Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Oya, Yasuhisa*; Li, X.*; Sato, Misaki*; Yuyama, Kenta*; Oyaizu, Makoto; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.402 - 405, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)The deuterium (D) permeation behaviors for ion damaged tungsten (W) by 3 keV D
 and 10 keV C
and 10 keV C were studied. The D permeability was obtained for un-damaged W at various temperatures. For both D
were studied. The D permeability was obtained for un-damaged W at various temperatures. For both D
 and C
and C implanted W, the permeability was clearly reduced. But, for the D
implanted W, the permeability was clearly reduced. But, for the D
 implanted W, the permeability was recovered by heating at 1173 K and it was almost consistent with that for un-damaged W. In the case of C
implanted W, the permeability was recovered by heating at 1173 K and it was almost consistent with that for un-damaged W. In the case of C implanted W, the permeability was not recovered even if the sample was heated at 1173 K, indicating that the existence of carbon would prevent the recovery of permeation path in W. In addition, TEM observation showed the voids were grown by heating at 1173 K and not removed, showing the existence of damages would not largely influence on the hydrogen permeation behavior in W in the present study.
implanted W, the permeability was not recovered even if the sample was heated at 1173 K, indicating that the existence of carbon would prevent the recovery of permeation path in W. In addition, TEM observation showed the voids were grown by heating at 1173 K and not removed, showing the existence of damages would not largely influence on the hydrogen permeation behavior in W in the present study.
Hayashi, Takumi; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*; Oyaizu, Makoto; Edao, Yuki; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(7-8), p.1520 - 1523, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:21.88(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium confinement is the most important safety issue in the fusion reactor. Tritium behavior on the water metal boundary is very important to design tritium plant with breading blanket system using cooling water. A series of tritium permeation experiment into pressurized water or water vapor jacket with He or Ar have been performed through pure iron piping with/without 7 micro-meter gold plating, which contained about 1 kPa of pure tritium gas at 423 K, with monitoring the chemical forms of tritium. Also, deuterium permeation experiments from heavy water vessel through various metal piping, such as pure iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), stainless steel (SS304), and pure iron with 10 micro-meter gold plating, were performed at 573 K and at 15 MPa. Recently, using the above heavy water system, we have succeeded to detect simultaneous hydrogen isotopes transfer from and to the metal surface by introducing H gas to the metal piping after stabilized deuterium permeation was detected.
gas to the metal piping after stabilized deuterium permeation was detected.
Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Oyaizu, Makoto; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 87(7-8), p.1333 - 1337, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:54.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to investigate the behavior of hydrogen isotope on the water-metal boundary, deuterium permeation experiments from heavy water vessel through various metal piping, such as pure iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), stainless steel (SS304), and pure iron with 10  m gold plating, were performed at 573 K and at 15 MPa. During the experiment, surfaces of metal piping except gold plating one were oxidized at the heavy water boundary and then deuterium would generate by the oxidation reactions. This deuterium could be detected by mass spectrometer, which monitored the inside gases of the piping under vacuum. The result showed clearly that the deuterium permeated through Fe, Ni, and SS304 piping was detected as deuterium gas (D
m gold plating, were performed at 573 K and at 15 MPa. During the experiment, surfaces of metal piping except gold plating one were oxidized at the heavy water boundary and then deuterium would generate by the oxidation reactions. This deuterium could be detected by mass spectrometer, which monitored the inside gases of the piping under vacuum. The result showed clearly that the deuterium permeated through Fe, Ni, and SS304 piping was detected as deuterium gas (D ) under vacuum, though that through gold plating one could not be detected effectively. The D
) under vacuum, though that through gold plating one could not be detected effectively. The D permeation rate through Fe, Ni, and SS304 piping reached some stabilized value. This paper summarizes the above experimental results and discusses the mechanism of deuterium behavior on the water metal boundary.
permeation rate through Fe, Ni, and SS304 piping reached some stabilized value. This paper summarizes the above experimental results and discusses the mechanism of deuterium behavior on the water metal boundary.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Hara, Masanori*; Sugiyama, Takahiko*; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 86(9-11), p.2152 - 2155, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is quite significant subject how to confine the tritium in a fusion reactor. Especially, it is strongly desired to get the data for tritiated water. This is because tritiated water is much hazardous than the hydrogen form of tritium. As for the behavior of high concentration tritium water, we could get a series of valuable data for the corrosion of the tritiated water against metal materials. In the case where a metal material is in water, an oxidized layer is formed at the surface of the metal. The oxidized layer functions as a passive layer for the corrosion. However, it has been observed that the formation of the oxidized layer was prevented by the presence of tritium in water (0.23 GBq/cc). The chemical exchange column has been applied in ITER as the tritium recovery system from tritiated water. A set of data for an advanced chemical exchange column has been obtained.
