, Shigeru; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ito, Masayoshi*
Journal of Materials Science, 39(18), p.5689 - 5694, 2004/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:30.86(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irradiation effect of  -ray on polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid organosilicon polymer, was investigated and the optimum curing condition to synthesize a minute SiC product with radiation curing was discussed. Room temperature and liquid nitrogen temperature (77K) were examined as the irradiation temperature. In both cases, the cured PVS maintaining its formed shape could be obtained by
-ray on polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid organosilicon polymer, was investigated and the optimum curing condition to synthesize a minute SiC product with radiation curing was discussed. Room temperature and liquid nitrogen temperature (77K) were examined as the irradiation temperature. In both cases, the cured PVS maintaining its formed shape could be obtained by  -ray irradiation under vacuum, and the cured PVS in solid state at room temperature was obtained by irradiation with dose of above 3-4MGy. It was found that the efficiency of crosslinking in case of the irradiation at room temperature is higher than that in case of irradiation at 77K. The PVS injected into a mold was irradiated by
-ray irradiation under vacuum, and the cured PVS in solid state at room temperature was obtained by irradiation with dose of above 3-4MGy. It was found that the efficiency of crosslinking in case of the irradiation at room temperature is higher than that in case of irradiation at 77K. The PVS injected into a mold was irradiated by  -ray with dose of 3.6MGy at room temperature under vacuum, and pyrolyzed at 1273 K in Ar gas atmosphere. As a result, minute SiC products which had similar shapes to the mold and the sizes of 30-60
-ray with dose of 3.6MGy at room temperature under vacuum, and pyrolyzed at 1273 K in Ar gas atmosphere. As a result, minute SiC products which had similar shapes to the mold and the sizes of 30-60 m were obtained.
m were obtained.
Sugimoto, Masaki; Morita, Yosuke; Tanaka, Shigeru; Seguchi, Tadao; Ito, Masayoshi*; Okamura, Kiyohito*
IAEA-SM-365/7, p.35 - 40, 2003/09
no abstracts in English
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Tanaka, Shigeru; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ito, Masayoshi*
International Symposium in Honor of Professor K. Okamura: Collected Abstracts, 3 Pages, 2003/04
Minute SiC products were synthesized from polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid organosilicon polymer, with radiation curing. The PVS was injected into molds whose patterns were square and circle with 50 m in side or diameter, and 10
m in side or diameter, and 10 m in depth. The molds containing the PVS were irradiated by
m in depth. The molds containing the PVS were irradiated by  -ray with dose of 3.6MGy at room temperature in vacuum, and heat-treated at 1273K in Ar gas atmosphere. The obtained SiC products had shapes similar to those of the molds, and the sizes of the products were about 30
-ray with dose of 3.6MGy at room temperature in vacuum, and heat-treated at 1273K in Ar gas atmosphere. The obtained SiC products had shapes similar to those of the molds, and the sizes of the products were about 30 m in side or diameter.
m in side or diameter.
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Tanaka, Shigeru; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ito, Masayoshi*
Key Engineering Materials, 247, p.129 - 132, 2003/00
Polyvinylsilane (PVS), a liquid organosilicon polymer at room temperature, is expected to be used as a precursor for SiC product with minute and complex shape. In the synthesis of the SiC product, it is necessary to cure the polymer in order to retain the shape during the pyrolysis. We have used a radiation for curing of the PVS. However, there is a problem that the PVS foams during electron beam irradiation at room temperature. In this report, the curing of PVS by  -ray irradiation was examined, and effect of irradiation temperature was studied in order to find out conditions that prevent the foaming of PVS. It was found that the PVS is cured without foaming by the
-ray irradiation was examined, and effect of irradiation temperature was studied in order to find out conditions that prevent the foaming of PVS. It was found that the PVS is cured without foaming by the  -ray irradiation in both cases of the irradiation temperature at liquid nitrogen temperature (77K) and at room temperature. From the results of measurement of gel fraction and TGA, it was found that the PVS is cured more efficiently by the irradiation at room temperature than at 77K.
-ray irradiation in both cases of the irradiation temperature at liquid nitrogen temperature (77K) and at room temperature. From the results of measurement of gel fraction and TGA, it was found that the PVS is cured more efficiently by the irradiation at room temperature than at 77K.
Sugimoto, Masaki; Idesaki, Akira; Tanaka, Shigeru; Okamura, Kiyohito*
Key Engineering Materials, 247, p.133 - 136, 2003/00
no abstracts in English
Idesaki, Akira; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Tanaka, Shigeru; Morita, Yosuke; Seguchi, Tadao; Ito, Masayoshi*
Journal of Materials Science, 36(23), p.5565 - 5569, 2001/12
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:77.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)A very fine silicon carbide (SiC) fiber with diameter of 6  m, about a half of that of a commercially available SiC fiber, was synthesized from a polymer blend of polycarbosilane (PCS) and polyvinylsilane (PVS). The fine SiC fiber was obtained by optimizing the composition and the spinning temperature of PCS-PVS polymer blends. In order to determine these optimum conditions, the relationship between temperature and melt viscosities of the polymer blends was investigated. As a result, it was found that the optimum spinning temperature range was within a temperature range where the melt viscosity is 5-10Pa
m, about a half of that of a commercially available SiC fiber, was synthesized from a polymer blend of polycarbosilane (PCS) and polyvinylsilane (PVS). The fine SiC fiber was obtained by optimizing the composition and the spinning temperature of PCS-PVS polymer blends. In order to determine these optimum conditions, the relationship between temperature and melt viscosities of the polymer blends was investigated. As a result, it was found that the optimum spinning temperature range was within a temperature range where the melt viscosity is 5-10Pa s. Moreover, by blending PVS with PCS, the spinning temperature of the polymer blends was lowered, the spinnability of polymer system was improved, and finer polymer fiber was obtained compared with PCS. The optimum content of PVS in the polymer blend was 15-20wt%.
s. Moreover, by blending PVS with PCS, the spinning temperature of the polymer blends was lowered, the spinnability of polymer system was improved, and finer polymer fiber was obtained compared with PCS. The optimum content of PVS in the polymer blend was 15-20wt%.
