Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus
-Orbital component in the Borromean nucleus  B
BYang, Z. H.*; Kubota, Yuki*; Corsi, A.*; Yoshida, Kazuki; Sun, X.-X.*; Li, J. G.*; Kimura, Masaaki*; Michel, N.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Yuan, C. X.*; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 126(8), p.082501_1 - 082501_8, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:95.90(Physics, Multidisciplinary)A quasifree ( ,
,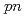 ) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus
) experiment was performed to study the structure of the Borromean nucleus  B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for
B, which had long been considered to have a neutron halo. By analyzing the momentum distributions and exclusive cross sections, we obtained the spectroscopic factors for  and
and  orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for
orbitals, and a surprisingly small percentage of 9(2)% was determined for  . Our finding of such a small
. Our finding of such a small  component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in
component and the halo features reported in prior experiments can be explained by the deformed relativistic Hartree-Bogoliubov theory in continuum, revealing a definite but not dominant neutron halo in  B. The present work gives the smallest
B. The present work gives the smallest  - or
- or  -orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of
-orbital component among known nuclei exhibiting halo features and implies that the dominant occupation of  or
or  orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
orbitals is not a prerequisite for the occurrence of a neutron halo.
Hayashi, Koichi*; Oyama, Kenji*; Happo, Naohisa*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Hosokawa, Shinya*; Harada, Masahide; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Nitani, Hiroaki*; Shishido, Toetsu*; Yubuta, Kunio*
Science Advances (Internet), 3(8), p.e1700294_1 - e1700294_7, 2017/08
Hayashi, Koichi*; Happo, Naohisa*; Hosokawa, Shinya*; Hu, W.; Matsushita, Tomohiro*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 24(9), p.093201_1 - 093201_15, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:95 Percentile:61.12(Physics, Condensed Matter)Ando, Masanori; Tezuka, Taiji*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Okawa, Tomohiro*; Enuma, Yasuhiro*; Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki
Proceedings of 2011 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2011) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/07
Ando, Masanori; Tezuka, Taiji*; Nakamura, Toshio*; Okawa, Tomohiro*; Enuma, Yasuhiro*; Kawasaki, Nobuchika; Tsukimori, Kazuyuki
Proceedings of 2011 ASME Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2011) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/07
Sako, Hiroyuki; Ueno, Akira; Okawa, Tomohiro*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Ikegami, Masanori*; Akikawa, Hisashi*
Proceedings of 24th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2008) (CD-ROM), p.260 - 262, 2009/00
In designed very high intensity proton beam of J-PARC LINAC, precise control of transverse beam dynamics is extremely important for suppression of beam loss. We present results of transverse beam matching and orbit corrections. Excellent matching performance has been achieved with mismatch factor less than 5% at beam current of 5 to 30 mA. Orbit deviations were suppressed within 1mm in horizontal and vertical directions in the whole LINAC.
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Ueno, Tomoaki; Togashi, Tomohito; Toyokawa, Ryoji; Takeda, Osamu; Watanabe, Masao; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kamiya, Junichiro; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 18(2), p.301 - 305, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.69(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Okawa, Tomohiro; Ikegami, Masanori*; Qiang, J.*; Saha, P. K.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 589(1), p.1 - 12, 2008/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.73(Instruments & Instrumentation)To realize the transverse emittance required for the ring injection, a transverse halo collimation system of the charge-exchange type has been developed for J-PARC linac. Negative hydrogen ions constituting a tail portion are charge-exchanged to protons with thin foil collimators. Then, the generated protons are separated by a bending magnet to be delivered to a beam dump. To avoid the uncontrolled beam loss, it is of practical importance to develop an accurate numerical model that has the capability of both particle tracking with space-charge effects and modeling of scattering at the charge-exchange foil. In this paper, a numerical model is developed for the collimation system using a three-dimensional particle-in-cell code, IMPACT, and a Monte-Carlo simulation tool kit, GEANT. Uncontrolled beam loss along the collimation system has been evaluated with this model, and the optimum foil thickness has been determined for the collimation system.
Morishita, Takatoshi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Asano, Hiroyuki; Ito, Takashi; Ueno, Akira; Okawa, Tomohiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ikegami, Masanori*; Naito, Fujio*; Tanaka, Hirokazu*; et al.
Proceedings of 10th International Workshop on Accelerator Alignment (IWAA 2008) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2008/02
It has been widely accepted that an accurate alignment is essential to achieve high beam quality and highly stable operation increasingly demanded in recent particle accelerators. The J-PARC linac components are finely aligned based on the precise survey network, where we have emphasized on attaining the smoothness between adjacent elements. A floor elevation of the accelerator tunnel has been periodically measured since the completion of the linac building to correct the error by the settlement. The alignment of the linac components have been finished at Sep. 2006 and the beam commissioning has been started at Nov. 2006. After a coarse adjustment of the RF phase and amplitude, nearly complete beam transmission was easily established without using steering magnet. This successful beam transport proves the validity of the alignment strategy and the accurateness of the alignment procedure.
Okawa, Tomohiro; Ao, Hiroyuki; Sako, Hiroyuki; Ueno, Akira; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ikegami, Masanori*
Proceedings of 2007 Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC '07) (Internet), p.3324 - 3326, 2007/08
In the beam commissioning of J-PARC linac, we use three simulations codes for accelerator modeling, which includes TRACE3D, XAL online model and PARMILA. TRACE3D is mainly used to determine the initial configuration for quadrupole magnets, XAL online model is mainly used for the transverse matching and orbit correction and PARMILA is mainly used to model phase-slip effects in a phase-scan tuning. We have compared the modeling with the experimental results obtained in the beam commissioning to date, where a basic agreement has been confirmed between the modeling and the actual beam behavior.
