Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Idesaki, Akira*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Ikeda, Takashi*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(49), p.23628 - 23633, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.61(Chemistry, Physical)Kitamura, Akihisa*; Okazaki, Sota*; Kondo, Mitsuru*; Watanabe, Takahiro; Nakanishi, Toshimichi*; Hori, Rie*; Ikeda, Masayuki*; Ichimura, Koji*; Nakagawa, Yuki*; Mori, Hideki*
Shizuoka Daigaku Chikyu Kagaku Kenkyu Hokoku, (49), p.73 - 86, 2022/07
On July 3 2021, a debris flow caused by a landslide from a landfill occurred along the Aizome River in the Izusan area of Atami City, Shizuoka. In this study, debris flow deposits and soil samples were characterized in terms of their sedimentology and geochemically analyzed.
Zhao, Y.*; Suzuki, T.*; Iimori, T.*; Kim, H.-W.*; Ahn, J. R.*; Horio, Masafumi*; Sato, Yusuke*; Fukaya, Yuki; Kanai, T.*; Okazaki, K.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 105(11), p.115304_1 - 115304_8, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yamada, Naoto*; Yamagata, Ryohei*
Proceedings of 18th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.850 - 854, 2021/10
no abstracts in English
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Nakanoya, Takamitsu; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Taguchi, Tomitsugu*; Yamada, Naoto*; Yamagata, Ryohei*
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011019_1 - 011019_7, 2021/03
The multi-turn charge-exchange H beam injection scheme with stripper foils is one of the key techniques to achieve a MW-class high power proton beam. The J-PARC RCS adopts Hybrid type Boron-doped Carbon (HBC) stripper foil, which was developed in KEK to improve the lifetime. Indeed, the RCS user operation confirmed that HBC foil has the great advantage of a longer lifetime against high beam irradiation. To examine characteristics of the HBC foils, various beam studies were performed, such as the stripping efficiency measurement and long-term observation with an H
beam injection scheme with stripper foils is one of the key techniques to achieve a MW-class high power proton beam. The J-PARC RCS adopts Hybrid type Boron-doped Carbon (HBC) stripper foil, which was developed in KEK to improve the lifetime. Indeed, the RCS user operation confirmed that HBC foil has the great advantage of a longer lifetime against high beam irradiation. To examine characteristics of the HBC foils, various beam studies were performed, such as the stripping efficiency measurement and long-term observation with an H beam in the J-PARC RCS, foil analysis using RBS, EDR and PIXE methods, and SEM and TEM observation after the ion beam irradiation in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) on National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST). Recently, the deposition apparatus for the HBC foils from the KEK Tsukuba-site was relocated to the JAEA Tokai-site, and we started fabrication of new HBC foil in 2017. (The new one fabricated in JAEA we call J-HBC foil.) And, we continue investigations in TIARA with the J-HBC foils. Furthermore, in-depth researches by changing the process parameters of the foil deposition are carried on. Recent results suggest that the amount of the boron doped in the foil is more important parameter than the ratio of the discharge amount of carbon from cathode and anode electrodes. In this presentation, we will report the details of recent analysis of the J-HBC foil.
beam in the J-PARC RCS, foil analysis using RBS, EDR and PIXE methods, and SEM and TEM observation after the ion beam irradiation in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application (TIARA) on National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST). Recently, the deposition apparatus for the HBC foils from the KEK Tsukuba-site was relocated to the JAEA Tokai-site, and we started fabrication of new HBC foil in 2017. (The new one fabricated in JAEA we call J-HBC foil.) And, we continue investigations in TIARA with the J-HBC foils. Furthermore, in-depth researches by changing the process parameters of the foil deposition are carried on. Recent results suggest that the amount of the boron doped in the foil is more important parameter than the ratio of the discharge amount of carbon from cathode and anode electrodes. In this presentation, we will report the details of recent analysis of the J-HBC foil.
Kuroda, Kenta*; Arai, Yosuke*; Rezaei, N.*; Kunisada, So*; Sakuragi, Shunsuke*; Alaei, M.*; Kinoshita, Yuto*; Bareille, C.*; Noguchi, Ryo*; Nakayama, Mitsuhiro*; et al.
