Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshiasa, Akira*; Arima, Hiroshi; Fukui, Hiroshi*; Okube, Maki*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Otaka, Osamu*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 51(1), p.66 - 69, 2009/02
We have determined a precise P-T phase diagram of AgI by high-temperature high-pressure synchrotron experiments. X-ray diffraction and X-ray absorption measurements were performed using a multi-anvil high pressure apparatus at SPring-8 synchrotron radiation facility. In a disordered rock-salt phase, Ag ions occupy both octahedral and tetrahedral sites. The occupancy of tetrahedral site has a maximum value, 20%, at 2 GPa. A change from rock-salt structure to disordered rock-salt structure is gradual in the X-ray diffraction measurements while it is clearly observed in the X-ray absorption measurements. Analysis of EXAFS Debye-Waller factor is useful because the force constant can be decided directly even at high pressure and high temperature. Pressure influences greatly the effective potential and anharmonicity decreases with increasing pressure.
Okube, Maki*; Yoshiasa, Akira*; Otaka, Osamu*; Katayama, Yoshinori
High Pressure Research, 23(3), p.247 - 251, 2003/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:38.86(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In order to examine the pressure effect on anharmonic thermal vibrations of Pt, Extended X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (EXAFS) spectra near Pt K-edge and L -edge were measured in the temperature range from 300 to 800K under pressures up to 6vGPa, using large volume high-pressure devices and synchrotron radiation. We have investigated the anharmonic interatomic potentials by a cumulant expansion method. The values of EXAFS Debye-Waller factors,
-edge were measured in the temperature range from 300 to 800K under pressures up to 6vGPa, using large volume high-pressure devices and synchrotron radiation. We have investigated the anharmonic interatomic potentials by a cumulant expansion method. The values of EXAFS Debye-Waller factors,  2 and
2 and  3, become smaller with increase of pressure. The anharmonic effective pair potential
3, become smaller with increase of pressure. The anharmonic effective pair potential 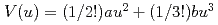 was evaluated and the potential coefficient a at 0.1MPa and 6GPa are 4.8 and 5.0eV/
was evaluated and the potential coefficient a at 0.1MPa and 6GPa are 4.8 and 5.0eV/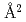 , respectively. The anharmonic potential parameter
, respectively. The anharmonic potential parameter  decreases with increasing pressure.
decreases with increasing pressure.
Okube, Maki*; Yoshiasa, Akira*; Otaka, Osamu*; Fukui, Hiroyuki*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Utsumi, Wataru
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 14(44), p.11511 - 11515, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.13(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 glass under pressure
glass under pressureOtaka, Osamu*; Yoshiasa, Akira*; Fukui, Hiroyuki*; Murai, Keiichiro*; Okube, Maki*; Takebe, Hitoshi*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Utsumi, Wataru
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 14(44), p.10521 - 10524, 2002/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:64.23(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
Okube, Maki*; Yoshiasa, Akira*; Otaka, Osamu*; Fukui, Hiroshi*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Utsumi, Wataru
Solid State Communications, 121(5), p.235 - 239, 2002/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:50.72(Physics, Condensed Matter)In order to examine the pressure effect on the anharmonicity of Au, EXAFS spectra near Au 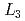 -edge were measured at the temperature range from 300 to 1000K under pressure up to 14GPa using large volume high-pressure devices and synchrotron radiation. The values of EXAFS Debye-Waller factors,
-edge were measured at the temperature range from 300 to 1000K under pressure up to 14GPa using large volume high-pressure devices and synchrotron radiation. The values of EXAFS Debye-Waller factors, 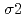 and
and 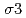 , become smaller with increase of pressure, which indicates that the potential width become narrower with pressure. The anharmonic effective pair potentials of Au,
, become smaller with increase of pressure, which indicates that the potential width become narrower with pressure. The anharmonic effective pair potentials of Au, 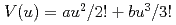 , at 0.1MPa, 6 and 14GPa have been calculated. The pressure dependence of the coefficient of thermal expansion has also been evaluated.
