Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kobayashi, Keita; Okumura, Masahiko; Nakamura, Hiroki; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Machida, Masahiko; Urata, Shingo*; Suzuya, Kentaro
Scientific Reports (Internet), 13, p.18721_1 - 18721_12, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0(Multidisciplinary Sciences)The first sharp peak diffraction peak (FSDP) in the structure factor of amorphous materials is thought to reflect the medium-range order structure in amorphous materials, and the structural origin of the FSDP has been a subject of ongoing debate. In this study, we employed machine learning molecular dynamics (MLMD) with nearly first-principles calculation accuracy to investigate the structural origin of the FSDP in high-density silica glass. First, we successfully reproduced various experimental data of high-density silica glass using MLMD. Furthermore, we revealed that the development (or reduction) of the FSDP in high-density silica glass is characterized by the deformation behavior of ring structures in Si-O covalent bond networks under compression.
Mori, Hideki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsunaka, Daisuke*; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(6), p.063605_1 - 063605_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The introduction of obstacles (e.g., precipitates) for controlling dislocation motion in molecular structures is a prevalent method for designing the mechanical strength of metals. Owing to the nanoscale size of the dislocation core ( 1 nm), atomic modeling is required to investigate the interactions between the dislocation and obstacles. However, conventional empirical potentials are not adequately accurate, in contrast to the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). Therefore, the atomic-level details of the interactions between the dislocations and obstacles remain unclarified. To this end, this study applied an artificial neural network (ANN) framework to construct an atomic potential by leveraging the high accuracy of DFT. Using the constructed ANN potential, we investigated the dynamic interaction between the
1 nm), atomic modeling is required to investigate the interactions between the dislocation and obstacles. However, conventional empirical potentials are not adequately accurate, in contrast to the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). Therefore, the atomic-level details of the interactions between the dislocations and obstacles remain unclarified. To this end, this study applied an artificial neural network (ANN) framework to construct an atomic potential by leveraging the high accuracy of DFT. Using the constructed ANN potential, we investigated the dynamic interaction between the 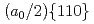 edge dislocation and obstacles in BCC iron. When the dislocation crossed the void, an ultrasmooth and symmetric half-loop was observed for the bowing-out dislocation. Except for the screw dislocation, the Peierls stress of all the dislocations predicted using the ANN was less than 100 MPa. More importantly, the results confirmed the formation of an Orowan loop in the interaction between a rigid sphere and dislocation. Furthermore, we discovered a phenomenon in which the Orowan loop disintegrated into two small loops during its interaction with the rigid sphere and dislocation.
edge dislocation and obstacles in BCC iron. When the dislocation crossed the void, an ultrasmooth and symmetric half-loop was observed for the bowing-out dislocation. Except for the screw dislocation, the Peierls stress of all the dislocations predicted using the ANN was less than 100 MPa. More importantly, the results confirmed the formation of an Orowan loop in the interaction between a rigid sphere and dislocation. Furthermore, we discovered a phenomenon in which the Orowan loop disintegrated into two small loops during its interaction with the rigid sphere and dislocation.
Yamazaki, Yasuhiro*; Shinomiya, Keisuke*; Okumura, Tadaharu*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Shobu, Takahisa; Nakamura, Yuiga*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.14_1 - 14_12, 2023/05
 -edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samples
-edge for Ce in bauxites using transition-edge sensors; Implications for Ti-rich geological samplesLi, W.*; Yamada, Shinya*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Okumura, Takuma*; Hayakawa, Ryota*; Nitta, Kiyofumi*; Sekizawa, Oki*; Suga, Hiroki*; Uruga, Tomoya*; Ichinohe, Yuto*; et al.
