Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 rays in the
rays in the  La(
La(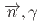 )
) La reaction
La reactionOkuizumi, Mao*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishizaki, Kohei*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Koga, Jun*; et al.
Physical Review C, 111(3), p.034611_1 - 034611_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
IEEJ Transactions on Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 19(11), p.1888 - 1894, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)Endo, Shunsuke; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Ino, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kawamura, Shiori*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kobayashi, Ryuju*; et al.
European Physical Journal A, 60(8), p.166_1 - 166_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear)Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2776, p.012009_1 - 012009_9, 2024/06
Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Hamon, 34(2), p.50 - 53, 2024/05
Spin-contrast-variation (SCV) small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) enabled us to determine structure of nano-ice crystals that were generated in rapidly frozen sugar solution. In the frozen glucose solution, we found that the nano-ice crystals formed a planar structure with a radius larger than several tens of nanometers and a thickness of 2-3 nm, which was close to the critical nucleation size of ice crystals in supercooled water. This result suggests that the glucose molecules were preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then blocked the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.
Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Masatoshi*; Ishimaru, Sora*; Yamauchi, Sara*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Watanabe, Masao; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 41, p.011010_1 - 011010_7, 2024/05
Kumada, Takayuki; Iwahara, Daisuke*; Nishitsuji, Shotaro*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Daisuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Torikai, Naoya*; Amino, Naoya*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(21), p.8797 - 8802, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)We elucidated the entanglement of polybutadiene and silane coupling agent (SCA) molecules bound to Si substrates using spin-contrast-variation (SCV) neutron reflectivity (NR). In an annealed integral blend film of polybutadiene and SCA, a SCA layer generated on the Si substrate was composed of 70 vol. percent SCA molecules extended perpendicularly from the silicon substrate and entangled with 30 vol. percent polybutadiene molecules. By contrast, in an SCA-precoated polybutadiene film, the SCA-precoated layer is composed of densely packed SCA molecules forming crystal-like structure, and thus did not become entangled with the postcoated polybutadiene molecules. This poor entanglement resulted in poor binding between polybutadiene and Si substrate.
 -odd/
-odd/ -odd interactions on the 0.75 eV
-odd interactions on the 0.75 eV  -wave resonance in
-wave resonance in 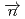 +
+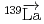 forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beam
forward transmission determined using a pulsed neutron beamNakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.L041602_1 - L041602_4, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:18.90(Physics, Nuclear) -wave resonance of
-wave resonance of 
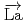 +
+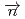
Okudaira, Takuya*; Nakabe, Rintaro*; Auton, C. J.*; Endo, Shunsuke; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Gudkov, V.*; Ide, Ikuo*; Ino, Takashi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Kambara, Wataru*; et al.
Physical Review C, 109(4), p.044606_1 - 044606_9, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Physics, Nuclear) He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scattering
He spin filter and small-angle X-ray scatteringRyoki, Akiyuki*; Watanabe, Fumi*; Okudaira, Takuya*; Takahashi, Shingo*; Oku, Takayuki; Hiroi, Kosuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Nakamura, Yo*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 160(11), p.114907_1 - 114907_9, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:37.13(Chemistry, Physical)Ishida, Takekazu*; Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 214(3-4), p.152 - 157, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied) single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensor
single crystals based on Bragg-dip analysis using a delay-line superconducting sensorShishido, Hiroaki*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(4), p.1108 - 1113, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:41.77(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(34), p.7638 - 7643, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of nano-ice crystals in rapidly frozen glucose solution was elucidated by using spin-contrast-variation small-angle neutron scattering, which distinguishes the nano-ice crystal signal from the frozen amorphous solution signal by the polarization-dependent neutron scattering. The analysis revealed that the nano-ice crystals form a planar structure with a diameter exceeding tens of nanometers and a thickness of 1 nm, which is close to the critical nucleation size. This result suggests that the glucose molecules are preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then block the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.
 rays in the
rays in the 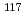 Sn(
Sn( )
)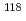 Sn reaction
Sn reactionEndo, Shunsuke; Okudaira, Takuya*; Abe, Ryota*; Fujioka, Hiroyuki*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Oku, Takayuki; Sakai, Kenji; Shima, Tatsushi*; et al.
