Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Kawai, Isao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Ueno, Akira
Proceedings of 21st Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.525 - 528, 2024/10
A decade has elapsed since the radio frequency (RF)-driven negative hydrogen (H ) ion source initiated operation at J-PARC. In the 2023/2024 campaign, a single RF-driven H
) ion source initiated operation at J-PARC. In the 2023/2024 campaign, a single RF-driven H ion source has generated H
ion source has generated H beams with a beam current of 60 mA, which enabled the J-PARC linac to inject them into the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) with a beam current of 50 mA. The continuous operation time of the ion source reached exceeding 4,900 hours in this campaign, which signifies a notable enhancement in operational longevity in comparison to the preceding longest campaign in 2022/2023, which spanned 4,412 hours. This paper provides the operational status of the RF-driven H
beams with a beam current of 60 mA, which enabled the J-PARC linac to inject them into the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) with a beam current of 50 mA. The continuous operation time of the ion source reached exceeding 4,900 hours in this campaign, which signifies a notable enhancement in operational longevity in comparison to the preceding longest campaign in 2022/2023, which spanned 4,412 hours. This paper provides the operational status of the RF-driven H ion source during this campaign and the current status of the J-PARC-made antenna, which is currently under development.
ion source during this campaign and the current status of the J-PARC-made antenna, which is currently under development.
 ion source
ion sourceShibata, Takanori*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ueno, Akira; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nammo, Kesao*; Kawai, Isao*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Kasokuki, 21(2), p.94 - 100, 2024/07
In the recent J-PARC user operation from Nov. 10th, 2022 to Jun. 22nd, 2023, continuous operation of 4,412 hours with hydrogen negative ion (H ion) beam current up to 60 mA was achieved by J-PARC radio frequency (RF) H
ion) beam current up to 60 mA was achieved by J-PARC radio frequency (RF) H ion source. This was also the first time to supply H
ion source. This was also the first time to supply H ion beam to the linac in the yearly J-PARC user operation term by a single ion source (w/o ion source exchange). To satisfy the requirements of the further upgrade in J-PARC, a soundness evaluation of the present ion source components has been performed. Furthermore, the RF ion source with a newly manufactured RF antenna coil has been under development.
ion beam to the linac in the yearly J-PARC user operation term by a single ion source (w/o ion source exchange). To satisfy the requirements of the further upgrade in J-PARC, a soundness evaluation of the present ion source components has been performed. Furthermore, the RF ion source with a newly manufactured RF antenna coil has been under development.
Shibata, Takanori*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nakano, Haruhisa*; Hoshino, Kazuo*; Miyamoto, Kenji*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Kawai, Isao*; Oguri, Hidetomo; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2743, p.012007_1 - 012007_5, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Particles & Fields)Oscillation of the negative hydrogen ion (H ) beam phase space in Radio Frequency (RF) ion source is investigated by a simple 3D Particle-In-Cell (PIC) model which takes into account the transport processes of electron, proton and H
) beam phase space in Radio Frequency (RF) ion source is investigated by a simple 3D Particle-In-Cell (PIC) model which takes into account the transport processes of electron, proton and H in the extraction region. The calculation domain is in vicinity of the single beam aperture in J-PARC ion source configuration. In order to understand relation between the plasma density oscillation and the extracted H
in the extraction region. The calculation domain is in vicinity of the single beam aperture in J-PARC ion source configuration. In order to understand relation between the plasma density oscillation and the extracted H beam characteristics, the input electron and proton fluxes from the driver region are varied parametrically with the 1st and the 2nd harmonics of the J-PARC RF frequency (2 or 4 MHz). The numerical results give an idea to the main physical processes between the oscillations of the plasma parameters and the extracted H
beam characteristics, the input electron and proton fluxes from the driver region are varied parametrically with the 1st and the 2nd harmonics of the J-PARC RF frequency (2 or 4 MHz). The numerical results give an idea to the main physical processes between the oscillations of the plasma parameters and the extracted H ion trajectories in the different RF phases. Countermeasures to reduce the oscillation mechanisms are also discussed in the presentation.
