Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugai, Hiroyuki; Maeta, Hiroshi*; Matsumoto, Norimasa*; Kato, Teruo; Haruna, Katsuji*; Sataka, Masao; Ono, Fumihisa*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 4(8), p.2963 - 2966, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The synthetic semiconductor diamond is potentially one of the best materials for electronic devices in severe environments like high temperature and radiation. We have studied the electrical transport properties of boron-doped synthetic semiconductor diamond and characterized natural and synthetic single crystal diamonds by measurements of the X-ray integrated scattering intensity, lattice parameter and diffuse scattering. The synthetic diamond were irradiated with 100 MeV carbon-ion at Tandem accelerator in JAEA-Tokai. After the irradiation, measurements of lattice parameters X-ray diffuse scattering were made at room temperature. The lattice parameters increased with ion fluence. The scattering intensity of the irradiated synthetic diamond diffuses asymmetrically to form a streak along the [-1 0 0] direction parallel to the reciprocal lattice vector. The result suggests that interstitial atoms and vacancies aggregate to form dislocation loop on the (100) plane.
Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Iwase, Akihiro*; Ono, Fumihisa*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 257(1-2), p.388 - 391, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:58.18(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have already found that high-energy heavy ion irradiation modifies magnetic properties in Fe-Ni invar alloys, i.e. that the Curie temperature,  , increases by the irradiation. In the present paper, in order to clarify the mechanism of the modification, we investigate a dominant irradiation parameter for the modification. Specimens of Fe-Ni and Fe-Ni-Mn alloy thin films (
, increases by the irradiation. In the present paper, in order to clarify the mechanism of the modification, we investigate a dominant irradiation parameter for the modification. Specimens of Fe-Ni and Fe-Ni-Mn alloy thin films ( 500 nm in thickness) are prepared on MgO(100) single crystal substrates by rf magnetron sputtering. The specimens are irradiated at room temperature with several kinds of ions in the energy and mass ranges of 1.0-200 MeV and
500 nm in thickness) are prepared on MgO(100) single crystal substrates by rf magnetron sputtering. The specimens are irradiated at room temperature with several kinds of ions in the energy and mass ranges of 1.0-200 MeV and  H-
H- Au. A large increase in
Au. A large increase in  is observed for comparatively low-energy ion irradiation. This result suggests that the dominant process for the modification is the elastic interaction between incident ions and target atoms. The dependence on ion energy and fluence of the increase in
is observed for comparatively low-energy ion irradiation. This result suggests that the dominant process for the modification is the elastic interaction between incident ions and target atoms. The dependence on ion energy and fluence of the increase in  gives information on a dominant irradiation parameter.
gives information on a dominant irradiation parameter.
Ono, Fumihisa*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kanamitsu, Hiroaki*; Matsushima, Yasushi*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Kambara, Tadashi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 257(1-2), p.402 - 405, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:40.25(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Zushi, Yoshihiro*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Ono, Fumihisa*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 256(1), p.434 - 437, 2007/03
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:80.50(Instruments & Instrumentation)Fe-50at.%Rh alloys were irradiated with swift heavy ions such as 120 MeV Ni, 150 MeV Kr, 200 MeV Xe, 200 MeV Au, and it is found that low-temperature antiferromagnetic state changes to ferromagnetic state after the irradiations. The ion-fluence dependence and ion-species dependence was investigated. It is found that saturated magnetization evolves as fluence increases, and the evolution behavior for different ion-species differs from each other, but it scales with single universal curve as a function of total energy deposition via elastic collision.
Iwase, Akihiro*; Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Zushi, Yoshihiro*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Takagaki, Masafumi*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Mizuki, Junichiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Ono, Fumihisa*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 256(1), p.429 - 433, 2007/01
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:75.49(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have studied the effects of swift heavy ion irradiation on the magnetic properties of Fe-Rh intermetallic compound by using Fe K-edge X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) at 20 K. For an unirrdaiated specimen, no signal of XMCD spectrum has been observed because Fe-Rh intermetallic compound is intrinsically anti-ferromagnetic below room temperature. For the specimens irradiated with 120-200 MeV Ni, Kr, Xe or Au ions, we have found XMCD spectra which are characterized by a dispersion-type profile with a positive peak and a negative peak near Fe K-edge. The intensity of XMCD spectra remarkably depends on ion-fluence and ion-mass. The experimental result implies that the ferromagnetic state is induced by the swift heavy ion irradiation. The change in magnetic state of Fe element is discussed in terms of energy deposition through the elastic and electronic processes.
