Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tobita, Minoru*; Goto, Katsunori*; Omori, Takeshi*; Osone, Osamu*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Konda, Miki; Tsuchida, Daiki; Mitsukai, Akina; Ishimori, Kenichiro
JAEA-Data/Code 2023-011, 32 Pages, 2023/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field as trench and pit. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to the study of radioactivity concentration evaluation methods for radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3, JRR-4 and JAERI Reprocessing Test Facility. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 23 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2021-2022.
Tamura, Fumihiko; Omori, Chihiro*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Tomizawa, Masahito*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Sugiyama, Yasuyuki*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Kobayashi, Aine*; Okita, Hidefumi
Proceedings of 19th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.175 - 178, 2023/01
J-PARC MR delivers high intensity proton beams to the neutrino experiment. Eight bunches with high peak currents are extracted from the MR by the extraction kicker, therefore the neutrino beam has the similar structure. Intermediate Water Cherenkov Detector (IWCD) will be installed for the future experiments and the IWCD requires a time structure with low peaks. We consider bunch manipulation at flattop of the MR for reducing the peak current. It should be quickly done to avoid the significant loss of the beam power. The beam gap for the kicker rise time must be kept. We propose a non-adiabatic bunch manipulation using the multiharmonic rf voltage. The longitudinal impedance in the MR can affect the beam stability. The feasibility of the manipulation is discussed by using the longitudinal simulations.
Tobita, Minoru*; Konda, Miki; Omori, Takeshi*; Nabatame, Tsutomu*; Onizawa, Takashi*; Kurosawa, Katsuaki*; Haraga, Tomoko; Aono, Ryuji; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsuchida, Daiki; et al.
JAEA-Data/Code 2022-007, 40 Pages, 2022/11
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete, ash, ceramic and brick samples generated from JRR-3, JRR4 and JRTF facilities. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 24 radionuclides ( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Tc,
Tc,  Ag,
Ag,  I,
I,  Cs,
Cs,  Ba,
Ba,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2020-2021.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples in fiscal years 2020-2021.
Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Hayashi, Naoki; Saha, P. K.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Tani, Norio; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Kamiya, Junichiro; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1174 - 1205, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:74.40(Nuclear Science & Technology)In the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex, the purpose of the 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) is to accelerate a 1 MW, high-intensity proton beam. To achieve beam operation at a repetition rate of 25 Hz at high intensities, the RCS was elaborately designed. After starting the RCS operation, we carefully verified the validity of its design and made certain improvements to establish a reliable operation at higher power as possible. Consequently, we demonstrated beam operation at a high power, namely, 1 MW. We then summarized the design, actual performance, and improvements of the RCS to achieve a 1 MW beam.
Tsuchida, Daiki; Haraga, Tomoko; Tobita, Minoru*; Omori, Hiroyuki*; Omori, Takeshi*; Murakami, Hideaki*; Mitsukai, Akina; Aono, Ryuji; Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-022, 34 Pages, 2021/03
Radioactive wastes generated from nuclear research facilities in Japan Atomic Energy Agency are planning to be buried in the near surface disposal field. Therefore, it is required to establish the method to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations of radioactive wastes until the beginning of disposal. In order to contribute to this work, we collected and analyzed concrete samples generated from JRR-3 and JPDR. In this report, we summarized the radioactivity concentrations of 22 radionuclides( H,
H,  C,
C,  Cl,
Cl,  Ca,
Ca,  Co,
Co,  Ni,
Ni,  Sr,
Sr,  Nb,
Nb,  Ag,
Ag,  Ba,
Ba,  Cs,
Cs,  Eu,
Eu,  Eu,
Eu,  Ho,
Ho,  U,
U,  U,
U,  Pu,
Pu,  Pu,
Pu,  Am,
Am,  Am,
Am,  Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Cm) which were obtained from radiochemical analysis of the samples.