Physical Review C, 106(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.48(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Kumada, Takayuki; Miura, Daisuke*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oku, Takayuki; Torikai, Naoya*; Niizeki, Tomotake*
Hamon, 32(4), p.165 - 168, 2022/11
We demonstrated the advantage of spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectometry on the structure analysis of buried interface between resin and porous silica layers. The interface structure was not reproduced by the normal Gaussian model, but by the asymmetric interface model where crosslinked polymer chains neither permeate the pore nor follow the surface roughness of the silica layer.
Kumada, Takayuki; Miura, Daisuke*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kawamura, Yukihiko*; Suzuki, Junichi*; Oku, Takayuki; Torikai, Naoya*; Niizeki, Tomotake*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 55(5), p.1147 - 1153, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.71(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Spin-contrast-variation neutron reflectivity obtains multiple reflectivity curves from a single sample and a single beam source. We used the strong point of the technique to reveal that, although methylated-perhydropolysilazane-derived silica layer has a higher porosity near the interface with acrylic urethane resin, the resin did not permeate the pore network.
Miura, Daisuke*; Kumada, Takayuki; Sekine, Yurina; Oku, Takayuki; Takata, Shinichi; Hiroi, Kosuke; Iwata, Takahiro*
J-PARC 22-02; J-PARC MLF Annual Report 2021, p.6 - 7, 2022/03
We carried out spin contrast variation neutron powder diffractometry of glutamic acid crystal. The diffraction peak intensities varied as a function of proton polarization. We extracted the structure factor of hydrogen atoms from the variation of peak intensities.
Shishido, Hiroaki*; Nishimura, Kazuma*; Vu, TheDang*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(9), p.2400505_1 - 2400505_5, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.73(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)In this study, we employed a superconducting detector, current-biased kinetic-inductance detector (CB-KID) for neutron imaging using a pulsed neutron source. We employed the delay-line method, and high spatial resolution imaging with only four reading channels was achieved. We also performed wavelength-resolved neutron imaging by the time-of-flight method. We obtained the neutron transmission images of a Gd-Al alloy sample, inside which single crystals of GdAl were grown, using the delay-line CB-KID. Single crystals were well imaged, in both shapes and distributions, throughout the Al-Gd alloy. We identified Gd nuclei via neutron transmissions that exhibited characteristic suppression above the neutron wavelength of 0.03 nm. In addition, the
were grown, using the delay-line CB-KID. Single crystals were well imaged, in both shapes and distributions, throughout the Al-Gd alloy. We identified Gd nuclei via neutron transmissions that exhibited characteristic suppression above the neutron wavelength of 0.03 nm. In addition, the 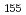 Gd resonance dip, a dip structure of the transmission caused by the nuclear reaction between an isotope and neutrons, was observed even when the number of events was summed over a limited area of 15
Gd resonance dip, a dip structure of the transmission caused by the nuclear reaction between an isotope and neutrons, was observed even when the number of events was summed over a limited area of 15  m
m  12
12  m. Gd selective imaging was performed using the resonance dip of
m. Gd selective imaging was performed using the resonance dip of 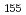 Gd, and it showed clear Gd distribution even with a limited neutron wavelength range of 1 pm.
Gd, and it showed clear Gd distribution even with a limited neutron wavelength range of 1 pm.
Wada, Yuki*; Matsumoto, Takahiro*; Enoto, Teruaki*; Nakazawa, Kazuhiro*; Yuasa, Takayuki*; Furuta, Yoshihiro*; Yonetoku, Daisuke*; Sawano, Tatsuya*; Okada, Go*; Nanto, Hidehito*; et al.
Physical Review Research (Internet), 3(4), p.043117_1 - 043117_31, 2021/12
Vu, TheDang; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Kojima, Kenji M*; Koyama, Tomio*; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Oku, Takayuki; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1006, p.165411_1 - 165411_8, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)