Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Zhang, Z.*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Namimoto, Takura*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Hosoda, Hirokazu*; Orimo, Satoshi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 83(5), p.053502_1 - 053502_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:60.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)X-ray line spectra ranging from 17 to 77 keV were quantitatively measured with a Laue spectrometer, composed of a cylindrically curved crystal and a detector. Either a visible CCD detector coupled with a CsI phosphor screen or an imaging plate can be chosen, depending on the signal intensities and exposure times. The absolute sensitivity of the spectrometer system was calibrated using pre-characterized laser-produced X-ray sources and radioisotopes. The integrated reflectivity for the crystal is in good agreement with predictions by an open code for X-ray diffraction. The energy transfer efficiency from incident laser beams to hot electrons, as the energy transfer agency for specific X-ray line emissions, is derived as a consequence of this work.
Zhang, Z.*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Ogura, Koichi; Yogo, Akifumi; Okano, Yasuaki*; et al.
Optics Express (Internet), 19(5), p.4560 - 4565, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:65.18(Optics)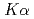 line emission from Mo and Ag plate were experimentally studied by using ultra-high intensity, clean femtosecond laser pulses. Absolutely yield of
line emission from Mo and Ag plate were experimentally studied by using ultra-high intensity, clean femtosecond laser pulses. Absolutely yield of 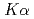 X-rays at 17 keV from Mo and 22 keV from Ag were measured as a function of the laser pulse contrast ratio and irradiation intensity. Significant enhancement of
X-rays at 17 keV from Mo and 22 keV from Ag were measured as a function of the laser pulse contrast ratio and irradiation intensity. Significant enhancement of 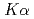 yields were obtained for both Mo and Ag with higher contrast ratios and high irradiance. The conversion efficiencies of 4.28
yields were obtained for both Mo and Ag with higher contrast ratios and high irradiance. The conversion efficiencies of 4.28  10
10 /sr for Mo and 4.84
/sr for Mo and 4.84  10
10 /sr for Ag, the highest values ever obtained, have been demonstarted with the contrast ratio of 10
/sr for Ag, the highest values ever obtained, have been demonstarted with the contrast ratio of 10 to 10
to 10 .
.
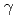 -H2AX and phosphorylated ATM focus formation in cancer cells after laser plasma X irradiation
-H2AX and phosphorylated ATM focus formation in cancer cells after laser plasma X irradiationSato, Katsutoshi; Nishikino, Masaharu; Okano, Yasuaki*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
Radiation Research, 174(4), p.436 - 445, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:47.49(Biology)Usefulness of laser-plasma X-ray pulse for medical and radiation biological studies was investigated and compared with that of conventional sources such as those obtained from a linear accelerator. A cell irradiation system was developed which uses Copper-K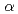 (8 keV) lines from an ultra-short high intensity laser to produce plasma. The absorbed dose of the 8 keV laser-plasma X-ray pulse was accurately estimated with Gafchromic EBT film. When the cells were irradiated with approximately 2 Gy of laser plasma X-ray, the circular regions on
(8 keV) lines from an ultra-short high intensity laser to produce plasma. The absorbed dose of the 8 keV laser-plasma X-ray pulse was accurately estimated with Gafchromic EBT film. When the cells were irradiated with approximately 2 Gy of laser plasma X-ray, the circular regions on 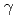 -H2AX positive cells could be clearly identified. Moreover, the number of
-H2AX positive cells could be clearly identified. Moreover, the number of 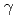 -H2AX and phosphorylated ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) foci induced by 8 keV laser plasma X-ray were comparable to those induced by 4MV X-ray. These results indicate that the laser plasma X-ray source can be useful for radiation biological studies.
-H2AX and phosphorylated ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) foci induced by 8 keV laser plasma X-ray were comparable to those induced by 4MV X-ray. These results indicate that the laser plasma X-ray source can be useful for radiation biological studies.
Zhang, Z.*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sagisaka, Akito; Orimo, Satoshi; Ogura, Koichi; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi; Okano, Yasuaki*; et al.
Reza Kenkyu, 38(9), p.698 - 701, 2010/09
Monochromatic X-ray generation from Cu plates was experimentally studied by using a high contrast femtosecond laser pulse. Absolute yield of Ka line at 8 keV was measured as a function of laser pulse contrast ration and irradiation intensity. The conversion efficiency of 8  10
10 /sr, the highest value ever obtained, has been demonstrated at 5.5
/sr, the highest value ever obtained, has been demonstrated at 5.5  10
10 W/cm
W/cm with a contrast ratio of 10
with a contrast ratio of 10 .
.
 X-ray probe in radiation biology
X-ray probe in radiation biologyNishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 81(2), p.026107_1 - 026107_3, 2010/02
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:66.38(Instruments & Instrumentation)An X-ray generation and exposure system dedicated for radiation biology is developed. An X-ray pulse of 8.0 keV in energy as short as 1 ps is generated with a fs-laser pulse, and sample cells are irradiated through a specially designed cell dish with a silicon nitride membrane. DNA double-strand breaks in a nucleus of a human caner cell are caused by X-ray irradiation, and similar DNA breaks are obtained to those with the conventional X-ray source. This result demonstrates feasibility of radiobiological study with a single burst of X-rays shining on a single cell specimen.