Kurihara, Momo*; Yasutaka, Tetsuo*; Aono, Tatsuo*; Ashikawa, Nobuo*; Ebina, Hiroyuki*; Iijima, Takeshi*; Ishimaru, Kei*; Kanai, Ramon*; Karube, Jinichi*; Konnai, Yae*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 322(2), p.477 - 485, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.09(Chemistry, Analytical)We assessed the repeatability and reproducibility of methods for determining low dissolved radiocesium concentrations in freshwater in Fukushima. Twenty-one laboratories pre-concentrated three of 10 L samples by five different pre-concentration methods (prussian-blue-impregnated filter cartridges, coprecipitation with ammonium phosphomolybdate, evaporation, solid-phase extraction disks, and ion-exchange resin columns), and activity of radiocesium was measured. The z-scores for all of the  Cs results were within
Cs results were within  2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
2, indicating that the methods were accurate. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) indicating the variability in the results from different laboratories were larger than the RSDs indicating the variability in the results from each separate laboratory.
Yoshida, Kensuke*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Higashiguchi, Takeshi*; Ugomori, Teruyuki*; Tanaka, Nozomi*; Kawasaki, Masato*; Suzuki, Yuhei*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tomita, Kentaro*; Hirose, Ryoichi*; et al.
Applied Physics Letters, 106(12), p.121109_1 - 121109_5, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:53.79(Physics, Applied)Yoshida, Kensuke*; Fujioka, Shinsuke*; Higashiguchi, Takeshi*; Ugomori, Teruyuki*; Tanaka, Nozomi*; Ohashi, Hayato*; Kawasaki, Masato*; Suzuki, Yuhei*; Suzuki, Chihiro*; Tomita, Kentaro*; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 7(8), p.086202_1 - 086202_4, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:74.37(Physics, Applied)We demonstrate high conversion efficiency for extreme ultraviolet (EUV) emission at 6.5-6.7 nm from multiple laser beam-produced one-dimensional spherical plasmas. Multiply charged-state ions produce strong resonance emission lines, which combine to yield intense unresolved transition arrays in Gd, Tb, and Mo. The maximum in-band EUV conversion efficiency was observed to be 0.8%, which is one of the highest values ever reported due to the reduction of plasma expansion loss.
Yamamoto, Masanobu; Nomura, Masahiro; Schnase, A.; Shimada, Taihei; Tamura, Fumihiko; Ezura, Eiji*; Hara, Keigo*; Hasegawa, Katsushi*; Omori, Chihiro*; Takagi, Akira*; et al.
Proceedings of 3rd International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '12) (Internet), p.2952 - 2954, 2012/05
In J-PARC RCS, the high intensity beam is delivered to the MR. The longitudinal beam emittance at the RCS extraction should be optimized to avoid the beam loss after the MR injection. In order to match the longitudinal emittance shape between the RCS and the MR, it is desirable to enlarge the longitudinal emittance during the RCS acceleration. We have performed the particle tracking simulation for the controlled longitudinal emittance blow up in the RCS.
Schnase, A.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Koseki, Tadashi*; Tomizawa, Masahito*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Nomura, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Toda, Makoto*; et al.
Proceedings of 7th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (DVD-ROM), p.1079 - 1081, 2010/08
Schnase, A.; Tamura, Fumihiko; Koseki, Tadashi*; Tomizawa, Masahito*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Omori, Chihiro*; Nomura, Masahiro; Yamamoto, Masanobu; Toda, Makoto*; et al.
Proceedings of 1st International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '10) (Internet), p.1446 - 1448, 2010/05
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Nakano, Tomohide; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; Iio, Shunji*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*; Ono, Yasushi*; Ozeki, Takahisa; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 82(7), p.448 - 450, 2006/07
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 82(2), p.109 - 110, 2006/02
no abstracts in English
Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Toi, Kazuo*; Fukuda, Takeshi*; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Fujita, Takaaki; Ogawa, Yuichi*; Takizuka, Tomonori; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Yagi, Masatoshi*; Yamada, Hiroshi*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(8), p.626 - 627, 2005/08
no abstracts in English
Kawano, Yasunori; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Kusama, Yoshinori; Sasao, Mamiko*; Sugie, Tatsuo; Mase, Atsushi*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kato, Takako*; Takamura, Shuichi*; Tanabe, Tetsuo*; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 81(2), p.128 - 130, 2005/02
no abstracts in English
Mori, Masahiro; Shoji, Teruaki; Araki, Masanori; Saito, Keiji*; Senda, Ikuo; Omori, Junji*; Sato, Shinichi*; Inoue, Takashi; Ono, Isamu*; Kataoka, Takahiro*; et al.