Sugimoto, Masaki; Tanaka, Shigeru; Ito, Masayoshi*; Okamura, Kiyohito*
High Temperature Ceramic Matrix Composites, p.357 - 361, 2001/10
no abstracts in English
Idesaki, Akira*; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Morita, Yosuke; Seguchi, Tadao; Ito, Masayoshi*
Journal of Materials Science, 36(2), p.357 - 362, 2001/01
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:53.54(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Idesaki, Akira; Sugimoto, Masaki; Tanaka, Shigeru; Morita, Yosuke; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ito, Masayoshi*
High Temperature Ceramic Matrix Composites, p.35 - 40, 2001/00
Silicon carbide (SiC) fiber, which is one of the likeliest candidates as a reinforcement fiber of ceramic matrix composites (CMCs), is synthesized from polycarbosilane (PCS). The diameter of thus SiC fibers is 10-15  m. In order to fabricate CMCs with 3-dimensional complex shapes, it is important to develop a SiC fiber with diameter of less than 10
m. In order to fabricate CMCs with 3-dimensional complex shapes, it is important to develop a SiC fiber with diameter of less than 10  m, flexibility, and high strength. In order to improve the spinnability of precursor polymer, we have blended polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid polymer at room temperature, to PCS as a spinning additive. According to relationship between temperature and melt viscosity of the polymer blend, it was found that the polymer can be melt-spun at about 490K, 110K lower than PCS (about 600K), and that the spinnability of the polymer is improved by blending PVS. Fine polymer fiber was obtained from the polymer blend, and finally, very fine SiC fiber with the average diameter of 6
m, flexibility, and high strength. In order to improve the spinnability of precursor polymer, we have blended polyvinylsilane (PVS), which is a liquid polymer at room temperature, to PCS as a spinning additive. According to relationship between temperature and melt viscosity of the polymer blend, it was found that the polymer can be melt-spun at about 490K, 110K lower than PCS (about 600K), and that the spinnability of the polymer is improved by blending PVS. Fine polymer fiber was obtained from the polymer blend, and finally, very fine SiC fiber with the average diameter of 6  m was synthesized from the PCS-PVS polymer blend.
m was synthesized from the PCS-PVS polymer blend.
Idesaki, Akira*; Narisawa, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Morita, Yosuke; Seguchi, Tadao; Ito, Masayoshi*
Proceedings of International Symposium on Prospect for Application of Radiation towards the 21st Century, p.139 - 140, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
*; *; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Sugimoto, Masaki; Seguchi, Tadao
Fine Ceramic Fibers, p.207 - 229, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Narisawa, M.*; Shimoda, M.*; Sugimoto, Masaki*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Seguchi, Tadao
Advanced Materials '93; Ceramics, Powders, Corrosion and Advanced Processing, p.827 - 830, 1994/00
no abstracts in English
Suzuya, Kentaro; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Ichikawa, Hiroshi*; Kohara, Shinji*
no journal, ,
The local atomic structure and intermediate-range order of Si-C-O fibers produced from the pyrolysis of a polycarbosilane precursor have been investigated by high-energy (61.6 keV) X-ray diffraction (HEXRD) at SPring-8 and reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling technique. In previous study (Okamura et. al., Key Eng. 352 (2007) 65), we suggest that the Si-C-O fibers basically have a network structure that consists of two tetrahedral units: SiC and SiO
and SiO from the pair distribution function analysis of HEXRD data. In the network model, 3-membered ring of SiC
from the pair distribution function analysis of HEXRD data. In the network model, 3-membered ring of SiC as that in SiC crystal and 6-membered ring of SiO
as that in SiC crystal and 6-membered ring of SiO as that in silica glass are assumed as intermediate-range order. Thus, we carried out RMC modelling analysis with the HEXRD data to study more detailed short- and intermediate-range ordering structure. The relationship between the intermediate-range ordering and these behaviors has also been discussed.
as that in silica glass are assumed as intermediate-range order. Thus, we carried out RMC modelling analysis with the HEXRD data to study more detailed short- and intermediate-range ordering structure. The relationship between the intermediate-range ordering and these behaviors has also been discussed.
Suzuya, Kentaro; Kohara, Shinji*; Okamura, Kiyohito*; Ichikawa, Hiroshi*; Suzuki, Kenji*
no journal, ,
Polymer-derived Si-C-O fibers have high tensile strength and characteristic electrical properties. The atomic scale structure of the polymer (Polycarbosilane) and the polymer-derived Si-C-O ceramics amorphous fibers has been investigated by high-energy X-ray diffraction. In addition, we applied the reverse Monte Carlo (RMC) modelling method to the diffraction data to visualize for better understanding of the complex structure. By the RMC modelling, the basic structures of the Si-C-O fibers are the three-dimensionally connected SiC
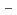
 O
O (x = 0-4) tetrahedral random-network structure which is the successive assembly of the SiC
(x = 0-4) tetrahedral random-network structure which is the successive assembly of the SiC
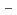
 O
O tetrahedral unit which share elements (corners and edges) and the excess carbon atoms which are interconnected and distributed widely in the network cage.
tetrahedral unit which share elements (corners and edges) and the excess carbon atoms which are interconnected and distributed widely in the network cage.