Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamamoto, Keisuke; Nakagawa, Takuya; Shimojo, Hiroto; Kijima, Jun; Miura, Daiya; Onose, Yoshihiko*; Namba, Koji*; Uchida, Hiroaki*; Sakamoto, Kazuhiko*; Ono, Chika*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2024-019, 211 Pages, 2025/02
The uranium enrichment facilities at the Nuclear Fuel Cycle Engineering Laboratories of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) were constructed sequentially to develop uranium enrichment technology with centrifugal separation method. The developed technologies were transferred to Japan Nuclear Fuel Limited until 2001. And the original purpose has been achieved. Wastewater Treatment Facility, one of the uranium enrichment facilities, was constructed in 1976 to treat radioactive liquid waste generated at the facilities, and it finished the role in 2008. In accordance with the Medium/Long-Term Management Plan of JAEA Facilities, interior equipment installed in this facility had been dismantled and removed since November 2021 to August 2023. This report summarizes the findings obtained through the work related to the contamination inspection methods cancellation the controlled area of Wastewater Treatment Facility from September 2023 to March 2024.
Tanabe, Kenji*; Chiba, Daichi*; Oe, Junichiro*; Kasai, Shinya*; Kono, Hideo*; Barnes, S. E.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Ono, Teruo*
Nature Communications (Internet), 3, p.845_1 - 845_5, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:44 Percentile:82.44(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Sugai, Hiroyuki; Maeta, Hiroshi*; Matsumoto, Norimasa*; Kato, Teruo; Haruna, Katsuji*; Sataka, Masao; Ono, Fumihisa*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 4(8), p.2963 - 2966, 2007/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)The synthetic semiconductor diamond is potentially one of the best materials for electronic devices in severe environments like high temperature and radiation. We have studied the electrical transport properties of boron-doped synthetic semiconductor diamond and characterized natural and synthetic single crystal diamonds by measurements of the X-ray integrated scattering intensity, lattice parameter and diffuse scattering. The synthetic diamond were irradiated with 100 MeV carbon-ion at Tandem accelerator in JAEA-Tokai. After the irradiation, measurements of lattice parameters X-ray diffuse scattering were made at room temperature. The lattice parameters increased with ion fluence. The scattering intensity of the irradiated synthetic diamond diffuses asymmetrically to form a streak along the [-1 0 0] direction parallel to the reciprocal lattice vector. The result suggests that interstitial atoms and vacancies aggregate to form dislocation loop on the (100) plane.
Nakamura, Jinichi; Uetsuka, Hiroshi; Kono, Nobuaki; ; ; Furuta, Teruo
HPR-345 (Vol. II), 0, 13 Pages, 1995/00
no abstracts in English
Maeta, Hiroshi; Yamakawa, Koiji*; ; Haruna, K.*; Kato, Teruo; Ono, Fumihisa*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 97, p.491 - 494, 1995/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Noda, Kenji; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; ; Matsuo, Hideto; Watanabe, Katsutoshi; Kikuchi, Teruo; Usui, Takeshi; Oyama, Yukio; Ono, Hideo; Kondo, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 191-194, p.1367 - 1371, 1992/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.65(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Noda, Kenji; Matsuo, Hideto; Watanabe, Katsutoshi; Sugimoto, Masayoshi; ; ; Kikuchi, Teruo; Oyama, Yukio; Ono, Hideo; Kondo, Tatsuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 179-181, p.1147 - 1150, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:68.95(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
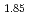 Sr
Sr CuO
CuO single crystal superconductor by X-ray diffraction
single crystal superconductor by X-ray diffractionMaeta, Hiroshi; Kato, Teruo; Ono, Fumihisa*; Haruna, K.*; ;
Physica C, 185-189, p.1383 - 1384, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:43.33(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
Hiroki, Akihiro; Iwanaga, Shigeru; Tamada, Masao; Okabe, Toshihiro*; Ono, Hiroyuki*; Hatayama, Ichiro*; Waguri, Atsushi*; Sawada, Yuzuru*; Nakane, Akio*; Sano, Teruo*