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 44(1), p.16 - 89, 2002/01
no abstracts in English
Omori, Junji*; Kobayashi, Takeshi; Yamada, Masao*; Iida, Hiromasa; Horie, Tomoyoshi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 9, p.207 - 211, 1989/00
no abstracts in English
Oka, Kiyoshi; Seki, Takeshi*; Komori, Yuki
no journal, ,
We developed a new minimally invasive laser device system using a composite-type optical fiberscope. The fiberscope consists of a centrally located  0.1 mm single fiber for laser treatment and its surrounding about 9,000 (
0.1 mm single fiber for laser treatment and its surrounding about 9,000 ( 5
5  m/piece) fibers for diagnosis. This system enables transmission of an image and 50 W Yb: fiber laser in parallel. By applying our fiberscope to laser treatment in various medical fields, it enables acquisition of an image, laser treatment, blood flow measurement, estimate of distance only in one fiberscope. By using this device for the PDT treatments applied to such as lung and cervical cancers, we expect to spot the irradiated area selectively while looking at a lesion. In this paper, we present a composition of minimally invasive laser therapy device using
m/piece) fibers for diagnosis. This system enables transmission of an image and 50 W Yb: fiber laser in parallel. By applying our fiberscope to laser treatment in various medical fields, it enables acquisition of an image, laser treatment, blood flow measurement, estimate of distance only in one fiberscope. By using this device for the PDT treatments applied to such as lung and cervical cancers, we expect to spot the irradiated area selectively while looking at a lesion. In this paper, we present a composition of minimally invasive laser therapy device using  1 mm composite-type optical fiberscope, the basics performance experiment result and an application to PDT therapy.
1 mm composite-type optical fiberscope, the basics performance experiment result and an application to PDT therapy.
 Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O
Yasui, Yukio*; Fujimura, Akio*; Omori, Kiyoshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
no journal, ,
The magnetic structure of Cs Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O with CuO
with CuO ribbon chains have been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. The magnetic reflections were observed below
ribbon chains have been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. The magnetic reflections were observed below 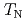 = 1.85 K and all of the magnetic reflections overlapped Bragg reflections. Considering that these are 16-Cu
= 1.85 K and all of the magnetic reflections overlapped Bragg reflections. Considering that these are 16-Cu ions in the unit cell, Cs
ions in the unit cell, Cs Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O has the collinear-antiferromagnetic structure.
has the collinear-antiferromagnetic structure.
 Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O with
with 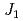 -
- 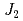 model
modelYasui, Yukio*; Fujimura, Akio*; Omori, Kiyoshi*; Igawa, Naoki; Matsukawa, Takeshi*; Yoshida, Yukihiko*; Hoshikawa, Akinori*; Ishigaki, Toru*
no journal, ,
The magnetic structure of Cs Cu
Cu Mo
Mo O
O has been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. Cu
has been studied by using the neutron powder diffraction. Cu spins collinearly ordinate along the
spins collinearly ordinate along the  axis and we found that this material has ferromagnetic structure in ribbon chains and antiferromagnetic structure between ribbon chains. Those results indicate that the magnetic structure is strongly inflected with ferromagnetic
axis and we found that this material has ferromagnetic structure in ribbon chains and antiferromagnetic structure between ribbon chains. Those results indicate that the magnetic structure is strongly inflected with ferromagnetic 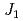 . In this presentation, the detail of magnetic structure of this material will be discussed.
. In this presentation, the detail of magnetic structure of this material will be discussed.