ion trajectories in the different RF phases. Countermeasures to reduce the oscillation mechanisms are also discussed in the presentation.
 ion source
ion sourceShinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Nammo, Kesao*; Kawai, Isao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2743, p.012023_1 - 012023_5, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have been conducting the test of a new J-PARC-made internal antenna for the J-PARC RF-driven cesiated H ion source. After the development of the first J-PARC-made antenna, the composition of the porcelain enamel coating of the antenna was changed because we were afraid of the outgassing of the impurities from the previous antenna coating. During the test of high-density plasma production by the new antenna, we monitored the outgassing characteristics of the new antenna by measuring mass spectrometry and optical spectrum analysis. It is confirmed that no remarkable impurities were emitted from the new antenna. We also carried out the H
ion source. After the development of the first J-PARC-made antenna, the composition of the porcelain enamel coating of the antenna was changed because we were afraid of the outgassing of the impurities from the previous antenna coating. During the test of high-density plasma production by the new antenna, we monitored the outgassing characteristics of the new antenna by measuring mass spectrometry and optical spectrum analysis. It is confirmed that no remarkable impurities were emitted from the new antenna. We also carried out the H beam extraction and measured the H
beam extraction and measured the H beam characteristics by using the new antenna. It is found that the emittances of the H
beam characteristics by using the new antenna. It is found that the emittances of the H beam extracted from the J-PARC RF-driven cesiated H
beam extracted from the J-PARC RF-driven cesiated H ion source by using the new antenna were similar to those in the case by using the SNS-made antenna. To accelerate the endurance test of the new antenna, we applied the antenna for the high-density plasma production to the 5% duty factor (1 ms pulse width with 50 Hz repetition rate) with the 2 MHz RF input power of approximately 60 kW, whose values were much higher than those in the J-PARC nominal operation; 0.8 ms pulse width with 25 Hz repetition rate (the duty factor of 2%) with the RF input power of approximately 30 kW. This presentation shows the results of the characteristics of the new J-PARC-made antenna and discusses the feasibility of the new antenna for use in the J-PARC accelerator operation.
ion source by using the new antenna were similar to those in the case by using the SNS-made antenna. To accelerate the endurance test of the new antenna, we applied the antenna for the high-density plasma production to the 5% duty factor (1 ms pulse width with 50 Hz repetition rate) with the 2 MHz RF input power of approximately 60 kW, whose values were much higher than those in the J-PARC nominal operation; 0.8 ms pulse width with 25 Hz repetition rate (the duty factor of 2%) with the RF input power of approximately 30 kW. This presentation shows the results of the characteristics of the new J-PARC-made antenna and discusses the feasibility of the new antenna for use in the J-PARC accelerator operation.
Shibata, Takanori*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nammo, Kesao*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Ishida, Masaki*; Wada, Motoi*
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 19(1), p.C01009_1 - C01009_8, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)From Nov. 2020 to Apr. 2021, the continuous ion source operation for 3,651 hours (5 months) was achieved. As the lifetime of the RF ion source is mainly limited by failure on the enamel coating of the RF antenna, detailed evaluation of the antenna surface is required to ensure feasibility of the further extension of the operation time. In the present study, surface discoloration on the RF antenna coil observed after the 5 months operation is investigated by application of digital microscope and SEM/EDS analyses. The material mapping and the line spectrum obtained by the EDS analysis show that depositions of the sputtered source chamber wall materials and the injected cesium on to the enamel coating are the most possible candidate for the discoloration. The dimension measurements of the RF antenna thickness before and after the long-term operation support the idea that the discoloration is due to the deposited materials and hence insulation of the RF antenna coil by enamel coating is maintained. The emittance measurement after the operation also shows that the RF plasma and the beam formations are not affected by the deposition on the antenna.
