Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Srinivasan, A. R.*; Sauers, R. R.*; Fenley, M. O.*; Boschitsch, A. H.*; Matsumoto, Atsushi; Colasanti, A. V.*; Olson, W. K.*
Biophysical Reviews, 1(1), p.13 - 20, 2009/03
Matsumoto, Atsushi; Olson, W. K.*
Multiscale Modeling & Simulation, 5(4), p.1227 - 1247, 2006/00
A newly developed, coarse-grained treatment of the low-frequency normal modes of DNA has been adapted to study the torsional properties of fully extended, double-helical molecules. The calculations show how the end-to-end constraints placed on a naturally straight DNA molecule, in combination with the natural conformational features of the double helix, can account for the substantially larger torsional moduli determined with state-of-the-art, single-molecule experiments compared to values extracted from solution measurements and/or incorporated in theories to account for the force-extension properties of single molecules. The computed normal-mode frequencies and torsional moduli increase substantially if base pairs are inclined with respect to the double helical axis and the deformations of selected conformational variables follow known interdependent patterns.
Matsumoto, Atsushi; Olson, W. K.*
Normal Mode Analysis; Theory and Applications to Biological and Chemical Systems, p.187 - 211, 2005/12
Recently, we developed a new computational approach for studying the dynamic properties of relatively long DNA molecules without losing track of the local sequence-dependent features of the double helix. We make use of a dimeric representation of DNA, which incorporates the known effects of base sequence on the intrinsic structure and the elastic deformability of the constituent dinucleotide steps. This low-resolution model of DNA provides a straightforward way to deduce the effects of local structure and deformability on the configurational properties of polymeric sequences. This review focuses on the subtle relationship between DNA base sequence and collective polymeric motions gleaned from the normal-mode analysis of representative double helical molecules. We also discuss the interplay of superhelical stress and the natural coupling of local conformational variables on the large-scale configurational rearrangements of closed circular molecules and the direct physical micromanipulation of single linear chains.
Matsumoto, Atsushi; Tobias, I.*; Olson, W. K.*
Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 1(1), p.117 - 129, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:35.77(Chemistry, Physical)We have extended a newly developed approach to study the low frequency normal modes of mesoscopic fragments of linear DNA in order to investigate the dynamics of closed circular molecules of comparable size, i.e., a few hundred base pairs. We have added restraint energy terms and a global minimization step to treat the more complicated, spatially constrained duplex in terms of the intrinsic conformation and flexibility of the constituent base-pair "step" parameters.
Matsumoto, Atsushi; Tobias, I.*; Olson, W. K.*
Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 1(1), p.130 - 142, 2005/01
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:30.07(Chemistry, Physical)Fine structural and energetic details embedded in the DNA base sequence, such as intrinsic curvature, are important to the packaging and processing of the genetic material. Here we investigate the internal dynamics of a 200 bp closed circular molecule with natural curvature using a newly developed normal-mode treatment of DNA in terms of neighboring base-pair "step" parameters. As superhelical stress is accumulated in the DNA, the frequency, i.e., energy, of the dominant bending mode decreases in value, and if the imposed stress is sufficiently large, a global configurational rearrangement of the circle to the figure-8 form takes place. We combine energy minimization with normal-mode calculations of the two states to decipher the configurational pathway between the two states.
 A
A MnO
MnO (A=Ca,Sr)
(A=Ca,Sr)Kang, J.-S.*; Kim, J. H.*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Kasai, Shuichi*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Han, S. W.*; Kim, K. H.*; Choi, E. J.*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*; Muro, Takayuki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 68(1), p.012410_1 - 012410_4, 2003/07
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:68.23(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
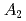 FeMoO
FeMoO double perovskites (
double perovskites ( =Sr, Ba)
=Sr, Ba)Kang, J.-S.*; Kim, J. H.*; Sekiyama, Akira*; Kasai, Shuichi*; Suga, Shigemasa*; Han, S. W.*; Kim, K. H.*; Muro, Takayuki*; Saito, Yuji; Hwang, C.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 66(11), p.113105_1 - 113105_4, 2002/09
Times Cited Count:65 Percentile:90.19(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The electronic structures of Sr FeMoO
FeMoO (SFMO) and Ba
(SFMO) and Ba FeMoO
FeMoO (BFMO) double perovskites have been investigated using Fe 2p-3d resonant photoemission spectroscopy (PES) and the Cooper minimum in the Mo 4d photoionization cross section. The states close to the Fermi level are found to have a strongly mixed Mo–Fe t
(BFMO) double perovskites have been investigated using Fe 2p-3d resonant photoemission spectroscopy (PES) and the Cooper minimum in the Mo 4d photoionization cross section. The states close to the Fermi level are found to have a strongly mixed Mo–Fe t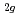 character, indicating that the Fe valence is far from pure 3+. The Fe 2p
character, indicating that the Fe valence is far from pure 3+. The Fe 2p x-ray absorption spectroscopy spectra reveal the mixed-valent Fe
x-ray absorption spectroscopy spectra reveal the mixed-valent Fe  –Fe
–Fe configurations, and a larger Fe
configurations, and a larger Fe component for BFMO than for SFMO, suggesting an operative double exchange interaction. The valence-band PES spectra reveal good agreement with the local-spin-density-approximation (LSDA+U) calculation.
component for BFMO than for SFMO, suggesting an operative double exchange interaction. The valence-band PES spectra reveal good agreement with the local-spin-density-approximation (LSDA+U) calculation.