Analytica Chimica Acta, 1240, p.340755_1 - 340755_9, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:31.9(Chemistry, Analytical)no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kunieda, Satoshi; Minato, Futoshi; Nakayama, Shinsuke; Abe, Yutaka*; Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(1), p.1 - 60, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:64 Percentile:99.99(Nuclear Science & Technology)Okumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I.-H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
IEEE Transactions on Applied Superconductivity, 31(5), p.2101704_1 - 2101704_4, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.15(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)A superconducting transition-edge sensor (TES) microcalorimeter is an ideal X-ray detector for experiments at accelerator facilities because of good energy resolution and high efficiency. To study the performance of the TES detector with a high-intensity pulsed charged-particle beam, we measured X-ray spectra with a pulsed muon beam at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) in Japan. We found substantial temporal shifts of the X-ray energy correlated with the arrival time of the pulsed muon beam, which was reasonably explained by pulse pileup due to the incidence of energetic particles from the initial pulsed beam.
 X rays
X raysOkumura, Takuma*; Azuma, Toshiyuki*; Bennet, D. A.*; Caradonna, P.*; Chiu, I. H.*; Doriese, W. B.*; Durkin, M. S.*; Fowler, J. W.*; Gard, J. D.*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 127(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:79.44(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We observed electronic  X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic
X rays emitted from muonic iron atoms using a superconducting transition-edge-type sensor microcalorimeter. The energy resolution of 5.2 eV in FWHM allowed us to observe the asymmetric broad profile of the electronic characteristic 
 and
and 
 X rays together with the hypersatellite
X rays together with the hypersatellite 
 X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the
X rays around 6 keV. This signature reflects the time-dependent screening of the nuclear charge by the negative muon and the  -shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic
-shell electrons, accompanied by electron side-feeding. Assisted by a simulation, this data clearly reveals the electronic  - and
- and  -shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
-shell hole production and their temporal evolution during the muon cascade process.
Mori, Kazuhiro*; Okumura, Ryo*; Yoshino, Hirofumi*; Kanayama, Masaya*; Sato, Setsuo*; Oba, Yojiro; Iwase, Kenji*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Hino, Masahiro*; Sano, Tadafumi*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011093_1 - 011093_6, 2021/03
no abstracts in English
Tsubakihara, Kosuke*; Okumura, Shin*; Ishizuka, Chikako*; Yoshida, Tadashi*; Minato, Futoshi; Chiba, Satoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 58(2), p.151 - 165, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:71.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sugita, Yutaka; Taniguchi, Naoki; Makino, Hitoshi; Kanamaru, Shinichiro*; Okumura, Taisei*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 19(3), p.121 - 135, 2020/09
A series of structural analysis of disposal containers for direct disposal of spent fuel was carried out to provide preliminary estimates of the required pressure resistance thickness of the disposal container. Disposal containers were designed to contain either 2, 3 or 4 spent fuel assemblies in linear, triangular or square arrangements, respectively. The required pressure resistance thickness was evaluated using separation distance of the housing space for each spent fuel assembly as a key model parameter to obtain the required thickness of the body and then the lid of the disposal container. This work also provides additional analytical technical knowledge, such as the validity of the setting of the stress evaluation line and the effect of the model length on the analysis. These can then be referred to and used again in the future as a basis for conducting similar evaluations under different conditions or proceeding with more detailed evaluations.