Fukuzumi, Masafumi*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Takagaki, Masafumi*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Ono, Fumihisa*; Neumann, R.*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.161 - 165, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:74.77(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have performed swift heavy ion irradiations in Fe-50at.%Rh alloys at room temperature. Before and after the irradiations, the magnetic properties and the lattice structure are measured using Superconducting QUantum Interference Device (SQUID) and X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD), respectively. We have also performed X-ray Magnetic Circular Dichroism (XMCD) measurement near the Fe K-edge at the synchrotron radiation facility, SPring-8, to examine the irradiation-induced ferromagnetic state near the specimen surface. We have found that the swift heavy ion irradiations induce the ferromagnetic state in Fe-50at.%Rh alloy below the antiferromagnetism-ferromagnetism transition temperature of the unirradiated alloy and the lattice expasion by 0.3%. For the specimens irradiated with swift heavy ions, we observe the XMCD spectra correponding to ferromagnetisim, which depend on the mass of irradiating ions and/or irradiation fluence. Effects of energy loss through electronic excitation and elastic collisions on lattice and magnetic structures of Fe-Rh alloy are discussed.
Ono, Fumihisa*; Kanamitsu, Hiroaki*; Matsushima, Yasushi*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kambara, Tadashi*; Iwase, Akihiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 245(1), p.166 - 170, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:33.81(Instruments & Instrumentation)Specimens of both ordered and disordered Fe-28.3at.%Pt alloys were irradiated with 200-MeV Xe ions to the fluence of 10 ions/cm
ions/cm . Measurements of AC-susceptibility-temperature curves were made for each specimen before and after the irradiation by using a specially designed apparatus for rapid measurements. In contrast to the expectation from the previous results for Fe-Ni alloys, in disordered Fe-Pt invar alloy the Curie temperature, T
. Measurements of AC-susceptibility-temperature curves were made for each specimen before and after the irradiation by using a specially designed apparatus for rapid measurements. In contrast to the expectation from the previous results for Fe-Ni alloys, in disordered Fe-Pt invar alloy the Curie temperature, T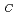 decreased about 15 K by the irradiation. This fact cannot be explained by considering the lattice expansion effect alone. In Fe-Pt invar alloys the effect of lattice expansion may be cancelled out by some other effects which may be originated from the large difference in atomic mass between the two elements. For ordered Fe-Pt alloy, T
decreased about 15 K by the irradiation. This fact cannot be explained by considering the lattice expansion effect alone. In Fe-Pt invar alloys the effect of lattice expansion may be cancelled out by some other effects which may be originated from the large difference in atomic mass between the two elements. For ordered Fe-Pt alloy, T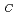 decreased as large as 60 K with the same fluence. The value of T
decreased as large as 60 K with the same fluence. The value of T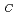 for both ordered and disordered Fe-Pt invar alloys coincide with each other after the irradiation. This fact can be explained by considering that the ordered state becomes disordered by the irradiation.
for both ordered and disordered Fe-Pt invar alloys coincide with each other after the irradiation. This fact can be explained by considering that the ordered state becomes disordered by the irradiation.
Maeta, Hiroshi*; Matsumoto, Norimasa*; Haruna, Katsuji*; Saotome, Takao*; Ono, Fumihisa*; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Otsuka, Hideo; Ohashi, Kazutoshi*
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 376-377, p.283 - 287, 2006/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:17.14(Physics, Condensed Matter)Natural and synthetic single crystal diamonds (type Ia, Ib, IIa and IIb) have been characterized by measurements of the X-ray integrated scattering intensity, lattice parameter and diffuse scattering. We found that the lattice parameter is smallest for natural diamond and largest for the B-doped diamond. We measured the diffuse scattering for (400) Bragg reflection for the four types of crystals. The scattering intensity of the natural crystals diffuses asymmetrically to form a streak along the [100] direction parallel to the reciprocal lattice vector. These results suggest the existence of the nitrogen atom platelets on (100) plane in the natural diamond. We also found the diffuse streaks along the [ 00] direction for (400) Bragg reflection for the B-doped crystal, suggesting that boron atoms are likely to form precipitates on the (100) plane.
