Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Nobuaki*; Kameo, Yutaka; Sato, Soichi; Kumagai, Yuta; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Nagai, Takayuki; Niibori, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masayuki; et al.
Introduction to Dismantling and Decommissioning Chemistry, 251 Pages, 2024/09
This book focuses on the dismantling and decommissioning of nuclear facilities and reactors that have suffered severe accidents. In Part 1, we introduce basic aspects ranging from fuel chemistry, analytical chemistry, radiation chemistry, corrosion, and decontamination chemistry to waste treatment and disposal. Then, Part 2 covers the chemistry involved in the decommissioning of various nuclear facilities, and discusses what chemical approaches are necessary and possible for the decommissioning of TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants, how decommissioning should be carried out, and what kind of research and development and also human resource development are required for this.
 /MOX fuel oxidation under severe light water reactor accident conditions
/MOX fuel oxidation under severe light water reactor accident conditionsLiu, J.; Miwa, Shuhei; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 37, p.101532_1 - 101532_5, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Sr (
Sr (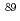 Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areas
Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areasMachida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(4), p.119 - 139, 2023/11
We estimate monthly discharged inventory of  Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of
Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of  Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Mohamad, A. B.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.215 - 222, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Machida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(3), p.258 - 276, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:60.29(Nuclear Science & Technology)We estimate monthly discharge inventory of tritium from the port of Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2020 using the Voronoi tessellation scheme, following the tritium monitoring results inside the port started in Jun. 2013. As for the missing period from the first month of 1F accident, Apr. 2011 to May 2013, we calculate the tritium discharge inventory by utilizing the concentration ratio of tritium to  Cs in stagnant contaminant water during the initial direct run-off period until Jun. 2011 and the discharge inventory correlation between tritium and
Cs in stagnant contaminant water during the initial direct run-off period until Jun. 2011 and the discharge inventory correlation between tritium and  Cs for the next-unknown continuous-discharge period from Jul. 2011 to May 2013. From all the estimated results over 9 years, we find that the monthly discharge inventory sharply dropped immediately after closing the seaside impermeable wall in Oct. 2015 and consequently coincided well with the sum of input inventories of drainage water and subdrain etc. purified water into the port. By comparing the above estimated results with those in the normal operation period before the accident, we point out that the discharge inventory from 1F port after the accident is not so large. Even the estimation value for the accident year 2011 is found to be comparable to the maximum of operating pressurized water reactors releasing relatively large inventories in the order. At the national level, the total domestic release inventory in Japan significantly decreased after the accident owing to the operational shutdown of most plants. Furthermore, the total Japanese discharge inventory including 1F are found to be minor compared with those of nuclear reprocessing plants and heavy-water reactors on a worldwide level. From the above results, we suggest that various scenarios can be openly discussed regarding the management of tritium stored inside 1F with the help of the present estimated data and its comparison with the past discharge inventory as well as those of other nuclear facilities.
Cs for the next-unknown continuous-discharge period from Jul. 2011 to May 2013. From all the estimated results over 9 years, we find that the monthly discharge inventory sharply dropped immediately after closing the seaside impermeable wall in Oct. 2015 and consequently coincided well with the sum of input inventories of drainage water and subdrain etc. purified water into the port. By comparing the above estimated results with those in the normal operation period before the accident, we point out that the discharge inventory from 1F port after the accident is not so large. Even the estimation value for the accident year 2011 is found to be comparable to the maximum of operating pressurized water reactors releasing relatively large inventories in the order. At the national level, the total domestic release inventory in Japan significantly decreased after the accident owing to the operational shutdown of most plants. Furthermore, the total Japanese discharge inventory including 1F are found to be minor compared with those of nuclear reprocessing plants and heavy-water reactors on a worldwide level. From the above results, we suggest that various scenarios can be openly discussed regarding the management of tritium stored inside 1F with the help of the present estimated data and its comparison with the past discharge inventory as well as those of other nuclear facilities.