Fedkin, M. V.*; Shin, Y. K.*; Dasgupta, N.*; Yeon, J.*; Zhang, W.*; van Duin, D.*; Van Duin, A. C. T.*; Mori, Kento*; Fujiwara, Atsushi*; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 123(10), p.2125 - 2141, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:94.92(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
Chiba, Satoshi*; Wakabayashi, Toshio*; Tachi, Yoshiaki; Takaki, Naoyuki*; Terashima, Atsunori*; Okumura, Shin*; Yoshida, Tadashi*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 7(1), p.13961_1 - 13961_10, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:96.31(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Transmutation of long-lived fission products (LLFPs:  Se,
Se,  Zr,
Zr,  Tc,
Tc,  Pd,
Pd,  I, and
I, and  Cs) into short-lived or non-radioactive nuclides by fast neutron spectrum reactors without isotope separation has been proposed as a solution to the problem of radioactive wastes disposal. Despite investigation of many methods, such transmutation remains technologically difficult. To establish an effective and efficient transmutation system, we propose a novel neutron moderator material, yttrium deuteride (YD
Cs) into short-lived or non-radioactive nuclides by fast neutron spectrum reactors without isotope separation has been proposed as a solution to the problem of radioactive wastes disposal. Despite investigation of many methods, such transmutation remains technologically difficult. To establish an effective and efficient transmutation system, we propose a novel neutron moderator material, yttrium deuteride (YD ), to soften the neutron spectrum leaking from the reactor core. Neutron energy spectra and effective half-lives of LLFPs, transmutation rates, and support ratios were evaluated with the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP-II/MVP-BURN and the JENDL-4.0 cross section library. With the YD
), to soften the neutron spectrum leaking from the reactor core. Neutron energy spectra and effective half-lives of LLFPs, transmutation rates, and support ratios were evaluated with the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP-II/MVP-BURN and the JENDL-4.0 cross section library. With the YD moderator in the radial blanket and shield regions, effective half-lives drastically decreased from 10
moderator in the radial blanket and shield regions, effective half-lives drastically decreased from 10 to 10
to 10 years and the support ratios reached 1.0 for all six LLFPs. This successful development and implementation of a transmutation system for LLFPs without isotope separation contribute to developing a self-consuming cycle of LLFPs using fast spectrum reactors to reduce radioactive waste.
years and the support ratios reached 1.0 for all six LLFPs. This successful development and implementation of a transmutation system for LLFPs without isotope separation contribute to developing a self-consuming cycle of LLFPs using fast spectrum reactors to reduce radioactive waste.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Okumura, Keisuke; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 153, p.06008_1 - 06008_6, 2017/09
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:95.25(Nuclear Science & Technology)Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, has been developed under the collaboration of several institutes in Japan and Europe. It can deal with the transport of nearly all particles up to 1 TeV (per nucleon for ion) using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. More than 2,500 researchers and technicians have used the code for a variety of applications such as accelerator design, radiation shielding and protection, medical physics, and space and geosciences. This paper briefly summarizes physics models and functions newly implemented in PHITS between versions 2.52 and 2.82.
Nakayama, Shinichi; Okumura, Masahiko*; Nagasaki, Shinya*; Enokida, Yoichi*; Umeki, Hiroyuki*; Takase, Hiroyasu*; Kawasaki, Daisuke*; Hasegawa, Shuichi*; Furuta, Kazuo*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(2), p.131 - 148, 2016/12
A symposium "Science of nuclear fuel cycle and backend - Research and education -" was held at the Univer-sity of Tokyo in June 25, 2016. This aimed at developing the research on nuclear fuel cycle and backend. The time and the number of participants of the symposium were limited, but the active discussion was conducted, and the common perception for the future was shared among the experienced participants in those fields. This paper provides the discussions made in the symposium, and also, as a memory to Professor Ahn, the University of California, Berkeley, his prominent achievements in academic research and education.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Niita, Koji*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Furuta, Takuya; Abe, Shinichiro; Kai, Takeshi; Matsuda, Norihiro; Iwase, Hiroshi*; et al.
JAEA-Conf 2016-004, p.63 - 69, 2016/09
A general purpose Monte Carlo Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System, PHITS, is being developed through the collaboration of several institutes. PHITS can deal with the transport of nearly all particles, including neutrons, protons, heavy ions, photons, and electrons, over wide energy ranges using various nuclear reaction models and data libraries. PHITS users apply the code to various research and development fields such as nuclear technology, accelerator design, medical physics, and cosmic-ray research. This presentation briefly summarizes the physics models implemented in PHITS, and introduces some new models such as muon-induced nuclear reaction model and a  de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
de-excitation model EBITEM. We will also present the radiation damage cross sections for materials, PKA spectra and kerma factors calculated by PHITS under the IAEA-CRP activity titled "Primary radiation damage cross section."