Nature Communications (Internet), 11, p.2888_1 - 2888_9, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:80.96(Multidisciplinary Sciences) irradiation
irradiationOkazaki, Hiroyuki*; Kakitani, Kenta*; Kimata, Tetsuya*; Idesaki, Akira*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 152(12), p.124708_1 - 124708_5, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.42(Chemistry, Physical)Okazaki, Yasuyuki*; Hayashi, Hisashi*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Morimoto, Shingo*; Shinji, Masato*
Proceedings of 5th ISRM Young Scholars' Symposium on Rock Mechanics and International Symposium on Rock Engineering for Innovative Future (YSRM 2019 and REIF 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 6 Pages, 2019/12
In the design of tunnel support, the behavior of the rock mass around a tunnel and the stress acting on the tunnel support may be predicted using a numerical analysis. However, in such a numerical analysis, it is common to assume that each stratum comprises a homogeneous material, ignoring the heterogeneity of the geomechanical properties inherent to the rock mass. For this reason, it is not unusual for the results of the numerical analysis to differ from the actual behavior. We performed a tunnel excavation analysis considering the heterogeneity of the geomechanical properties in the rock mass to investigate the local increase in the tunnel support stress obtained in the 350 m gallery at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory. The results revealed that, in order to predict the locally increased support stress in advance, it is necessary to carry out a tunneling excavation analysis considering the heterogeneity of the geomechanical properties. It was also revealed that the scale at which the geomechanical properties fluctuate is an important factor.
Tomiyasu, Keisuke*; Ito, Naoko*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Takahashi, Yuki*; Onodera, Mitsugi*; Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Nojima, Tsutomu*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; et al.
Advanced Quantum Technologies (Internet), 1(3), p.1800057_1 - 1800057_7, 2018/12
Spin-state transition, also known as spin crossover, plays a key role in diverse systems. In theory, the boundary range between the low- and high-spin states is expected to enrich the transition and give rise to unusual physical states. However, no compound that realizes a nearly degenerate critical range as the ground state without requiring special external conditions has yet been experimentally identified. This study reports that the Sc substitution in LaCoO3 destabilizes its nonmagnetic low-spin state and generates an anomalous paramagnetic state accompanied by the enhancement of transport gap and magneto-lattice-expansion as well as the contraction of Co-O distance with the increase of electron site transfer. These phenomena are not well described by the mixture of conventional low- and high-spin states, but by their quantum superposition occurring on the verge of a spin-state transition.
Kato, Masaji*; Nara, Yoshitaka*; Okazaki, Yuki*; Kono, Masanori*; Sato, Toshinori; Sato, Tsutomu*; Takahashi, Manabu*
Materials Transactions, 59(9), p.1427 - 1432, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:38.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To ensure the safe geological disposal of radioactive waste, it is important to determine the permeability (hydraulic conductivity) of clays. The transient pulse method is suitable for low-permeability materials because it requires a relatively short time to determine their permeability. Upstream pore pressure typically increases in the measurement conducted via the transient pulse method. However, this procedure cannot be used to determine the permeability of clays due to the increase in pore pressure. Therefore, the transient pulse method has never been applied to determine clay permeability. In this study, we applied the transient pulse method to a clay sample to determine its permeability while decreasing the downstream pore pressure.
Kato, Masaji*; Nara, Yoshitaka*; Okazaki, Yuki*; Kono, Masanori*; Sato, Toshinori; Sato, Tsutomu*; Takahashi, Manabu*
Zairyo, 67(3), p.318 - 323, 2018/03
To ensure the safe geological disposal of radioactive wastes, it is important to determine the permeability of clays. The transient pulse test is suitable to apply to the low permeability materials, because it takes relatively short term to determine the permeability. Usually we increase the upstream pore pressure in the measurement with the transient pulse test. However, it is impossible to determine the permeability of clay in this procedure because of the increase of pore pressure. Therefore, the transient pulse test has never been applied to the determination of permeability of clays. In this study, we tried to apply the transient pulse test to a clay obtained in Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory to determine the permeability with decreasing the downstream pore pressure. It was clarified that the transient pulse test with decreasing downstream pore pressure is appropriate from the measurements of granite and sandstone. It was shown that the permeability of a clay was determined by the transient pulse test with decreasing the downstream pore pressure, which agreed with the permeability determined from the falling head test. The measurement time of the transient pulse test is much shorter than that of the falling head test. It is concluded that the transient pulse test is appropriate for the determination of the permeability of clays.