Machida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(1), p.12 - 24, 2023/01
We estimate inventory of tritium in two sea areas corresponding to coastal and offshore ones around Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) based on the measurement results of sea-water tritium concentration monitored constantly from 2013 to Jan. 2021 by using Voronoi tessellation scheme. The obtained results show that the offshore area inventory and its temporal variation amount correspond to approximately 1/5 and 1/40 of that of the treated-water accumulated inside 1F, respectively. These results just suggest that the presence of tritium already included in sea-water as the background is non negligible in evaluating the environmental impact by releasing the accumulated treated-water into the sea region. We also estimate the offshore area inventory before 1F accident and find that it had exceeded over 1F stored inventory over about 30 years from 1960s to 1980s with approximately 4 times larger in the peak decade, 1960s. This fact means that we had already experienced more contaminated situation over 30 years in the past compared to the conservative case appeared by just releasing whole the present 1F inventory. Here, it should be also emphasized that the past contaminated situation was shared by the entire world. We further extend the estimation region into a wider region including an offshore area from Miyagi to Chiba prefectures and find that the area average inventory is now comparable to a half of the present 1F one. Finally, we estimate internal dose per year via ingesting fishes caught inside the area when 1F inventory is just added inside the area and kept for a year. The result indicates that it approximately corresponds to 1.0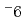 of the dose from natural radiation sources. From these estimation results, it is found that all the tritium inventory stored inside 1F never contribute to significant dose increment even when it is instantly released into the area.
of the dose from natural radiation sources. From these estimation results, it is found that all the tritium inventory stored inside 1F never contribute to significant dose increment even when it is instantly released into the area.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Koyama, Shinichi; Osaka, Masahiko; Takano, Masahide; Nakamura, Satoshi; Onozawa, Atsushi; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Maeda, Koji; Kirishima, Akira*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2022-021, 224 Pages, 2022/10
A set of technology, including acid dissolving, has to be established for the analysis of content of elements/nuclides in the fuel debris samples. In this project, a blind test was performed for the purpose of clarifying the current level of analytical accuracy and establishing the alternative methods in case that the insoluble residue remains. Overall composition of the simulated fuel debris (homogenized powder having a specific composition) were quantitatively determined in the four analytical institutions in Japan by using their own dissolving and analytical techniques. The merit and drawback for each technique were then evaluated, based on which a tentative flow of the analyses of fuel debris was constructed.
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
ACS Omega (Internet), 7(33), p.29326 - 29336, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.08(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Liu, J.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Miwa, Shuhei; Shirasu, Noriko; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(4), p.484 - 490, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Suzuki, Chikashi; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.345 - 356, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)During a severe accident (SA) such as the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, fission products (FP) can be retained on the surface of structural materials in reactors. Cesium (Cs) is an important FP, and various Cs compounds such as Cs silicates are formed on the surface of stainless steel (SS) in a reactor during a SA. We calculated total energies of Cs-Si-O compounds for evaluation on phase stability within an adiabatic approximation. The calculations indicate that Cs Si
Si O
O is the most stable of the Cs-Si-O compounds. We calculated, furthermore, total energies of Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds. These calculations indicate that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds are more stable than C-Si-O compounds and that CsSi
is the most stable of the Cs-Si-O compounds. We calculated, furthermore, total energies of Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds. These calculations indicate that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds are more stable than C-Si-O compounds and that CsSi FeO
FeO is the most stable of these C-Si-O and Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds within an adiabatic approximation. The results of our present calculations and our previous experiments lead to the conclusion that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds can be stably formed on SS surface by Cs chemisorption.
is the most stable of these C-Si-O and Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds within an adiabatic approximation. The results of our present calculations and our previous experiments lead to the conclusion that Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds can be stably formed on SS surface by Cs chemisorption.
Osaka, Masahiko; Gou llo, M.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa
llo, M.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(3), p.292 - 305, 2022/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)Research on the fission product chemistry made after the severe accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station were reviewed with focus on the Cesium chemistry in terms of two regimes, namely the accidental source term and the long-term source term via aqueous phase towards the decommissioning. For the accidental source term, Cs chemical interaction with Mo, B and Si were reviewed. Regarding the unique issue of long-term source term via aqueous phase, Cs penetration into concrete and fuel debris leaching were mentioned as the main sources of FPs. Efforts on the preparation of thermodynamic data for the Cs complex oxides were described. All these Cs chemical behaviors should be modelled and validated/verified through the analysis and evaluation of the actual samples including fuel debris that would be taken from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station in near future.