Hoshino, Kazuo; Matsunaga, Go; Okumura, Yoshikazu
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 92(2), p.146 - 147, 2016/02
no abstracts in English
Okumura, Yoshikazu; Gobin, R.*; Knaster, J.*; Heidinger, R.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Cara, P.*; Chauvin, N.*; Chel, S.*; Gex, D.*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02A739_1 - 02A739_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.23(Instruments & Instrumentation)IFMIF is an accelerator based neutron facility having two set of linear accelerators each producing 125mA/CW deuterium ion beams (250mA in total) at 40MeV. The LIPAc (Linear IFMIF Prototype Accelerator) being developed in the IFMIF-EVEDA project consists of an injector, a RFQ accelerator, and a part of superconducting Linac, whose target is to demonstrate 125mA/CW deuterium ion beam acceleration up to 9MeV. The injector has been developed in CEA Saclay and already demonstrated 140mA/100keV deuterium beam. The injector was disassembled and delivered to the International Fusion Energy Research Center (IFERC) in Rokkasho, Japan, and the commissioning has started after its reassembly 2014; the first beam production has been achieved in November 2014. Up to now, 100keV/120mA/CW hydrogen ion beam has been produced with a low beam emittance of 0.2  .mm.mrad (rms, normalized).
.mm.mrad (rms, normalized).
 /D
/D ion source for IFMIF (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility)
ion source for IFMIF (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility)Shinto, Katsuhiro; Sen e, F.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Chauvin, N.*; Gobin, R.*; Ichimiya, Ryo; Ihara, Akira; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kasugai, Atsushi; et al.
e, F.*; Ayala, J.-M.*; Bolzon, B.*; Chauvin, N.*; Gobin, R.*; Ichimiya, Ryo; Ihara, Akira; Ikeda, Yukiharu; Kasugai, Atsushi; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 87(2), p.02A727_1 - 02A727_3, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:39.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)Hoshino, Kazuo; Matsunaga, Go; Okumura, Yoshikazu
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 91(12), p.802 - 803, 2015/12
Holding of the 17th IFERC Project Committee (PC), the 16th IFMIF/EVEDA-PC and the progress of the JT-60SA were reported. In the IFERC-PC, total 33 participated including Maisonnier chairperson, JA-EU committee, experts and project members. They reported the status of each activity, discussed the planning of project 2016 and revised plan, and concluded technical advice to the BA Steering Committee (SC). In the IFMIF/EVEDA-PC, total 27 participated including Takatsu chairperson, JA-EU committee, experts and project members. They reported the status of each activity, discussed the planning of project 2016 and revised plan, and the BA-SC recommended the endorsement of the new project plan. In the JT-60SA, a rotary crane for assembly of the troidal field coil has been installed. The disassembly of the constraint jigs of the vacuum vessel which completed 340 assembly has been progressed. 6 high temperature superconductor current leads for the troidal field coils had been delivered from EU.
assembly has been progressed. 6 high temperature superconductor current leads for the troidal field coils had been delivered from EU.
Hoshino, Kazuo; Matsunaga, Go; Okumura, Yoshikazu
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 91(10), p.700 - 701, 2015/10
The progress of IFMIF Prototype Accelerator in the IFERC site and the Satellite Tokamak (JT-60SA) project were reported. For the IFMIF Prototype Accelerator, two radio frequency (RF) sources of the RF quadrupole accelerator, seven high-voltage power supplies, and distribution cabinets were delivered from the CIEMAT institute in Spain and the installation was started. In the Satellite Tokamak project, the development for long term operation technique of the neutral beam injector has been achieved and thereby confirmed to be feasible for long term operation of JT-60SA. The 340 torus assembly of vacuum vessel of the JT-60SA, which was started from May last year, has been completed. To send out information to the domestic community a major event in the BA activities.
torus assembly of vacuum vessel of the JT-60SA, which was started from May last year, has been completed. To send out information to the domestic community a major event in the BA activities.