Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kristo, M. J.*; Williams, R.*; Gaffney, A. M.*; Kayzar-Boggs, T. M.*; Schorzman, K. C.*; Lagerkvist, P.*; Vesterlund, A.*; Rameb ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
ck, H.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Kotze, D.*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.425 - 434, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:79.90(Chemistry, Analytical)In a recent international exercise, 10 international nuclear forensics laboratories successfully performed radiochronometry on three low enriched uranium oxide samples, providing 12 analytical results using three different parent-daughter pairs serving as independent chronometers. The vast majority of the results were consistent with one another and consistent with the known processing history of the materials. In general, for these particular samples, mass spectrometry gave more accurate and more precise analytical results than decay counting measurements. In addition, the concordance of the  U-
U-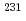 Pa and
Pa and  U-
U- Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Th chronometers confirmed the validity of the age dating assumptions, increasing confidence in the resulting conclusions.
Ho, D. M. L.*; Nelwamondo, A. N.*; Okubo, Ayako; Rameb ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; Kataoka, Osamu; et al.
ck, H.*; Song, K.*; Han, S.-H.*; Hancke, J. J.*; Holmgren, S.*; Jonsson, S.*; Kataoka, Osamu; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 315(2), p.353 - 363, 2018/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.04(Chemistry, Analytical)The Fourth Collaborative Material Exercise (CMX-4) of the Nuclear Forensics International Technical Working Group (ITWG) registered the largest participation for this exercise in nuclear forensics, with seven of the 17 laboratories participating for the first time. In this paper, participants from five of the first-time laboratories shared their individual experience in this exercise, from preparation to analysis of samples. The exercise proved to be highly useful for testing procedures, repurposing established methods, exercising skills, and improving the understanding of nuclear forensic signatures and their interpretation trough the post-exercise review meeting.
Okubo, Ayako; Shinohara, Nobuo; Magara, Masaaki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 314(1), p.231 - 234, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.14(Chemistry, Analytical)The model date of two enriched uranium materials were determined using a new method for nuclear forensics investigation. In this method, the  Th/
Th/ U ratio was calculated without spike addition from measured ratios of
U ratio was calculated without spike addition from measured ratios of  Th/
Th/ Th and
Th and  U/
U/ U, and calculated
U, and calculated  Th/
Th/ U ratio in secular equilibrium. The obtained model date for the low-enriched uranium material was agreed with the known production date within uncertainty. For the highly enriched uranium material, slightly younger model date than the known production date was obtained. The
U ratio in secular equilibrium. The obtained model date for the low-enriched uranium material was agreed with the known production date within uncertainty. For the highly enriched uranium material, slightly younger model date than the known production date was obtained. The  U interference on
U interference on  Th counting in thermal ionization mass spectrometry measurement was suspected as a potential cause.
Th counting in thermal ionization mass spectrometry measurement was suspected as a potential cause.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Okubo, Ayako; Kimura, Yoshiki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Tazaki, Makiko; Shimizu, Ryo; Suda, Kazunori; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Proceedings of INMM 58th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2017/07
Nuclear forensics is a technical measure to analyse and collate samples of illegally used nuclear materials, etc., to clarify their origins, routes, etc. and contribute to criminal identifications. Close collaboration with police and judicial organizations is essential. The national response framework is being built up with international cooperation. Discussions on promoting technical capability and regional cooperation are presented.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Okubo, Ayako; Kimura, Yoshiki; Kokaji, Lisa; Shinohara, Nobuo; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
Dai-37-Kai Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nihon Shibu Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/02
Nuclear Forensics capability has been developed under the international collaborations. For its effective function, technical development in analysis of seized nuclear materials as well as the institutional development in comprehensive response framework are required under individual national responsibility. In order to keep the "chain of custody" in the proper operation of sample collection at the event scene, radiological analysis at the laboratory, storage of the samples, and further inspection and trial, close cooperation and information sharing between relevant organisations are essential. IAEA issues the Implementing Guide to provide the model action plan and assists individual national development. International cooperation for the technical improvement and awareness cultivation is promoted. Examples in such national developments will be introduced and prospective technical/institutional prerequisite for nuclear forensics response framework will be studied.
 Th-
Th- U age dating of bulk uranium for nuclear forensics
U age dating of bulk uranium for nuclear forensicsGaffney, A.*; Hubert, A.*; Kinman, W. S.*; Magara, Masaaki; Okubo, Ayako; Pointurier, F.*; Schorzman, K. C.*; Steiner, R. E.*; Williams, R. W.*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 307(3), p.2055 - 2060, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:26 Percentile:90.18(Chemistry, Analytical)In and inter-laboratory measurement comparison study, four laboratories (LLNL, LANL, CEA, JAEA) determined  Th-
Th- U model ages of uranium certified reference material NBL U050 using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The model dates determined by the participating laboratories range from 9 March 1956 to 19 October 1957, and are indistinguishable given the associated measurement uncertainties. These model ages are concordant with to slightly older than the known production age of NBL U050, indicating unsufficient purification of U050.