Machida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 21(1), p.33 - 49, 2022/03
We estimate monthly discharge inventory of tritium from the port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun 2013 to Mar 2020 by using the Voronoi tessellation scheme, following that the tritium monitoring inside the port has started since Jun 2013. As for the missing period from the initial month, Apr 2011 to May 2013, we calculate it by utilizing the concentration ratio of tritium to that of  Cs in stagnant contaminant water during the initial direct discharged period to Jun 2011 and the discharge inventory correlation between tritium and
Cs in stagnant contaminant water during the initial direct discharged period to Jun 2011 and the discharge inventory correlation between tritium and  Cs for the next-unknown continuously-discharged period up to May 2013. From the all- estimated results over 9 years, we find that the monthly discharge inventory sharply dropped just after closing the sea-side impermeable sea-wall in Oct. 2015 and subsequently coincided well with the sum of those of drainage and subdrain. By comparing the estimated results with those in the normal operation period before the accident, we point out that the discharge inventory from 1F port is not so large compared to those during the normal operation. Even the estimated one in year 2011 is found to be comparable to the maximum of operating pressurized water reactors discharging relatively large inventory in the order. In the nation level, the whole Japan domestic discharge inventory significantly decreased after the accident due to operation shutdown of most plants. Furthermore, 1F and even Japanese total discharge inventory are found to be entirely minor when comparing those of nuclear reprocessing plants and heavy-water reactors in world-wide level. From the above, we suggest that various scenarios can be openly discussed on the management in tritium stored inside 1F with help of the present estimated data and its comparison with the past discharge inventory.
Cs for the next-unknown continuously-discharged period up to May 2013. From the all- estimated results over 9 years, we find that the monthly discharge inventory sharply dropped just after closing the sea-side impermeable sea-wall in Oct. 2015 and subsequently coincided well with the sum of those of drainage and subdrain. By comparing the estimated results with those in the normal operation period before the accident, we point out that the discharge inventory from 1F port is not so large compared to those during the normal operation. Even the estimated one in year 2011 is found to be comparable to the maximum of operating pressurized water reactors discharging relatively large inventory in the order. In the nation level, the whole Japan domestic discharge inventory significantly decreased after the accident due to operation shutdown of most plants. Furthermore, 1F and even Japanese total discharge inventory are found to be entirely minor when comparing those of nuclear reprocessing plants and heavy-water reactors in world-wide level. From the above, we suggest that various scenarios can be openly discussed on the management in tritium stored inside 1F with help of the present estimated data and its comparison with the past discharge inventory.
Rizaal, M.; Miwa, Shuhei; Suzuki, Eriko; Imoto, Jumpei; Osaka, Masahiko; Gou llo, M.*
llo, M.*
ACS Omega (Internet), 6(48), p.32695 - 32708, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:24.90(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Imoto, Jumpei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 20(4), p.179 - 187, 2021/12
Some of the Cs inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station would be deposited in chemical forms such as CsI and Cs MoO
MoO . Since Cs compounds are generally water-soluble, it is predicted that the migration of Cs through the aqueous phase occurs in the long term. Knowledge of the solubility in water is required as basic data for such migration behavior evaluation. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the dissolution properties of CsI and Cs
. Since Cs compounds are generally water-soluble, it is predicted that the migration of Cs through the aqueous phase occurs in the long term. Knowledge of the solubility in water is required as basic data for such migration behavior evaluation. Therefore, this study was conducted to investigate the dissolution properties of CsI and Cs MoO
MoO in water at 20
in water at 20 C and 25
C and 25 C. The solubilities of CsI at 25
C. The solubilities of CsI at 25 C calculated using thermodynamic data and the Pitzer ion interaction model were in good agreement with the literature value. It was found that the literature value of CsI at around room temperature is highly reliable. The experimental value of CsI at 20
C calculated using thermodynamic data and the Pitzer ion interaction model were in good agreement with the literature value. It was found that the literature value of CsI at around room temperature is highly reliable. The experimental value of CsI at 20 C obtained by the OECD test guideline 105 flask method (test guideline) was also in good agreement with the literature value. The measured solubility of Cs
C obtained by the OECD test guideline 105 flask method (test guideline) was also in good agreement with the literature value. The measured solubility of Cs MoO
MoO was 256.8
was 256.8  6.2 (g/100 g H
6.2 (g/100 g H O) at 20
O) at 20 C using the test guideline. This measured solubility of Cs
C using the test guideline. This measured solubility of Cs MoO
MoO was found to be comparable to those of other alkaline molybdates and considered to be more reliable than the literature value.
was found to be comparable to those of other alkaline molybdates and considered to be more reliable than the literature value.
Koyama, Shinichi; Nakagiri, Toshio; Osaka, Masahiko; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Kurata, Masaki; Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Maeda, Koji; Sasaki, Shinji; Onishi, Takashi; Takano, Masahide; et al.