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Kawai, Isao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Ueno, Akira
Proceedings of 20th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.928 - 931, 2023/11
J-PARC initiated the operation of the high-intensity rf-driven negative hydrogen (H ) ion source in 2014 autumn. The ion source produces the H
) ion source in 2014 autumn. The ion source produces the H beam with the beam current of 60 mA and the beam energy of 50 keV in order to inject the H
beam with the beam current of 60 mA and the beam energy of 50 keV in order to inject the H beam into the 3 GeV RCS with the beam current of 50 mA and the beam energy of 400 MeV from the J-PARC linac. We have achieved the longest continuous operation time of 4001 hours in the previous (2021/2022) campaign. The 2022/2023 campaign was the first time that the continuous operation of the H
beam into the 3 GeV RCS with the beam current of 50 mA and the beam energy of 400 MeV from the J-PARC linac. We have achieved the longest continuous operation time of 4001 hours in the previous (2021/2022) campaign. The 2022/2023 campaign was the first time that the continuous operation of the H ion source without any exchanges of the ion source until the end of the campaign was examined. We present the operation status of the J-PARC H
ion source without any exchanges of the ion source until the end of the campaign was examined. We present the operation status of the J-PARC H ion source in this campaign as well as the status of the J-PARC-made internal antenna test.
ion source in this campaign as well as the status of the J-PARC-made internal antenna test.
 ion source
ion sourceUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Journal of Instrumentation (Internet), 18(8), p.C08002_1 - C08002_8, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:27.04(Instruments & Instrumentation)On 2020, the stable operation of the J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H ion source (IS) with a 65 keV 110 mA beam, whose emittances were suitable for the radio-frequency quadrupole LINAC, was reported. In the J-PARC IS operation, the stable plasma production with a 50 kW 2 MHz RF power for more than 3 months, an RF power efficiency higher than 2.6 mA/kW and the possibility of the space charge limited beam intensity pulling up by increasing the extraction and acceleration voltages (V
ion source (IS) with a 65 keV 110 mA beam, whose emittances were suitable for the radio-frequency quadrupole LINAC, was reported. In the J-PARC IS operation, the stable plasma production with a 50 kW 2 MHz RF power for more than 3 months, an RF power efficiency higher than 2.6 mA/kW and the possibility of the space charge limited beam intensity pulling up by increasing the extraction and acceleration voltages (V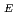 and V
and V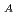 ) were proven. The stable operation results with a 69.9 keV 120 mA beam realized by increasing the withstand voltage around the 2 MHz RF matching circuit are presented. The 107.8 mA of the beam was measured inside the emittances used for the RFQ design.
) were proven. The stable operation results with a 69.9 keV 120 mA beam realized by increasing the withstand voltage around the 2 MHz RF matching circuit are presented. The 107.8 mA of the beam was measured inside the emittances used for the RFQ design.
 ion source
ion sourceShinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.675 - 679, 2023/01
In J-PARC, we have been conducting the test of a J-PARC-made internal antenna in order to establish the production method and understand the beam characteristics of the antenna. At this time, we investigated the outgas characteristics during the production of a high-density plasma by using the J-PARC-made antenna. It is confirmed that no remarkable impurities are emitted from the antenna by a residual gas analysis using a quadrupole mass analyzer installed downstream the ion source and a spectroscopic analysis of the plasma in the ion source. It is found that the emittances of the H beam extracted from the J-PARC radio-frequency H
beam extracted from the J-PARC radio-frequency H ion source by using the antenna was similar as those in case by using SNS antenna.
ion source by using the antenna was similar as those in case by using SNS antenna.
Shibata, Takanori*; Ishida, Masaki*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.863 - 867, 2023/01
Continuous operation duration of the J-PARC Radio Frequency (RF) ion source has been extended step by step these years for the goal to supply stable beam during the entire period of J-PARC user operation (around 7 months) each year. A 3651 hours (5 months) continuous ion source operation has been achieved from Nov. 2020 to Apr. 2021. As the lifetime of the ion source is mainly limited by failure on the RF antenna coil, detailed evaluation of the antenna surface condition is required to ensure the feasibility of the further extension of the operation time. In the present study, dimension measurements and SEM/EDS analyses were applied to understand the surface discoloration of the RF antenna. The discoloration after the long-term continuous operation is due to deposition of injected cesium (for H surface production process) and of stainless used steel (Fe, Cr, Ni) from the ion source components sputtered by plasma. The results show that the enamel coating of the RF antenna has not worn out in the long-term continuous operation for several months and, hence, extension of the ion source continuous operation duration can be extended.
surface production process) and of stainless used steel (Fe, Cr, Ni) from the ion source components sputtered by plasma. The results show that the enamel coating of the RF antenna has not worn out in the long-term continuous operation for several months and, hence, extension of the ion source continuous operation duration can be extended.