U model ages of uranium certified reference material NBL U050 using isotope dilution mass spectrometry. The model dates determined by the participating laboratories range from 9 March 1956 to 19 October 1957, and are indistinguishable given the associated measurement uncertainties. These model ages are concordant with to slightly older than the known production age of NBL U050, indicating unsufficient purification of U050.
Kimura, Yoshiki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Okubo, Ayako
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 57(12), p.782 - 786, 2015/12
, 57(12), p.782 - 786, 2015/12
no abstracts in English
Okubo, Ayako; Kimura, Yoshiki; Shinohara, Nobuo; Toda, Nobufumi; Funatake, Yoshio; Watahiki, Masaru; Sakurai, Satoshi; Kuno, Yusuke
JAEA-Technology 2015-001, 185 Pages, 2015/03
Nuclear forensics is the analysis of intercepted illicit nuclear or radioactive material and any associated material to provide evidence for nuclear attribution by determining origin, history, transit routes and purpose involving such material. Nuclear forensics activity includes sampling of the illicit material, analysis of the samples and evaluation of the attribution by comparing the analyzed data with database or numerical simulation. Because the nuclear forensics technologies specify the origin of the nuclear materials used illegal dealings or nuclear terrorism, it becomes possible to identify and indict offenders, hence to enhance deterrent effect against such terrorism. Worldwide network on nuclear forensics can contribute to strengthen global nuclear security regime. In this paper, the results of research and development of fundamental nuclear forensics technologies performed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency during the fiscal term of 2011-2013 were reported.
Okubo, Ayako; Obata, Hajime*; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Ogawa, Hiroshi*
Analytica Chimica Acta, 804, p.120 - 125, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.97(Chemistry, Analytical)This work introduces a novel method of recovery of iron hydroxide using a DIAION CR-20 chelating resin column to determine Th isotopes in seawater with a sector field (SF) inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). Thorium isotopes in seawater were coprecipitated with iron hydroxide, and this precipitate was sent to chelating resin column. The chelating column quantitatively collected  Th with iron hydroxide in seawater at flow rates of 20-25 mL/min. Based on this flow rate, a 5 L sample was processed within 3-4 h.
Th with iron hydroxide in seawater at flow rates of 20-25 mL/min. Based on this flow rate, a 5 L sample was processed within 3-4 h.
Okubo, Ayako; Takeda, Shigenobu*; Obata, Hajime*
Atmospheric Research, 129-130, p.20 - 32, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:41 Percentile:69.76(Meteorology & Atmospheric Sciences)To understand the atmospheric input of trace metals to surface seawaters, the total deposition samples were collected simultaneously from three coastal station in Japan. The observed flux was within the lower limit of the previous estimation based on a model. Except for Sc and Fe, all the elements showed a increasing tendency toward dissolution with decreasing the pH. We calculated the Sc-normalized enrichment factors. The increasing tendency toward dissolution with decreasing the pH was higher for Al than that of Fe.
 Th and
Th and  Th distributions in mid-latitudes of the North Pacific Ocean; Effect of bottom scavenging
Th distributions in mid-latitudes of the North Pacific Ocean; Effect of bottom scavengingOkubo, Ayako; Obata, Hajime*; Gamo, Toshitaka*; Yamada, Masatoshi*
Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 339-340, p.139 - 150, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:72.06(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Vertical distributions of total  Th and dissolved
Th and dissolved  Th were determined in the mid-latitudes of the North Pacific Ocean. Th in the Pacific Ocean have been described well using the reversible-scavenging model. However, we observed the depletion of total Th. The enhanced vertical eddy diffusion derived from the complex topography of the western Pacific Ocean might promote bottom scavenging and transport of the low Th in deep water to the upper layers.
Th were determined in the mid-latitudes of the North Pacific Ocean. Th in the Pacific Ocean have been described well using the reversible-scavenging model. However, we observed the depletion of total Th. The enhanced vertical eddy diffusion derived from the complex topography of the western Pacific Ocean might promote bottom scavenging and transport of the low Th in deep water to the upper layers.
Sakurai, Satoshi; Kimura, Yoshiki; Sato, Kaneaki; Toda, Nobufumi; Shinoda, Yoshiharu; Okubo, Ayako; Magara, Masaaki; Watahiki, Masaru; Kuno, Yusuke
no journal, ,
The national statement made by the Japan Government at 2010 Nuclear Security Summit (Washington D.C., U.S.A.) was to develop its nuclear forensics detection and analysis technologies in a three-year period and to share them with the international community to contribute to strengthening the nuclear security regime. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency, the organization that possesses analytical capabilities with the potential to fulfill this nuclear forensics mission, started R&D on nuclear forensics technology from JFY 2011. The main areas of development are isotopic ratio analysis, impurity analysis, uranium age determination, etc. The cooperation with US-DOE and EC-JRC were also started to effectively promote the technical development. In the presentation reported will be progress in R&D to establish nuclear forensics analytical capabilities and international cooperation.