Hairo, Osensui Taisaku jigyo jimukyoku Homu Peji (Internet), 144 Pages, 2021/08
JAEA performed the subsidy program for the "Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management (Development of Analysis and Estimation Technology for Characterization of Fuel Debris (Development of Technologies for Enhanced Analysis Accuracy and Thermal Behavior Estimation of Fuel Debris))" in 2020JFY. This presentation summarized briefly the results of the project, which will be available shortly on the website of Management Office for the Project of Decommissioning and Contaminated Water Management.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Kino, Chiaki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 380, p.111256_1 - 111256_19, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:55.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is essential to grasp the long-term distributions of FP as well as fuel debris all over the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) for safe completion of its decommissioning projects. The fuel debris is going to be removed from the plant under the severe conditions of FP being scattered during major decommissioning work, and then, the decommissioning projects are going to be terminated by storing safely the removed debris as recovered fertile materials or as materials for final radioactive disposal. In order to determine the FP distribution in the plant for the long period from the accident occurrence to the termination of the plant decommissioning, procedures for analyzing multi-term FP behaviors were proposed. The proposed procedures should be improved by applying the FP data measured in the plant and validated based on the feedback data. Then, the accuracy-improved procedures should be applied to estimate FP distribution during each period of the decommissioning projects.
Liu, J.; Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 26, p.100916_1 - 100916_6, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:30.71(Nuclear Science & Technology)Miyahara, Naoya; Miwa, Shuhei; Gou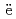 llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
llo, M.*; Imoto, Jumpei; Horiguchi, Naoki; Sato, Isamu*; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(12), p.1287 - 1296, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:64.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to clarify the cesium iodide (CsI) transport behavior with a focus on the mechanisms of gaseous iodine formation in the reactor coolant system of LWR under a severe accident condition, a reproductive experiment of CsI transport behavior was conducted using a facility equipped with a thermal gradient tube. Various analyses on deposits and airborne materials during transportation could elucidate two mechanisms for the gaseous iodine formation. One was the gaseous phase chemical reaction in Cs-I-O-H system at relatively high-temperature region, which led to gaseous iodine transport to the lower temperature region without any further changes in gas species due to the kinetics limitation effects. The other one was the chemical reactions related to condensed phase of CsI, namely those of CsI deposits on walls with surface of stainless steel to form Cs CrO
CrO compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
compound and CsI aerosol particles with steam, which were newly found in this study.
Miwa, Shuhei; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Chikashi; Rizaal, M.; Suzuki, Eriko; Horiguchi, Naoki; Osaka, Masahiko
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.253 - 260, 2020/12
We have proceeded the fundamental study for the improvement of the evaluation of fission product (FP) chemistry and the treatment of fine space resolution which are main issues for the evaluation of FP behaviors in a severe accident (SA). We have been developing FP chemistry database named ECUME for the improvement of SA analysis codes. We prepared thermodynamic data for Cs compounds which is no experimental data available by computational approach. Regarding the space resolution issue, we have been developing analysis tool named CHASER based on 3D-CFD code with the model for FP chemistry. More accurate evaluation of FP behavior can be achieved by incorporating ECUME to the CHASER.
Suzuki, Chikashi; Osaka, Masahiko; Nakagiri, Toshio
Proceedings of Joint International Conference on Supercomputing in Nuclear Applications + Monte Carlo 2020 (SNA + MC 2020), p.131 - 136, 2020/10
In order to evaluate uranium migration behavior in Ningyo-toge area, we are examining the stability of uranium minerals using DFT calculation. As the first step, we investigated the crystal structure and unit cell composition of ningyoite with its structural details unclear, which is a major uranium mineral there. We analyzed the reported XRD pattern of ningyoite to evaluate a crystal structure of ningyoite using XRD analysis code. This XRD analysis indicates that the distance between U atoms is 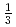
 along
along  axis. We constructed the structure of [CaU(PO
axis. We constructed the structure of [CaU(PO )
) ]
] with three U or Ca atoms aligned along
with three U or Ca atoms aligned along  axis on the basis of this examination, and conducted structural optimization with this structure as initial one using DFT calculation. The theoretical XRD pattern has the maximum peak near 30
axis on the basis of this examination, and conducted structural optimization with this structure as initial one using DFT calculation. The theoretical XRD pattern has the maximum peak near 30 , which the reported XRD pattern of ningyoite has. This result suggests that the structure of ningyoite is based on that of [CaU(PO
, which the reported XRD pattern of ningyoite has. This result suggests that the structure of ningyoite is based on that of [CaU(PO )
) ]
] .
.