 -ray Spectrometry of Environmental Samples Collected in Fukushima
-ray Spectrometry of Environmental Samples Collected in FukushimaSaegusa, Jun; Yoda, Tomoyuki; Maeda, Satoshi; Okazaki, Tsutomu; Otani, Shuichi; Yamaguchi, Toshio; Kurita, Yoshiyuki; Hasumi, Atsushi; Yonezawa, Chushiro*; Takeishi, Minoru
Proceedings of 14th International Congress of the International Radiation Protection Association (IRPA-14), Vol.3 (Internet), p.1078 - 1085, 2017/11
After the nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in March 2011, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has newly set up a laboratory for radioactivity analysis in Fukushima. At the laboratory, radioactivity concentrations of environmental samples such as soil, water, dust filter, plant, etc., approximately 1,000 samples in a month, are measured with high-resolution  -ray spectrometry systems. The systems employ n-type HPGe detectors from Ortec. Since September 2012, characterization and upgrade of the systems have been performed aimed at enhancing reliability of analysis and convenience of customers. Resolving both systematic and technical issues, the laboratory has been accredited the ISO/IEC 17025 standard as a testing laboratory for radioactivity analysis.
-ray spectrometry systems. The systems employ n-type HPGe detectors from Ortec. Since September 2012, characterization and upgrade of the systems have been performed aimed at enhancing reliability of analysis and convenience of customers. Resolving both systematic and technical issues, the laboratory has been accredited the ISO/IEC 17025 standard as a testing laboratory for radioactivity analysis.
Sakasai, Kaoru; Sato, Setsuo*; Seya, Tomohiro*; Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Yamagishi, Hideshi*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Yamazaki, Dai; Maruyama, Ryuji; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 1(2), p.10_1 - 10_35, 2017/09
Neutron devices such as neutron detectors, optical devices including supermirror devices and  He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
He neutron spin filters, and choppers are successfully developed and installed at the Materials Life Science Facility (MLF) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC), Tokai, Japan. Four software components of MLF computational environment, instrument control, data acquisition, data analysis, and a database, have been developed and equipped at MLF. MLF also provides a wide variety of sample environment options including high and low temperatures, high magnetic fields, and high pressures. This paper describes the current status of neutron devices, computational and sample environments at MLF.
Okazaki, Yasuyuki*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Kumasaka, Hiroo*; Shinji, Masato*
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, F1 (Tonneru Kogaku) (Internet), 72(3), p.I_1 - I_15, 2016/00
In the rational tunnel support design, numerical analysis is powerful tool to know the estimation of the behavior before tunnel construction in the case of the special ground condition and limited similar construction. In order to evaluate the support structure quantitatively, it is necessary to understand the effect of the inhomogeneity of rock mass to the tunnel support stress in advance. In this study, tunnel excavation analysis considering the inhomogeneity of rock mass was carried out. The analysis results were compared with the stress measured in the tunnel support in the Horonobe underground research laboratory. As a result, it was revealed that the local stress measured in the tunnel support can be simulated by considering the inhomogeneity of rock mass stochastically. In addition, this study evaluated the effect of the inhomogeneity of rock mass to the tunnel support stress quantitatively by processing analysis results statistically.
Okazaki, Soichiro*; Ezure, Toshiki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kawara, Zensaku*; Yokomine, Takehiko*; Kunugi, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 10th Pacific Symposium on Flow Visualization and Image Processing (PSFVIP-10), 8 Pages, 2015/06
A visualization study is performed under suction vortex geometry in water. In the experiment, the shear-sensitive liquid crystal coating (SSLCC) is applied to grasp the distribution of wall shear stress under the suction votex flow. As the result, it was found that the peak value of wall shear stress is appeared at the center and edge of the projected area of suction pipe. The non-dimensional profile of wall shear stress obtained by suction vortex flow experiment agrees well with that of numerical simulation.