Shibata, Takanori*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2244, p.012041_1 - 012041_5, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:55.69(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In the J-PARC user operation from Nov. 2020 - Apr. 2021, continuous operation of J-PARC Radio Frequency (RF) negative hydrogen ion (H ) source up to 3,651 hours (5 months) has been achieved. The ion source was operated with the output H
) source up to 3,651 hours (5 months) has been achieved. The ion source was operated with the output H current of 60 mA, the duty factor (for plasma generation) 2% and the input RF power up to 30 kW. After the operation, phase space diagrams at the Radio Frequency Quadrupole (RFQ) entrance were measured by the emittance monitor at the ion source test stand (IS-TS) under the same operation condition as in the J-PARC Linac. Comparison of the phase spaces and the beam emittances between the ion sources in the present and the previous operations shows slight difference. From the direct observation of the antenna coil, no exhaustion or the decrease in the thickness of the enamel coating of the coil have been confirmed. The results indicate the possibility of the next goal of the long-run up to 7 months, which is the same as the full duration of the J-PARC user operation in 1 year.
current of 60 mA, the duty factor (for plasma generation) 2% and the input RF power up to 30 kW. After the operation, phase space diagrams at the Radio Frequency Quadrupole (RFQ) entrance were measured by the emittance monitor at the ion source test stand (IS-TS) under the same operation condition as in the J-PARC Linac. Comparison of the phase spaces and the beam emittances between the ion sources in the present and the previous operations shows slight difference. From the direct observation of the antenna coil, no exhaustion or the decrease in the thickness of the enamel coating of the coil have been confirmed. The results indicate the possibility of the next goal of the long-run up to 7 months, which is the same as the full duration of the J-PARC user operation in 1 year.
 ion source with new parts exposed to plasma
ion source with new parts exposed to plasmaUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Oguri, Hidetomo
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2244, p.012029_1 - 012029_5, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H ion source is stably suppling about 58 mA beam with a duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 ms
ion source is stably suppling about 58 mA beam with a duty factor of 1.25 % (0.5 ms 25 Hz) for the J-PARC LINAC 50 mA operations. For them, only three plasma chambers (PCHs) of #7, #8 and #9PCHs among ten PCHs have been used since the transverse emittances are more superior than others for unknown reasons. However, the emittances were enlarged by 16 % with the #7PCH, in which the plasma electrode (PE) temperature control plate (PETCP) was replaced to brand-new one to solve the air leak at the VCR vacuum fitting. The impurities from the new parts exposed to the plasma seemed to cause the degradation. The beam with almost the best emittances was reproduced by #4PCH with a new PETCP, in which sapphire tubes were used instead of the 99.7 % alumina ceramics tubes, after a new 2-MHz RF power scanning impurities reduction conditioning for 48 hours.
25 Hz) for the J-PARC LINAC 50 mA operations. For them, only three plasma chambers (PCHs) of #7, #8 and #9PCHs among ten PCHs have been used since the transverse emittances are more superior than others for unknown reasons. However, the emittances were enlarged by 16 % with the #7PCH, in which the plasma electrode (PE) temperature control plate (PETCP) was replaced to brand-new one to solve the air leak at the VCR vacuum fitting. The impurities from the new parts exposed to the plasma seemed to cause the degradation. The beam with almost the best emittances was reproduced by #4PCH with a new PETCP, in which sapphire tubes were used instead of the 99.7 % alumina ceramics tubes, after a new 2-MHz RF power scanning impurities reduction conditioning for 48 hours.