, at 0.1MPa, 6 and 14GPa have been calculated. The pressure dependence of the coefficient of thermal expansion has also been evaluated.
 under pressure
under pressureOtaka, Osamu*; Yoshiasa, Akira*; Fukui, Hiroyuki*; Murai, Keiichiro*; Okube, Maki*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Utsumi, Wataru; Nishihata, Yasuo
Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 8(Part2), p.791 - 793, 2001/03
no abstracts in English
 and
and  CuBr at high pressure
CuBr at high pressureYoshiasa, Akira*; Okube, Maki*; Otaka, Osamu*; Kamishima, Osamu*; Katayama, Yoshinori
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, Part 1, 39(12A), p.6747 - 6751, 2000/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:44.21(Physics, Applied)The anharmonic effective pair potentials 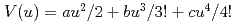 for Br-Cu bond in
for Br-Cu bond in 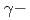 and
and 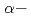 CuBr under pressure have been investigated by an extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) technique. The EXAFS spectra near the Br K-edge were measured under high temperature and high pressure using a large-volume uniaxial press and synchrotron radiation from SPring-8. The anharmonic effective pair potential for each phase is influenced by pressure and become steeper with increasing pressure. The potential parameter
CuBr under pressure have been investigated by an extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) technique. The EXAFS spectra near the Br K-edge were measured under high temperature and high pressure using a large-volume uniaxial press and synchrotron radiation from SPring-8. The anharmonic effective pair potential for each phase is influenced by pressure and become steeper with increasing pressure. The potential parameter  for
for  -phase at 0.1MPa increases by about 20% at the pressure of 4.8GPa. The stastical distribution of Cu in
-phase at 0.1MPa increases by about 20% at the pressure of 4.8GPa. The stastical distribution of Cu in  -CuBr and superionic conduction mechanism have been discussed based on the effective pair potential and distribution of Br-Cu distances.
-CuBr and superionic conduction mechanism have been discussed based on the effective pair potential and distribution of Br-Cu distances.
 O
O by neutron and X-ray diffraction
by neutron and X-ray diffractionTakayasu, Shunichi*; Yoshizaki, Jumpei*; Okube, Maki*; Toyoda, Takeshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Sasaki, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Hexagonal barium ferrites have been traditionally used as permanent magnets and microwave devices because of their high coercivity and large uniaxial anisotropy. It is recognized that the magnetic anisotropy can be optimized by Fe ion for several magnetic and non-magnetic ions, which makes M-type ferrites suitable for microwave absorber in 1 - 75 GHz range. In this study to use neutron and X-ray powder diffraction, site preference and magnetic structure of iron sites on BaTiCoFe
ion for several magnetic and non-magnetic ions, which makes M-type ferrites suitable for microwave absorber in 1 - 75 GHz range. In this study to use neutron and X-ray powder diffraction, site preference and magnetic structure of iron sites on BaTiCoFe O
O are examined.
are examined.
 O
O ferrite determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction methods
ferrite determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction methodsTakayasu, Shunichi*; Yoshizaki, Jumpei*; Okube, Maki*; Toyoda, Takeshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Sasaki, Satoshi*
no journal, ,
Site preferences of Ti and Mn and the magnetic structure of M-type BaTiMnFe O
O ferrite were analyzed using the X rays and neutron powder diffraction method. The intensity difference on the magnetic scattering was clearly observed below and above the
ferrite were analyzed using the X rays and neutron powder diffraction method. The intensity difference on the magnetic scattering was clearly observed below and above the  c, showing the ferrimagnetic spin arrangement along with the
c, showing the ferrimagnetic spin arrangement along with the  axis. Site-occupancy refinements give the results that Ti ions occupy the 4
axis. Site-occupancy refinements give the results that Ti ions occupy the 4 1 (24%), 2
1 (24%), 2 (15%) and 2
(15%) and 2 (15%) sites, while Mn ions prefer to 4
(15%) sites, while Mn ions prefer to 4 2 (24%) and 12
2 (24%) and 12 (24%). Magnetic moments were obtained from the Rietveld refinements, which are 3.56, 3.37, -3.86, -3.72 and 3.68
(24%). Magnetic moments were obtained from the Rietveld refinements, which are 3.56, 3.37, -3.86, -3.72 and 3.68 
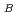 at
at  = 8 K for 2
= 8 K for 2 , 2
, 2 , 4
, 4 1, 4
1, 4 2 and 12
2 and 12 sites, respectively.
sites, respectively.