Kobayashi, Makoto*; Wang, W.*; Kurata, Rie; Matsuyama, Masao*; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Asakura, Yamato*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(1), p.403 - 406, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The trapping and release mechanisms of hydrogen isotopes for the stainless steel (SS) oxidized at various temperatures were investigated. The oxide layer was mainly consisted of iron oxides (Fe O
O ) and its decomposition temperature was almost consistent with the release temperature of deuterium, where major chemical form was a molecular deuterium (D
) and its decomposition temperature was almost consistent with the release temperature of deuterium, where major chemical form was a molecular deuterium (D ). The deuterium retention was increased as the oxidation temperature increased. It was considered that the thickness of oxide layer would make a large influence on the retention of hydrogen isotopes. On the other hand, the amount of released deuterium as heavy water (D
). The deuterium retention was increased as the oxidation temperature increased. It was considered that the thickness of oxide layer would make a large influence on the retention of hydrogen isotopes. On the other hand, the amount of released deuterium as heavy water (D O) was independent with oxidation temperature. It was considered that the formation of hydrogen isotope as water form was depended on the amount of Fe
O) was independent with oxidation temperature. It was considered that the formation of hydrogen isotope as water form was depended on the amount of Fe O
O on the top most surface layer of SS.
on the top most surface layer of SS.
Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Oyaizu, Makoto; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Science and Technology, 60(1), p.369 - 372, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.52(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kawamura, Yoshinori; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Okuno, Kenji*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 86(4), p.250 - 256, 2010/04
In case of nuclear fusion reactor, the most of the fuel injected is discharged without the reaction. Therefore, the system that can reuse the fuel discharged is necessary. And, at blanket located around the core plasma, tritium is made by the reaction of neutron and lithium, is recovered and is used as fuel. In the research and development of these fueling systems, the collaboration with US having the facility that can handle the large amount of tritium has become important. In this section, the results of the US-Japan collaboration related to the development of fueling system technology will be presented.
Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Hayashi, Takumi; Iwai, Yasunori; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Hara, Masanori*; Sugiyama, Takahiko*; Okuno, Kenji*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 85(10), p.716 - 725, 2009/10
In a fusion reactor, tritium must be handled in a vacuum vessel, a fuel cycle, and other systems. It is quite significant subject how to confine the tritium in these systems. ITER is the first machine in the world where the tritium confinement would be demonstrated. It is essential to establish a series of database for tritium handling technology to analyze the data obtained at ITER. Especially, it is strongly desired to get the data for tritium water. This is because tritium water is much hazardous than the hydrogen form of tritium. For these reasons, our attention is focused on the study on the behavior of tritium water in the fuel cycle system and structural materials of the system. As for the behavior of high concentration tritium water, we could get the first series of valuable data for the corrosion of the tritium water against metal materials in the world. The behavior of tritium in a surface area of metal and organic compounds was also discussed. As for tritium recovery from tritium water, we could get the data on an advanced chemical exchange column. The chemical exchange column has been applied in ITER as the tritium recovery system from tritium water. Our data showed that the column performance could be remarkably improved. Tritium durability and catalyst tests have also been carried out for the chemical exchange column. Some other possible method for the tritium recovery has also been studied such as an advance adsorption method.
Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Oyaizu, Makoto; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Ishikawa, Hirotada*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Science and Technology, 56(2), p.836 - 840, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:58.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kawamura, Yoshinori; Onishi, Yoshihiro*; Okuno, Kenji*; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(10-12), p.1384 - 1387, 2008/12
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:65.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)A gas chromatograph using a cryogenic separation column is one of the methods for hydrogen isotope analysis. However, use of liquid nitrogen is a cause of long analysis time and is not suitable for easy installation. The development of the column material having separation capability at comparatively high temperature is one of the solutions for these weak points. Mordenite (MOR) is a kind of the synthesis zeolite, and it has been reported that the separation column using MOR has possibility to separate hydrogen isotope mixture at comparatively high temperature. In this work, the separation columns using MOR were made and tested. The peaks of H and D
and D were mostly separated at 144 K, but they were not separated at 195 K. MOR column adjusted in this work was still not for the practical use. However, this result suggests the possibility of the existence of the synthesis zeolite that can separate hydrogen isotope mixture at comparatively high temperature.
were mostly separated at 144 K, but they were not separated at 195 K. MOR column adjusted in this work was still not for the practical use. However, this result suggests the possibility of the existence of the synthesis zeolite that can separate hydrogen isotope mixture at comparatively high temperature.