Shibata, Takanori*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Wada, Motoi*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Nammo, Kesao*
AIP Conference Proceedings 2373, p.050002_1 - 050002_9, 2021/08
Oscillation of emittance and Twiss parameters in the negative ion beam from the J-PARC 2-MHz RF ion source is measured by applications of a double-slit emittance monitor located at the RFQ (Radio Frequency Quadrupole) entrance. The emittance monitor is equipped with a newly-developed 60 MS/s data acquisition system, so that beam current oscillation in a few MHz can be observed with enough time resolution. From the measurement, it is shown that the beam phase space consists of (1) a DC component in the beam core, (2) a 2-MHz oscillating component which takes place both in the beam core and the halo and (3) a doubled RF frequency (4 MHz) oscillation which slightly exists in the beam halo. The major component is the 2-MHz component, which resultantly decides the beam emittance oscillation frequency. A typical value of the beam emittance in the present experiment is 0.34  mm-mrad, while the amplitude of the 2 MHz oscillation is around 0.04
mm-mrad, while the amplitude of the 2 MHz oscillation is around 0.04  mm-mrad. The results indicate that the high-frequency oscillation component occupying about ten-percent of the beam from the RF source travels a few meters passing through a magnetic lens focusing system.
mm-mrad. The results indicate that the high-frequency oscillation component occupying about ten-percent of the beam from the RF source travels a few meters passing through a magnetic lens focusing system.
 ion source
ion sourceUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2373, p.040002_1 - 040002_8, 2021/07
On 2018, the stable operation of the J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H ion source (IS) with a 62 keV 100 mA beam, whose emittances were suitable for the radio-frequency quadrupole LINAC (RFQ), was reported. In the J-PARC IS operation, the stable plasma production with a 50 kW 2 MHz RF power for more than 3 months, an RF power efficiency higher than 2.4 mA/kW and the possibility of the space charge limited beam intensity pulling up by increasing the extraction and acceleration voltages were proven. On the other hand, the withstand voltage for the stable operation with an RF plasma production of the present 2 MHz matching circuit and the high voltage power supply was measured as about 66 kV. In the operation with the presently highest beam energy of 65 keV, a 110 mA beam with emittances suitable for the RFQ was stably produced. Since 102.5 mA of the beam was measured inside the emittances used for the RFQ design, the next generation 100 mA LINAC will be possible with the IS.
ion source (IS) with a 62 keV 100 mA beam, whose emittances were suitable for the radio-frequency quadrupole LINAC (RFQ), was reported. In the J-PARC IS operation, the stable plasma production with a 50 kW 2 MHz RF power for more than 3 months, an RF power efficiency higher than 2.4 mA/kW and the possibility of the space charge limited beam intensity pulling up by increasing the extraction and acceleration voltages were proven. On the other hand, the withstand voltage for the stable operation with an RF plasma production of the present 2 MHz matching circuit and the high voltage power supply was measured as about 66 kV. In the operation with the presently highest beam energy of 65 keV, a 110 mA beam with emittances suitable for the RFQ was stably produced. Since 102.5 mA of the beam was measured inside the emittances used for the RFQ design, the next generation 100 mA LINAC will be possible with the IS.
Shibata, Takanori*; Sugimura, Takashi*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Sato, Masaharu*; Naito, Fujio*; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Hasegawa, Kazuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011009_1 - 011009_6, 2021/03
Upgrade of beam current in the Linac of Ibaraki Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (iBNCT) is one of the most important requirements to realize clinical trial. By 2018, the measurement of the produced neutrons characteristics and the neutron irradiation experiment for living cells have been done by producing 8-MeV proton beam current at the beryllium target with average current up to 2 mA. In order to satisfy the original clinical trial conditions, 5 mA average beam current is required at the target. For this goal, peak beam current extracted from the ion source should be increased to 60 mA from the present 30 mA with duty factor up to more than 10% (pulse width up to 1 ms and repetition rate up to more than 100 Hz). Stability of the peak current in the macro pulse is also important for the clinical application.