Ito, Toshimichi; Kinoshita, Masataka*; Saito, Saneatsu*; Machiyama, Hideaki*; Shima, Shigeki*; Gasa, Shinichi*; Togawa, Orihiko; Okano, Masaharu*
JAERI-Research 2005-028, 121 Pages, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
 ray measurement by NaI(Tl) scintillation spectrometers installed on manned submersibles, ROV and sea bottom long term observatory
ray measurement by NaI(Tl) scintillation spectrometers installed on manned submersibles, ROV and sea bottom long term observatoryHattori, Mutsuo*; Okano, Masaharu*; Togawa, Orihiko
Proceedings of 2000 International Symposium on Underwater Technology, p.212 - 217, 2000/05
no abstracts in English
Sato, Katsutoshi*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Okano, Yasuaki*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishikino, Masaharu; Okano, Yasuaki*; Sato, Katsutoshi*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
Recently, high energy, monochromatic X-rays emanating from laser-produced plasma (LPP) are attracting much attention as a new radiation source indispensable for high energy density physics, bioscience, and material sciences. Aiming at these applications, we have been improving performances of Ka lines emitted from and soft X-ray lasers. The monochromaticity is particularly important when X-rays are handled with a narrow-band optics or used to selectively excite a specific material involved in matters. In addition, time-duration of such sources is typically an order of pico-second, and it could be comparable or even shorter than recovery time of radiatively-damaged biological cell, so that the LPP source can be a new source for investigating the mechanisms of irradiation survival and death of biological cells. We propose to develop an ultrashort, intense X-ray microbeam system to study the radiobiological effect and the bystander effect.
Nishiyama, Tomokazu; Okano, Fuminori; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Sasaki, Noboru*; Meguro, Masashi*; Tajika, Masaharu*; Sato, Yoji; Sato, Masayasu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okano, Yasuaki*; Nishikino, Masaharu; Nakahara, Shogo*; Tokita, Shigeki*; Masuno, Shinichiro*; Hashida, Masaki*; Sakabe, Shuji*; Nakano, Hidetoshi*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The generation of monoenergetic hard X-rays more than 10 keV has attracted much attention for X-ray imaging in the field of high density physics and biomedical applications. Our group is currently developing an X-ray microbeam system to study radiobiological effects of cells as fundamental study of radiation therapy. In such applications, improvement of conversion efficiency (CE) from the driving laser to X-rays is an important issue and some approaches for efficient X-ray generation up to several keV have been proposed so far using low density, surface-structured targets, such as porous metals, velvet targets, and carbon nanotubes (CNTs), with the concepts of improvement of the laser absorption efficiency. In this work, we investigated the yields of K-alpha emission from bare and aligned CNT-array coated metal targets to take baseline data aiming to improve the CE in hard X-ray region (multi-keV to tens of keV) by adapting such kind of method.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Ishino, Masahiko; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Okano, Yasuaki*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
We have started to develop a laser plasma X-ray microbeam irradiation system, and demonstrated a preliminary study of the cell survival and  -H2AX focus formation in the culture cells irradiated with laser-produced plasma X-ray.
-H2AX focus formation in the culture cells irradiated with laser-produced plasma X-ray.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Sato, Katsutoshi; Ishino, Masahiko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kado, Masataka; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
A dedicated radiation biologyn X-ray generation and exposure system has been dedicated for radiation biology is developed. An X-ray pulse of 8.0 keV in energy X-ray pulses is generated with an fs-laser pulse were used to irradiate, and sample cells are irradiated through a custom-made culture dish with a silicon nitride membrane. The X-ray irradiation resulted in DNA double-strand breaks in thea nucleus of a culture cell are caused by X-ray irradiation that were, and similar DNA breaks are obtained to those obtained with athe conventional X-ray source, thus. This result demonstrating thees feasibility of radiobiological studiesy utilizing with a single burst of X-rays focused shining on a single cell specimens.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Ishino, Masahiko; Hasegawa, Noboru; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Sato, Katsutoshi*; Numasaki, Hodaka*; Teshima, Teruki*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*
no journal, ,
Recently, high energy, monochromatic X-rays emanating from laser-produced plasma (LPP) are attracting much attention as a new radiation source indispensable for high energy density physics, bioscience, and material sciences. Aiming at these applications, we have been improving performances of Ka lines emitted from LPP and soft X-ray lasers (XRLs). The monochromaticity is particularly important when X-rays are handled with a narrowband optics or used to selectively excite a specific material involved in matters. In addition, timeduration of such sources is typically an order of picosecond, and it could be comparable or even shorter than recovery time of radiatively-damaged biological cell, so that the LPP source can be a new source for investigating the mechanisms of irradiation survival and death of biological cells. We propose to develop an ultrashort, intense X-ray microbeam system to study the radiobiological effect and the bystander effect.
Nishikino, Masaharu; Zhang, Z.*; Nishimura, Hiroaki*; Kawachi, Tetsuya; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Sagisaka, Akito; Ogura, Koichi; Orimo, Satoshi; Okano, Yasuaki*; Oshima, Shinsuke*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishiyama, Tomokazu; Okano, Fuminori; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Sato, Yoji; Honda, Masao*; Sakasai, Akira; Sato, Masayasu; Meguro, Masashi*; Tajika, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English