Isobe, Kanetsugu; Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Science and Technology, 54(2), p.533 - 536, 2008/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:43.28(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tritium permeation is one of key issues from the viewpoint of safety and tritium cycle. The oxide formed on metal surface was reported to act as barrier for hydrogen permeation due to its characters, such as low diffusivity and low solubility of hydrogen. On the other hand, the tritium behavior in the oxide as well as the interface of oxide (oxide-metal, oxide-water) is not clarified. The tritium permeation through pure iron, which was coated with its oxide, into water has been studied. Although some characteristics of tritium permeation through the oxide were found, the permeation mechanism through the oxide has not been clarified yet. The tritium distribution in the oxide can give us useful information of tritium behavior in the oxide / oxide-interface and help to understand the mechanism of tritium permeation through the oxide. In the present study, tritium distribution in the iron oxide is observed with tritium micro autoradiography.
Kawamura, Yoshinori; Onishi, Yoshihiro*; Okuno, Kenji*; Yamanishi, Toshihiko
Fusion Engineering and Design, 83(4), p.655 - 660, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:62.72(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a fusion reactor system, a monitoring of hydrogen isotopes including tritium is necessary from the viewpoint of safety control. A gas chromatography using a cryogenic separation column is one of the methods for hydrogen isotope analysis. However, use of a refrigerant such as liquid nitrogen is a cause of long analysis time and is not suitable for easy installation. The development of the column material having separation capability at fairly high temperature is one of the solutions for these weak points. Synthesis zeolite such as molecular sieve 5A is a probable candidate. If the factor effected to the hydrogen adsorption property of the synthesis zeolite is clarified, it may lead to the development of the new zeolite optimized to the separation column. So, in this work, adsorption isotherms of hydrogen and deuterium for mordenite were investigated. The amount of adsorption per unit weight was larger than that of molecular sieve 5A.
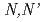 -dimethyl-
-dimethyl-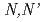 -diphenylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxyamide complexes
-diphenylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxyamide complexesFujiwara, Asako; Nakano, Yoshiharu*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 456(1-2), p.429 - 435, 2008/05
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:63.04(Chemistry, Physical)The tridentate ligand 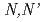 -dimethyl-
-dimethyl-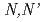 -diphenylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxyamide (DMDPhPDA) and the corresponding lanthanum complex [La(NO
-diphenylpyridine-2,6-dicarboxyamide (DMDPhPDA) and the corresponding lanthanum complex [La(NO )
) (DMDPhPDA)
(DMDPhPDA) ] have been prepared and structurally characterised. In the lanthanum complex, two DMDPhPDA molecules coordinated to La(III) in a tridentate fashion and to three nitrate ions in a bidentate fashion make the lanthanum atom 12-coordinate. The stability constants determined by spectrophotometric titration suggest that [Ln(DMDPhPDA)
] have been prepared and structurally characterised. In the lanthanum complex, two DMDPhPDA molecules coordinated to La(III) in a tridentate fashion and to three nitrate ions in a bidentate fashion make the lanthanum atom 12-coordinate. The stability constants determined by spectrophotometric titration suggest that [Ln(DMDPhPDA) ]
] is the primary product in nitrate media and [Ln(DMDPhPDA)
is the primary product in nitrate media and [Ln(DMDPhPDA) ]
] is difficult to form. However, [Ln(DMDPhPDA)
is difficult to form. However, [Ln(DMDPhPDA) ]
] could not be distinguished in
could not be distinguished in  C NMR spectra. The
C NMR spectra. The  C NMR titration results imply that a fast ligand exchange process takes place.
C NMR titration results imply that a fast ligand exchange process takes place.
Ushigusa, Kenkichi; Seki, Masahiro; Ninomiya, Hiromasa; Norimatsu, Takayoshi*; Kamada, Yutaka; Mori, Masahiro; Okuno, Kiyoshi; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Inoue, Takashi; Sakamoto, Keishi; et al.
Genshiryoku Handobukku, p.906 - 1029, 2007/11
no abstracts in English
Masaki, Kei; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Shibahara, Takahiro*; Hayashi, Takao; Sugiyama, Kazuyoshi*; Arai, Takashi; Okuno, Kenji*; Miya, Naoyuki
Nuclear Fusion, 47(11), p.1577 - 1582, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:43.79(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In JT-60U, erosion/deposition analyses for the plasma facing wall have shown that deposition was dominant at the inner-middle first wall and the inner divertor, whereas erosion dominant at the upper first wall and the outer divertor. Assuming toroidal symmetry in the erosion and deposition patterns, the net carbon erosion and deposition in the divertor area were estimated to be 0.34 kg and 0.55 kg, respectively. In a whole, the increment of carbon in the divertor region was 0.21 kg, which should be originated from the first wall. The hydrogen concentration in the thick deposition layer of the inner divertor was 0.02 in (H+D)/C. In the plasma-shadowed area underneath the divertor region at around 420 K, re-deposited layers of 2  m-thick were found with high hydrogen concentration of 0.8 in (H+D)/C. The carbon deposition rate in the plasma-shadowed area, however, was 8
m-thick were found with high hydrogen concentration of 0.8 in (H+D)/C. The carbon deposition rate in the plasma-shadowed area, however, was 8 10
10 atoms/s, which was one order smaller than that (6
atoms/s, which was one order smaller than that (6 10
10 atoms/s) on the wall surface.
atoms/s) on the wall surface.
