Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy
scintillators by gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopyFujimori, Kosuke*; Kitaura, Mamoru*; Taira, Yoshitaka*; Fujimoto, Masaki*; Zen, H.*; Watanabe, Shinta*; Kamada, Kei*; Okano, Yasuaki*; Kato, Masahiro*; Hosaka, Masahito*; et al.
Applied Physics Express, 13(8), p.085505_1 - 085505_4, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.01(Physics, Applied)To clarify the existence of cation vacancies in Ce-doped Gd Al
Al Ga
Ga O
O (Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y
(Ce:GAGG) scintillators, we performed gamma-ray-induced positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (GiPALS). GiPAL spectra of GAGG and Ce:GAGG comprised two exponential decay components, which were assigned to positron annihilation at bulk and defect states. By an analogy with Ce:Y Al
Al O
O , the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg
, the defect-related component was attributed to Al/Ga-O divacancy complexes. This component was weaker for Ce, Mg:GAGG, which correlated with the suppression of shallow electron traps responsible for phosphorescence. Oxygen vacancies were charge compensators for Al/Ga vacancies. The lifetime of the defect-related component was significantly changed by Mg co-doping. This was understood by considering aggregates of Mg ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
ions at Al/Ga sites with oxygen vacancies, which resulted in the formation of vacancy clusters.
Onoe, Hironori; Kosaka, Hiroshi*; Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Komatsu, Tetsuya; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Yasue, Kenichi
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 26(1), p.3 - 14, 2019/06
In this study, it is focused on topographic changes due to uplift and denudation, also climate perturbations, a method which is able to assess the long-term variability of groundwater flow conditions using the coefficient variation based on some steady-state groundwater flow simulation results was developed. Spatial distribution of long residence time area which is not much influenced due to long-term topographic change and recharge rate change during the past one million years was able to estimate through the case study of the Tono area, Central Japan. By applying this evaluation method, it is possible to identify the local area that has low variability of groundwater flow conditions due to topographic changes and climate perturbations from the regional area quantitatively and spatially.
Hosaka, Atsushi; Hiyama, Emiko; Kim, S.-H.*; Kim, H.-C.*; Nagahiro, Hideko*; Noumi, Hiroyuki*; Oka, Makoto; Shirotori, Kotaro*; Yoshida, Tetsuya*; Yasui, Shigehiro*
Nuclear Physics A, 954, p.341 - 351, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:26.8(Physics, Nuclear)In this paper, we discuss reactions involving charmed baryons to explore their unique features. A well known phenomenon, the separation of the two internal motions of the  and
and  types of a three-quark system is revisited. First we discuss the mass spectrum of low-lying excitations as functions of the heavy quark mass, smoothly connecting the
types of a three-quark system is revisited. First we discuss the mass spectrum of low-lying excitations as functions of the heavy quark mass, smoothly connecting the 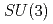 and heavy quark limits. The properties of these modes can be tested in the production and decay reactions of the baryons. For the productions, we consider a one step process which excites dominantly
and heavy quark limits. The properties of these modes can be tested in the production and decay reactions of the baryons. For the productions, we consider a one step process which excites dominantly  mode excitations. We find abundant production rates for some of excited states. For decays, we study pion emission process, which provides a clean tool to test the structure of heavy quark systems due to well controlled low energy dynamics of the pion and quark. Both productions and decays of the charmed baryons are the issues of the future experiments at J-PARC.
mode excitations. We find abundant production rates for some of excited states. For decays, we study pion emission process, which provides a clean tool to test the structure of heavy quark systems due to well controlled low energy dynamics of the pion and quark. Both productions and decays of the charmed baryons are the issues of the future experiments at J-PARC.
Yoshida, Tetsuya*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Hosaka, Atsushi*; Oka, Makoto; Sadato, Katsunori*
Physical Review D, 92(11), p.114029_1 - 114029_19, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:173 Percentile:99.11(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Single- and double-heavy baryons are studied in the constituent quark model. The model Hamiltonian is chosen as a standard one with two exceptions: (1) the color-Coulomb term depends on quark masses and (2) an antisymmetric 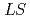 (spin-orbit) force is introduced. Model parameters are fixed by the strange baryon spectra,
(spin-orbit) force is introduced. Model parameters are fixed by the strange baryon spectra,  and
and  baryons. The masses of the observed charmed and bottomed baryons are, then, fairly well reproduced. Our focus is on the low-lying negative-parity states, in which the heavy baryons show specific excitation modes reflecting the mass differences of heavy and light quarks. By changing quark masses from the SU(3) limit to the strange quark mass, and, further, to the charm and bottom quark masses, we demonstrate that the spectra change from the SU(3) symmetry patterns to the heavy-quark-symmetry ones.
baryons. The masses of the observed charmed and bottomed baryons are, then, fairly well reproduced. Our focus is on the low-lying negative-parity states, in which the heavy baryons show specific excitation modes reflecting the mass differences of heavy and light quarks. By changing quark masses from the SU(3) limit to the strange quark mass, and, further, to the charm and bottom quark masses, we demonstrate that the spectra change from the SU(3) symmetry patterns to the heavy-quark-symmetry ones.
Yabashi, Makina*; Tanaka, Hitoshi*; Tanaka, Takashi*; Tomizawa, Hiromitsu*; Togashi, Tadashi*; Nagasono, Mitsuru*; Ishikawa, Tetsuya*; Harries, J.; Hikosaka, Yasumasa*; Hishikawa, Akiyoshi*; et al.
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 46(16), p.164001_1 - 164001_19, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:71 Percentile:95.16(Optics)Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Asamori, Koichi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Matsuura, Yuki*; Kosaka, Hideki*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.407 - 413, 2010/10
In this study, we present the preliminary results for the estimation of a horizontal crustal movement by using geodetic and geological approach in the Horonobe area, northern Hokkaido, Japan. The estimations have been carried out by using a GPS data and a geological cross section obtained by applying balanced-section method. As results of this study, both of the shortening rates estimated by GPS data and balanced-section method indicate several millimeters per year. Namely, there is no contradiction between geodetic and geological data, and it is considered that Horonobe area is still situated similar tendency and magnitude of a crustal movement. Geodetic data is not usually used to evaluate the long-term crustal movement. However, the results of this study indicate that geodetic data provide valuable information for estimating the long-term crustal movement in the area.
Agui, Akane; Asahi, Toru*; Sayama, Junichi*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Tanaka, Masahito*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 320(22), p.3015 - 3018, 2008/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.32(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 Co
Co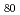 /Pd multilayered films
/Pd multilayered filmsTanaka, Masahito*; Asahi, Toru*; Agui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Sayama, Junichi*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 41(5), p.055003_1 - 055003_4, 2008/03
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.74(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English
 Co
Co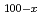 measured using soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroism
measured using soft X-ray magnetic circular dichroismAgui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Matsumoto, Koji*; Morikawa, Tsuyoshi*; Sayama, Junichi*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 68(11), p.2148 - 2152, 2007/11
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:41.74(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Masahito*; Nakamura, Naomichi*; Asahi, Toru*; Tsumori, Toshihiro*; Agui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
Physica Status Solidi (C), 3(8), p.2783 - 2786, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:45.61(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 -added and B-doped effect in Co/Pd multilayered films using soft X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism
-added and B-doped effect in Co/Pd multilayered films using soft X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroismAgui, Akane; Asahi, Toru*; Sayama, Junichi*; Kawaji, Jun*; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Tanaka, Masahito*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 39(14), p.2881 - 2885, 2006/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.45(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English