 beam with orifice in J-PARC front-end
beam with orifice in J-PARC front-endShibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Nammo, Kesao*; Liu, Y.*; Otani, Masashi*; Naito, Fujio*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Okabe, Kota; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011010_1 - 011010_6, 2021/03
Together with the intensity upgrade in J-PARC Linac Front-End, improvement of RFQ transmission ratio is an important task. This RFQ transmission ratio depends strongly upon the solenoid current settings in the low energy beam transport line (LEBT). In the present study, high beam current cases (72 mA and 88 mA H beam current in LEBT) are investigated at a test-stand. Phase space distributions of the H
beam current in LEBT) are investigated at a test-stand. Phase space distributions of the H beam particles at the RFQ entrance are measured and compared with numerical results by Particle-In-Cell simulation. As a result, it has been clarified that a 15 mm
beam particles at the RFQ entrance are measured and compared with numerical results by Particle-In-Cell simulation. As a result, it has been clarified that a 15 mm  orifice for differential pumping of H
orifice for differential pumping of H gas coming from the ion source plays a role as a collimator in these beam conditions. This leads to change the beam emittance and Twiss parameters at the RFQ entrance. Especially in the condition with the beam current up to 88 mA in LEBT, the beam collimation contributes to optimize the phase space distribution to the RFQ acceptance with relatively low solenoid current settings. As a higher solenoid current setting would be necessary to suppress the beam expansion due to high space charge effect, these results suggest that current-saving of the solenoids can be possible even in the higher beam intensity operations.
gas coming from the ion source plays a role as a collimator in these beam conditions. This leads to change the beam emittance and Twiss parameters at the RFQ entrance. Especially in the condition with the beam current up to 88 mA in LEBT, the beam collimation contributes to optimize the phase space distribution to the RFQ acceptance with relatively low solenoid current settings. As a higher solenoid current setting would be necessary to suppress the beam expansion due to high space charge effect, these results suggest that current-saving of the solenoids can be possible even in the higher beam intensity operations.
 ion source
ion sourceOguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Shibata, Takanori*; Nammo, Kesao*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011008_1 - 011008_7, 2021/03
A cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion source was initiated to operate in September, 2014 in response to the need for upgrading J-PARC's linac beam current. The ion source mainly comprises a stainless-steel plasma chamber, a beam extractor and a large vacuum chamber equipped with two turbo molecular pumps, each having the pumping speed of 1500 L/s, for differential pumping. The user operation was started with the beam current of 33 mA from the ion source. We gradually increased both beam current and continuous operation time of the ion source. In July, 2018 (Run#79), approximately 2,200 hours operation was achieved with the typical beam current, pulse length and repetition rate of 47 mA, 300  s and 25 Hz, respectively. Since October, 2018 (Run#80), the ion source has been delivering a nominal beam current of approximately 60 mA.
s and 25 Hz, respectively. Since October, 2018 (Run#80), the ion source has been delivering a nominal beam current of approximately 60 mA.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:69.74(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
 ion source
ion sourceOkoshi, Kiyonori; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Nammo, Kesao*; Shibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Ueno, Akira; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.554 - 557, 2019/07
In September 2014, a cesiated RF-driven negative hydrogen ion (H ) source was initiated to operate at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The extracted H
) source was initiated to operate at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). The extracted H beam current and the continuous operation time of the ion source have been improved upon their own records. In the RUN#79 (from April to July 2018), the ion source delivered the H
beam current and the continuous operation time of the ion source have been improved upon their own records. In the RUN#79 (from April to July 2018), the ion source delivered the H beam current of 47 mA to the post-accelerators for 2,201 hours continuously. In October 2018, the beam current from the ion source was increased to 60 mA in order to inject the beam current of 50 mA into the 3 GeV synchrotron. In the RUN#80 (from October to December 2018), the continuous operation time of 1,791 hours was achieved. For the past year, we had the antenna failures twice during the operation, and needed to replace to a spare ion source. We have been developed the J-PARC-made antenna by using a test-stand. Recent experiment result showed the continuous operation time of 2,083 hours was achieved with the J-PARC-made antenna.