Okubo, Ayako; Shinohara, Nobuo; Toda, Nobufumi; Kataoka, Osamu; Matsumoto, Tetsuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shinohara, Nobuo; Kimura, Yoshiki; Okubo, Ayako
no journal, ,
Nuclear forensics is the analysis of intercepted illicit nuclear or radioactive material and any associated material to provide evidence for nuclear attribution by determining origin, history, transit routes and purpose involving such material. Because the nuclear forensics methodologies provide hints of the origin of the nuclear materials used in illegal dealings or nuclear terrorism, it contributes to identify and indict offenders, hence to enhance deterrent effect against such terrorism. In the 59th Symposium on Radiochemistry, the results of research and development of fundamental nuclear forensics technologies (analysis of isotopic composition, impurity analysis, age dating of nuclear material, particle shape analysis by electron microscope, and nuclear forensics library) performed in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are reported. Japan's capability and the role of radiochemistry on nuclear forensics are also discussed in the Symposium.
Okubo, Ayako; Shinohara, Nobuo; Magara, Masaaki
no journal, ,
As an effort of strengthening nuclear security in the world, capacity building of nuclear forensics in each state have been required. The age-dating of nuclear material is to estimate an elapsed time since the final purified day of the nuclear material. Because age-dating result could enable us to better constrain the origin of unidentified material, which is recognized as an important parameter for nuclear forensics. The isotope dilution mass spectrometry (ID-MS) method is recognized as the most reliable method to estimate  U/
U/ Th ratio for uranium age-dating. Uranium-234 and
Th ratio for uranium age-dating. Uranium-234 and  Th amounts in a uranium material were respectively measured by ID method using spikes (
Th amounts in a uranium material were respectively measured by ID method using spikes ( U and
U and  Th). The isotopic equilibrium between the isotopes in-situ the sample and added spikes is assumed in ID method. In order to obtain the accurate concentrations of
Th). The isotopic equilibrium between the isotopes in-situ the sample and added spikes is assumed in ID method. In order to obtain the accurate concentrations of  U and
U and  Th, precise determination of sample weight and control of spike concentration are required. We have developed a new method to estimate
Th, precise determination of sample weight and control of spike concentration are required. We have developed a new method to estimate  U/
U/ Th ratio without spike addition for uranium age-dating. In this method, using secular equilibrium between
Th ratio without spike addition for uranium age-dating. In this method, using secular equilibrium between  U and
U and  Th (
Th ( Th/
Th/ U = 1.45 E-11),
U = 1.45 E-11),  U/
U/ Th ratio is calculated from measured isotope ratios of U and Th. This new method does not require precise sample weighing and control spike concentration, and is suitable for routine analysis in developing of nuclear forensics database.
Th ratio is calculated from measured isotope ratios of U and Th. This new method does not require precise sample weighing and control spike concentration, and is suitable for routine analysis in developing of nuclear forensics database.
Tamai, Hiroshi; Kimura, Yoshiki; Okubo, Ayako; Shinohara, Nobuo; Tomikawa, Hirofumi
no journal, ,
Nuclear forensics is effective measure for strengthening nuclear security through the analysis of origin and characteristics of nuclear materials or radio-isotopes collected at the crime scene inspections. In the development of nuclear forensics laboratory/library, "Chain of Custody" should be kept in mind on the view point of juridical process. Each nation should develop own national response plan to stipulate the framework for integrated nuclear forensics activities. Good practices for stipulating national frameworks for nuclear forensics are investigated in advancing nations such as US, EU and Canada. Issues and measures are proposed aiming at improving its framework.
Kimura, Yoshiki; Okubo, Ayako; Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Matsumoto, Tetsuya*; Umino, Yuji*; Hosoi, Masaharu*
no journal, ,
Tomikawa, Hirofumi; Kimura, Yoshiki; Okubo, Ayako
no journal, ,
Okubo, Ayako; Obata, Hajime*; Magara, Masaaki; Kimura, Takaumi; Ogawa, Hiroshi*
no journal, ,
This work introduces a novel method of recovery of iron hydroxide with thorium using a DIAION CR-20 chelating resin column to determine Th isotopes in seawater with a sector field (SF) inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). Thorium isotopes in seawater were co-precipitated with iron hydroxide, and this precipitate was sent to chelating resin column. The chelating column quantitatively collect  Th with iron hydroxide in seawater at flow rate of 20-25 mL/min. Based on this flow rate, 5 L sample was processed within 3-4 h. The aging of iron hydroxide tends to reduce the recovery of
Th with iron hydroxide in seawater at flow rate of 20-25 mL/min. Based on this flow rate, 5 L sample was processed within 3-4 h. The aging of iron hydroxide tends to reduce the recovery of  Th. The rapid collection method was successfully applied to the determination of
Th. The rapid collection method was successfully applied to the determination of  Th and
Th and  Th in open-ocean seawater samples.
Th in open-ocean seawater samples.
Kips, R.*; Lindvall, R.*; Marks, N.*; Gluschenko, V.*; Okubo, Ayako; Szeles, E.*
no journal, ,