Oya, Yasuhisa*; Hirohata, Yuko*; Nakahata, Toshihiko*; Suda, Taichi*; Yoshida, Masashi*; Arai, Takashi; Masaki, Kei; Okuno, Kenji*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*
Fusion Science and Technology, 52(3), p.554 - 558, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)To investigate retention characteristics of hydrogen isotopes in the first wall tiles of JT-60U, surface morphology, erosion/deposition profiles and hydrogen isotope retentions were examined by SEM, XPS, TDS and SIMS. It was found that poloidal deuterium retention profile was rather uniform, while the thermal desorption behavior of deuterium was quite different depending on the locations of the tiles. Deuterium retained in the upper first wall, where was covered by thick boron layers with high concentration of B, was desorbed at lower temperature than that in the lower area covered by carbon layers with much less B content. D/H ratio in the first wall tiles was appreciably higher than that observed in the divertor tiles, suggesting the injection of high energy deuteron originating from NBI into the first wall. In addition, the lower temperature of the first wall compared to that of the divertor tiles would prohibit desorption of the implanted deuterium and/or its replacement by subsequent D or H impingement.
Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Science and Technology, 52(3), p.696 - 700, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a fusion reactor of high safety and acceptability, safe confinement of tritium is one of key issues for the fusion reactor. Tritium should be well-controlled and not excessively released to the environment and to prevent workers from excess exposure. Especially, the hot cell and tritium facilities of ITER will use various construction materials. For tritium decontamination processes, so-called soaking effect is important. This effect is based on sorption of tritiated water vapor on the materials and subsequent desorption from them. Therefore, in order to develop for the optimal decontamination technique, the decontamination experiment was carried out as a function of water vapor concentration in the purging gas for epoxy paint, acrylic resin and butyl rubber. As the result, about 70% of the adsorbed tritium on the epoxy paint was removed by adding water vapor in purging gas for 12 hrs. The effect of adding water vapor was found on the decontamination for epoxy paint.
Hayashi, Takumi; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Okuno, Kenji*
Fusion Science and Technology, 52(3), p.687 - 691, 2007/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:56.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)How to confine tritium within high temperature breeding blanket is the key issue for safety and fuel economy of the fusion reactor. Specially, tritium permeation into cooling water is very important, however, there is little report of the systematic experiment comparing with that into gaseous coolant. Therefore, a series of tritium transportation experiments into water was performed through pure iron piping samples, which contained more than 1 kPa of pure tritium gas and fixed inside the water jacket under controlled temperature and pressure. Chemical species of tritium in water were measured during the experiment until reaching enough stable permeation, and tritium distribution/situation on the metal surface layer was also measured using autoradiography etc. after the experiment. In this paper, the results of tritium transportation experiments were summarized and tritium behavior on the boundary surface between metal piping and cooling water was discussed.
Nakahata, Toshihiko*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Oyaizu, Makoto*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Ishimoto, Yuki*; Kizu, Kaname; Yagyu, Junichi; Ashikawa, Naoko*; Nishimura, Kiyohiko*; Miya, Naoyuki; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 367-370(2), p.1170 - 1174, 2007/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.34(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Retention and desorption behavior of deuterium implanted into pure boron films has been studied by means of the secondary ion mass spectroscopy. It was found that the factor dominating deuterium desorption was the sample temperature. At stage 1, below 573 K, the desorption of deuterium from B-D-B bond dominated and diffusion was the rate-determining process in this stage. Above 573 K, deuterium was mainly desorbed from B-D bonds, and recombination was the rate-determining process in this stage. The effective molecular recombination rate constant of deuterium trapped as B-D bond was determined by an isothermal annealing experiment.
Ashikawa, Naoko*; Kizu, Kaname; Yagyu, Junichi; Nakahata, Toshihiko*; Nobuta, Yuji; Nishimura, Kiyohiko*; Yoshikawa, Akira*; Ishimoto, Yuki*; Oya, Yasuhisa*; Okuno, Kenji*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 363-365, p.1352 - 1357, 2007/06
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:59.87(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English