Okawa, Tomohiro; Ikegami, Masanori*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 576(2-3), p.274 - 286, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:40.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)Dispersion matching is known to be important in injecting a high-intensity beam from a linac to a circular accelerator. It is required to take both of the momentum centroid jitter and the momentum spread into consideration in the dispersion matching at injection. As the momentum centroid jitter affects the transverse beam dynamics through the dispersion without space-charge and the momentum spread that with space-charge, both of the dispersions should be optimized at the ring injection to realize an ideal matching. For this purpose, we have established a formalism to calculate the dispersion with space-charge swiftly for a bunched beam. The optimization procedure based on this formalism is demonstrated for an actual beam transport line as a practical example. Then, the validity of the procedure is confirmed with particle simulations.
Ikegami, Masanori*; Lee, S.*; Akikawa, Hisashi*; Igarashi, Zenei*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Okawa, Tomohiro; Ueno, Akira; Sako, Hiroyuki; Ao, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; et al.
KEK Proceedings 2006-15 (CD-ROM), p.347 - 349, 2007/03
We plan to start the beam commissioning of J-PARC linac with reduced energy of 181 MeV in the end of this year. Detailed commissioning strategies for the linac and the succeeding beam transport line, to which we refer as L3BT or Linac-to-3-GeV-synchrotron Beam Transport, will be presented in this talk. The emphasis will be put on the commissioning procedures for two debuncher cavities and a transverse collimator system located in L3BT, because they are key elements in determining the final beam quality at the injection point to the succeeding 3-GeV synchrotron. The unique design and features of the collimator system are also presented.
Okawa, Tomohiro; Ikegami, Masanori*
Proceedings of 4th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 32nd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.766 - 768, 2007/00
L3BT is a beam transport line from J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) linac to the succeeding 3-GeV RCS (Rapid Cycling Synchrotron). The beam commissioning of the L3BT has been started since December 2006. In this paper, we present the results of the beam commissioning of the L3BT to date.
Sako, Hiroyuki; Shen, G.; Ueno, Akira; Okawa, Tomohiro; Akikawa, Hisashi*; Ikegami, Masanori*
Proceedings of 4th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 32nd Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.598 - 600, 2007/00
Transverse matching has been performed at J-PARC LINAC for matching sections at DTL-SDTL, S01A-S03B, MEBT2-ACS, and L3BT. Each matching section consists of 4 wire scanners and upstream 4 quadrupole magnets. From r.m.s. of beam profiles measured at 4 wire scanners, transverse Twiss parameters and emittance are fitted with Newton method based on an online model. Field of quadrupole magnets with matching conditions is calculated based on the model. At beam current of 5 mA and 25 mA, matching factors of within 4% were achieved.
Okawa, Tomohiro; Ao, Hiroyuki; Ikegami, Masanori*
Proceedings of 3rd Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 31st Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan (CD-ROM), p.355 - 357, 2006/00
L3BT is a beam transport line from J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) linac to the succeeding 3-GeV RCS (Rapid Cycling Synchrotron). The construction of the L3BT has been almost finished. The beam commissioning of the L3BT will be started soon. On the other hand we have performed 3D particle simulations with IMPACT to evaluate the performance of the halo scraping and beam loss in the scraper section and beam dump line. In this paper, results of the beam simulation of the L3BT are presented. The construction status of the L3BT is also presented in brief.
Okawa, Tomohiro*; Ao, Hiroyuki; Ikegami, Masanori*
Proceedings of 2nd Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan and 30th Linear Accelerator Meeting in Japan, p.251 - 253, 2005/07
L3BT is a beam transport line from J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) linac to the succeeding 3-GeV RCS (Rapid Cycling Synchrotron). Recently, the positions of the debunchers in L3BT are revised to optimize the momentum spread at the RCS injection. In this paper, results of the beam simulation of the L3BT with the new debuncher locations are presented. The construction status of the L3BT is also presented in brief.
Okawa, Tomohiro*; Ikegami, Masanori*
Proceedings of 2005 Particle Accelerator Conference (PAC '05) (CD-ROM), p.3091 - 3093, 2005/00
L3BT is beam transportation line from the linac to the 3-GeV RCS which is the part of the accelerators for the High-Intensity Proton Accelerator Facility Project, J-PARC. In this paper, especially results of the beam simulation of the injection section of the L3BT are presented. The injection section is necessary for a successful adjustment to the transported beam to the required parameters for ring injection. The matching of beams envelopes and dispersion function for space charge dominative beams are also discussed.
Okawa, Tomohiro*; Ikegami, Masanori*
Proceedings of 9th European Particle Accelerator Conference (EPAC 2004), p.1342 - 1344, 2004/00
The accelerators for the High-Intensity Proton Accelerator Facility Project, J-PARC, consist of a 180-MeV linac, a 3-GeV RCS (Rapid Cycling Synchrotorn), and a 50-GeV MR (Main Ring). L3BT is a beam transport line from the linac to the RCS. To meet the requirement for the beam loss minimization, the L3BT does not only connect the linac to the 3GeV RCS, but also modifies the linac beam to be acceptable for the RCS. The required beam parameters at the injection point of the RCS are momentum spread 
 0.1
0.1 and transverse emittance
and transverse emittance  4
4 mm
mm mrad. To achieve these beam qualities, the L3BT should have following functions: momentum compaction, transverse halo scraping and beam diagnostics. In this paper, results of the design and beam simulation of the L3BT are presented.
mrad. To achieve these beam qualities, the L3BT should have following functions: momentum compaction, transverse halo scraping and beam diagnostics. In this paper, results of the design and beam simulation of the L3BT are presented.