beam current of 47 mA to the post-accelerators for 2,201 hours continuously. In October 2018, the beam current from the ion source was increased to 60 mA in order to inject the beam current of 50 mA into the 3 GeV synchrotron. In the RUN#80 (from October to December 2018), the continuous operation time of 1,791 hours was achieved. For the past year, we had the antenna failures twice during the operation, and needed to replace to a spare ion source. We have been developed the J-PARC-made antenna by using a test-stand. Recent experiment result showed the continuous operation time of 2,083 hours was achieved with the J-PARC-made antenna.
 beam dynamics in J-PARC LEBT
beam dynamics in J-PARC LEBTShibata, Takanori*; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Liu, Y.*; Miura, Akihiko; Naito, Fujio*; Nammo, Kesao*; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Otani, Masashi*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 29th International Linear Accelerator Conference (LINAC 2018) (Internet), p.519 - 521, 2019/01
Transport process of negative hydrogen ion (H ) in LEBT (Low Energy Beam Transport) is investigated by comparison of experimental and numerical results. A three dimensional Particle-In-Cell (PIC) particle transport model has been developed in order to take into account (i) axial magnetic field by two solenoids in J-PARC LEBT and (ii) radial electric field by space charge (SC) effect. Ratio of H
) in LEBT (Low Energy Beam Transport) is investigated by comparison of experimental and numerical results. A three dimensional Particle-In-Cell (PIC) particle transport model has been developed in order to take into account (i) axial magnetic field by two solenoids in J-PARC LEBT and (ii) radial electric field by space charge (SC) effect. Ratio of H beam particles inside the RFQ (Radio Frequency Quadrupole) acceptance to the total particles at the RFQ entrance is calculated for different current conditions in LEBT solenoid 1 and 2. The results are compared with RFQ transmission rate measured in the J-PARC linac commissioning. The double peak of RFQ transmission rate to the solenoid applied current seen in the measurement is explained by the calculation results. The results indicate that presence of the LEBT orifice for differential pumping plays a role as a collimator to reduce emittance at RFQ entrance.
beam particles inside the RFQ (Radio Frequency Quadrupole) acceptance to the total particles at the RFQ entrance is calculated for different current conditions in LEBT solenoid 1 and 2. The results are compared with RFQ transmission rate measured in the J-PARC linac commissioning. The double peak of RFQ transmission rate to the solenoid applied current seen in the measurement is explained by the calculation results. The results indicate that presence of the LEBT orifice for differential pumping plays a role as a collimator to reduce emittance at RFQ entrance.
 ion source
ion sourceUeno, Akira; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Ikegami, Kiyoshi*; Takagi, Akira*; Shinto, Katsuhiro; Oguri, Hidetomo
AIP Conference Proceedings 2052, p.050003_1 - 050003_7, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:78.70(Physics, Applied)In order to specify the beam intensity bottlenecks of the J-PARC cesiated RF-driven H ion source, the extraction and acceleration voltages (V
ion source, the extraction and acceleration voltages (V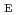 and V
and V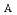 ) higher than the design values of 10 kV and 40 kV were examined. A 100 mA beam, whose about 93 mA has transverse emittances used for a common RFQ design, was stably operated with a duty factor of 5% (1 ms
) higher than the design values of 10 kV and 40 kV were examined. A 100 mA beam, whose about 93 mA has transverse emittances used for a common RFQ design, was stably operated with a duty factor of 5% (1 ms  50 Hz) by using the V
50 Hz) by using the V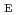 and V
and V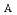 of 12.4 kV and 49.6 kV, respectively. This breakthrough with important information on the space-charge limited bottlenecks in the extraction and acceleration gaps will derive the optimal electrode shapes for the source operated with a beam intensity higher than 100 mA and realize the next generation benchmark H
of 12.4 kV and 49.6 kV, respectively. This breakthrough with important information on the space-charge limited bottlenecks in the extraction and acceleration gaps will derive the optimal electrode shapes for the source operated with a beam intensity higher than 100 mA and realize the next generation benchmark H ion source for high intensity and high energy H
ion source for high intensity and high energy H LINACs.
LINACs.