00] direction for (400) Bragg reflection for the B-doped crystal, suggesting that boron atoms are likely to form precipitates on the (100) plane.
Matsushima, Yasushi*; Sun, N. Q.*; Kanamitsu, Hiroaki*; Matsushita, Masafumi*; Iwase, Akihiro*; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Ishikawa, Norito; Kambara, Tadashi*; Ono, Fumihisa*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 298(1), p.14 - 18, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:37.35(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Pressure dependence of the irradiation-induced ferromagnetism recently found in Fe-Ni invar alloys was investigated under hydrostatic pressures up to 7.5 GPa. A rectangular sheet of Fe-30.2at% Ni invar alloy was irradiated with 80-MeV Xe ions. The range was much smaller than the thickness of the sample. The Curie temperature of the irradiated part increased by 63 K, and the absolute value of the pressure coefficient, d
 /d
/d was smaller than that of non-irradiated part. The relation
was smaller than that of non-irradiated part. The relation 
 (
(
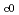 -
- 
 )
)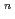 holds with n = 2 for both non-irradiated and irradiated part. The itinerant character was not so much modified by irradiation.
holds with n = 2 for both non-irradiated and irradiated part. The itinerant character was not so much modified by irradiation.
Iwase, Akihiro; Hamatani, Yutaro*; Mukumoto, Yoshinori*; Ishikawa, Norito; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Kambara, Tadashi*; M ller, C.*; Neumann, R.*; Ono, Fumihisa*
ller, C.*; Neumann, R.*; Ono, Fumihisa*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 209(1-4), p.323 - 328, 2003/08
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:78.93(Instruments & Instrumentation)Fe=Ni Invar alloy is irradiated with GeV Xe and U ions at room temperature. By the irradiation, the Curie temperature of the soecimens increases, which is correlated with the electronic stopping power. This phenomenon can be explained as due to the lattice expansion and/or the local increase in Ni concentration.
Maeta, Hiroshi; Yamakawa, Koiji*; ; Haruna, K.*; Kato, Teruo; Ono, Fumihisa*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 97, p.491 - 494, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Maeta, Hiroshi; Haruna, K.*; B.Lu*; Ono, Fumihisa*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 80-81, p.1477 - 1479, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:57.21(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO single crystal superconductor by X-ray diffraction
single crystal superconductor by X-ray diffractionMaeta, Hiroshi; Kato, Teruo; Ono, Fumihisa*; Haruna, K.*; ;
Physica C, 185-189, p.1383 - 1384, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Norito; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Takagaki, Masafumi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Mizuki, Junichiro; Zushi, Yoshihiro*; Fujita, Naoki*; Hori, Fuminobu*; Seki, Shuhei*; Tsukuda, Satoshi*; et al.
no journal, ,
It is already found that magnetic transition temperature of Fe-50at.%Rh changes by high-energy ion irradiation. This irradiation-induced changes in magnetic properties has been investigated by magnetic force microscopy. It has been found that microscopic magnetic structure appears after ion-irradiation, and the structure changes depending on the ion-fluence. The observed structure was not the same as that observed for Fe-rich ferromagnetic Fe-45at.%Rh alloys.
Chuto, Toshinori; Nagase, Fumihisa; Ono, Katsuto; Fuketa, Toyoshi
no journal, ,
In order to investigate effect of burnup on high temperature oxidation of the advanced cladding alloys, isothermal oxidation tests were performed with specimens prepared from high burnup fuel cladding which were irradiated up to 79 MWd/kg as well as non-irradiated cladding. Oxidation kinetics was evaluated from weight gain and oxide layer growth. Oxide layer thickness on the cladding outside diameter (OD) is smaller in the irradiated cladding. It is considered that the oxidation at the cladding OD was suppressed by the pre-formed corrosion layer. Results of the weight gain measurement also suggest lower oxidation rates in the irradiated cladding. Difference in the alloy composition hardly affected the oxidation rates.