 -edge of perpendicular magnetic Dy
-edge of perpendicular magnetic Dy Co
Co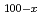 films
filmsAgui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Sayama, Junichi*; Matsumoto, Koji*; Morikawa, Tsuyoshi*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Osaka, Tetsuya*; Miura, Yoshimasa*
Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 408-412, p.741 - 745, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.38(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English

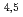 -edges of Tb
-edges of Tb Fe
Fe Co
Co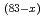 perpendicular magnetization films
perpendicular magnetization filmsAgui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Sayama, Junichi*; Matsumoto, Koji*; Morikawa, Tsuyoshi*; Nakatani, Takeshi; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Osaka, Tetsuya*; Miura, Yoshimasa*
Transactions of the Magnetics Society of Japan, 4(4-2), p.326 - 329, 2004/11
The electronic and spin state of the perpendicular magnetization film Tb Fe
Fe Co
Co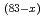 was investigated by means of magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy for each element. The samples are Tb
was investigated by means of magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy for each element. The samples are Tb Fe
Fe Co
Co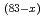 while the ratio of a rare-earth metal Tb to transition metals Fe and Co is constant, the composition ratio of Fe and Co is changed. Changing the ratio, we estimated the expected orbital moments
while the ratio of a rare-earth metal Tb to transition metals Fe and Co is constant, the composition ratio of Fe and Co is changed. Changing the ratio, we estimated the expected orbital moments 

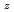
 of Tb 4f electrons. The macroscopic magnetic property is studied from the microscopic point of view.
of Tb 4f electrons. The macroscopic magnetic property is studied from the microscopic point of view.
Agui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Matsushita, Tomohiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Kawaji, Jun*; Sayama, Junichi*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
Journal of Applied Physics, 95(12), p.7825 - 7831, 2004/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:27.83(Physics, Applied)The electronic and spin states of [Co/Pd] multilayered perpendicular magnetization films with various seedlayers have been investigated by means of soft X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy at the Co 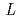
 -edges. The expectation values of the orbital angular momentum
-edges. The expectation values of the orbital angular momentum 
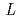
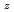
 and the spin angular momentum
and the spin angular momentum 
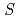
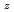
 of Co atom in the [Co/Pd] multilayered film were estimated using the sum rule. It was found that the seedlayer changes macroscopic magnetic properties of the [Co/Pd] multilayered film without affecting the electronic and spin states of the upper layers of Co.
of Co atom in the [Co/Pd] multilayered film were estimated using the sum rule. It was found that the seedlayer changes macroscopic magnetic properties of the [Co/Pd] multilayered film without affecting the electronic and spin states of the upper layers of Co.
 Co
Co
Agui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Kagomiya, Isao*; Matsumoto, Koji*; Sayama, Junichi*; Morikawa, Tsuyoshi*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Agui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Sayama, Junichi*; Kagomiya, Isao*; Matsumoto, Koji*; Morikawa, Tsuyoshi*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Co
Co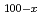 by means of magnetic circular dichroism
by means of magnetic circular dichroismAgui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Sayama, Junichi*; Kagomiya, Isao*; Matsumoto, Koji*; Morikawa, Tsuyoshi*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanaka, Masahito*; Nakamura, Naomichi*; Asahi, Toru*; Osaka, Tetsuya*; Tsumori, Toshihiro*; Agui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Co
Co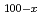 perpendicular magnetic films
perpendicular magnetic filmsAgui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Matsumoto, Koji*; Sayama, Junichi*; Morikawa, Tsuyoshi*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Agui, Akane; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Asahi, Toru*; Matsumoto, Koji*; Morikawa, Tsuyoshi*; Tanaka, Masahito*; Sayama, Junichi*; Osaka, Tetsuya*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English