no journal, ,
Aomori Hiba oil is oil of the natural thing origin extracted from the sawdust generated during lumbering of Aomori Hiba that is the tree in Aomori prefecture by the steam distillation. The extracted Aomori Hiba oil has excellent antibacterial and insecticidal effects. To heighten the added value of the Aomori Hiba oil, the water-soluble nano-hiba oil with about 10 nm of particle size was developed by applying emulsification technology to the oil. The emulsified Aomori Hiba oils showed no signs of phase separation and remained intact even six months after its preparation. Since the nano-hiba oil can be sprayed quickly, antibacterial examinations were carried out to explore potential applications in preventions of hospital infection and damages caused by blight and insect in agricultural environments. Furthermore, a novel antibacterial material composed of nano-hiba oil and water-absorption biodegradable gel was investigated. Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) hydrogels as support materials for the nano-hiba oil were prepared by irradiating to paste-like aqueous solutions of HPC. Degree of swelling of the HPC hydrogels was influenced by compositions in nano-hiba oils. Subsequently, absorbability in nano-hiba oil as well as the antibacterial effects was evaluated. The HPC hydrogels swollen in the nano-hiba oil mixing silica showed excellent antibacterial effect up to three weeks. Therefore, it was suggested that the hydrogels containing nano-hiba oil are suitable as antibacterial materials.
Yamashita, Teruo; Miura, Akihiko; Kato, Junya; Shiotsuki, Masao; Ono, Isamu*; Fukui, Toshiki*; Yamasaki, Akito*; Matsumoto, Shiro*
no journal, ,
The objective of this development is to extend vitrification melter life-time to reduce burden of the high level radioactive waste management by applying advanced technologies. The candidate concepts of the long-life melter were studied with evaluation of adopted important advanced technologies such as skull layer conditions and the commutative electrode structure. It was concluded that such technology has a potential to extend melter life as 20 years even in the preliminary studies. Based on the obtained results, after the following fiscal year, evaluation of each component, small scale melter examination, and development and evaluation of simulation tool are carried out.
Yamashita, Teruo; Masaki, Toshio; Shiotsuki, Masao; Yamasaki, Akito*; Ito, Toshiyuki*; Ono, Isamu*; Matsumoto, Shiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamashita, Teruo; Masaki, Toshio; Kojima, Keizo; Shiotsuki, Masao; Ito, Toshiyuki*; Ono, Isamu*; Matsumoto, Shiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Okabe, Toshihiro*; Ono, Hiroyuki*; Hatayama, Ichiro*; Waguri, Atsushi*; Sawada, Yuzuru*; Tsugawa, Hidehito*; Ichida, Tadao*; Nakane, Akio*; Sano, Teruo*; Tanaka, Kazuaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Nishihara, Kenji; Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Nakayama, Shinichi; Fujiwara, Takeshi; Kobayashi, Hidekazu; Kano, Shigeru; Sasage, Kenichi; Yamashita, Teruo; Ono, Kiyoshi; Shiotani, Hiroki
no journal, ,
The reduction of the storage facility and repository were evaluated for the cases with or without partitioning of Sr-Cs and transmutation of MA in the advanced FBR fuel cycle with the cost estimation for the storage facilities, transporting and repository. As the result, the transmutation of minor actinides is inevitable for the small repository because the heat generation by  Am is considerable in FBR. The introduction of partitioning, transmutation and long-term storage enable the very compact layout in the repository like TRU wastes such as hulls and end-pieces of the fuel assembly. The cost for the storage and disposal in this case is much smaller than that in other cases, which mitigates the cost increase by the separation process and transmutor.
Am is considerable in FBR. The introduction of partitioning, transmutation and long-term storage enable the very compact layout in the repository like TRU wastes such as hulls and end-pieces of the fuel assembly. The cost for the storage and disposal in this case is much smaller than that in other cases, which mitigates the cost increase by the separation process and transmutor.