 ions for LaCo
ions for LaCo Rh
Rh O
O
Asai, Shinichiro*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Igawa, Naoki; Kakurai, Kazuhisa
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 3, p.014034_1 - 014034_6, 2014/06
We have carried out the neutron scattering measurements for a single crystal of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O in order to investigate the ferromagnetic ordering induced by Rh
in order to investigate the ferromagnetic ordering induced by Rh substitution for Co
substitution for Co of LaCoO
of LaCoO . The ordered moment is evaluated to be 0.4
. The ordered moment is evaluated to be 0.4 0.2
0.2
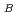 , which is consistent with the saturation magnetization of LaCo
, which is consistent with the saturation magnetization of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O . It indicates that the ferromagnetic ordering of LaCo
. It indicates that the ferromagnetic ordering of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O originates from the short-range ferromagnetic ordering disordered by Rh
originates from the short-range ferromagnetic ordering disordered by Rh ions.
ions.
 in LaCo
in LaCo Rh
Rh O
O investigated by structural phenomena
investigated by structural phenomenaAsai, Shinichiro*; Okazaki, Ryuji*; Terasaki, Ichiro*; Yasui, Yukio*; Kobayashi, Wataru*; Nakao, Akiko*; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Kumai, Reiji*; Nakao, Hironori*; Murakami, Yoichi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 82(11), p.114606_1 - 114606_6, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.01(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Neutron and synchrotron X-ray diffraction for LaCo Rh
Rh O
O have been carried out in order to investigate the structural properties related with the spin state of Co
have been carried out in order to investigate the structural properties related with the spin state of Co ions. We have found that the values of the Co(Rh)-O bond lengths in the Co(Rh)O
ions. We have found that the values of the Co(Rh)-O bond lengths in the Co(Rh)O octahedron of LaCo
octahedron of LaCo Rh
Rh O
O are nearly identical at 10 K. The lattice volume for the Rh
are nearly identical at 10 K. The lattice volume for the Rh substituted samples decreases with the thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of LaCoO
substituted samples decreases with the thermal expansion coefficient similar to that of LaCoO from room temperature, and ceases to decrease around 70 K. These experimental results favor a mixed state consisting of the high-spin state and low-spin state Co
from room temperature, and ceases to decrease around 70 K. These experimental results favor a mixed state consisting of the high-spin state and low-spin state Co ions, and suggest that the high-spin state Co
ions, and suggest that the high-spin state Co ions are thermally excited in addition to those pinned by the substituted Rh
ions are thermally excited in addition to those pinned by the substituted Rh ions.
ions.
Ashida, Takashi; Miyamoto, Kazuyuki; Okazaki, Yoshihiro*; Ito, Hideaki
JAEA-Technology 2012-047, 106 Pages, 2013/06
In the experimental fast reactor Joyo, failure of disconnecting the irradiation test subassembly MARICO-2 (Material Testing Irradiation Rig with Temperature Control) was occurred and top of the MARICO-2 test subassembly was bent onto the in-vessel storage rack. As a result of this incident, the operation area of rotating plug for the fuel exchange in Joyo is limited. The replacement of the damaged UCS and retrieving the bent MARICO-2 are required to Joyo restoration. This report describes about investigations and some tests to know the status of MARICO-2 test subassembly and the optimized detail design of retrieval device reflecting those results.
 O
O
Kambe, Takashi*; Fukada, Yukimasa*; Kano, Jun*; Nagata, Tomoko*; Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Yokoya, Takayoshi*; Wakimoto, Shuichi; Kakurai, Kazuhisa; Ikeda, Naoshi*
Physical Review Letters, 110(11), p.117602_1 - 117602_5, 2013/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:75.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Imaizumi, Kazuyuki; Saito, Takakazu; Tobita, Shigeharu; Nagai, Akinori; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Okazaki, Yoshihiro
JAEA-Technology 2012-027, 49 Pages, 2012/08
In-Vessel Observations (IVO) techniques for Sodium cooled Fast Reactors (SFRs) are important in confirming its safety and integrity. In order to secure the reliability of IVO techniques, it was necessary to demonstrate the performance under the actual reactor environment with high temperature, high radiation dose and remained sodium. During the investigation of an incident occurred in Joyo, the following observation systems were specifically developed for Joyo. And the following two observations were conducted. (1) Simple overhead observation using a standard video camera for the top of the sub-assemblies and the in-vessel storage rack (2) Narrow space observation using remote handling device equipped with radiation-resistant fiberscope for the bottom face of the upper core structure. As a result, the observations under the actual reactor environment were successfully made even in the narrow space in the reactor vessel and the results provided useful information on incident investigations and planning of restoration work.