Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ni
Ni In
In
Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 106(23), p.235152_1 - 235152_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.98(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigate the electronic state of Ni-substituted CeCo Ni
Ni In
In by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below
by nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques. The heavy fermion superconductivity below 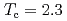 K for
K for 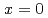 is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and
is suppressed by Ni substitutions, and  reaches zero for
reaches zero for 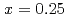 . The
. The  In NQR spectra for
In NQR spectra for 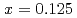 and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate
and 0.25 can be explained by simulating the electrical field gradient that is calculated for a virtual supercell with density functional theory. The spin-lattice relaxation rate  indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature (
indicates that Ni substitution weakens antiferromagnetic correlations that are not localized near the substituent but instead are uniform in space. The temperature ( ) dependence of
) dependence of  for
for 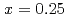 shows a maximum around
shows a maximum around 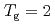 K and
K and  decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through
decreases toward almost zero when temperature is further reduced as if a gap might be opening in the magnetic excitation spectrum; however, the magnetic specific heat and the static magnetic susceptibility evolve smoothly through 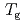 with a
with a 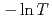 dependence. The peculiar T dependence of
dependence. The peculiar T dependence of  and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
and non-Fermi-liquid specific heat and susceptibility can be interpreted in a unified way by assuming nested antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations in a quasi-two-dimensional electronic system.
 ;
;  In NQR/NMR and
In NQR/NMR and  Co NMR study
Co NMR studySakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
Physical Review B, 104(8), p.085106_1 - 085106_12, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:30.04(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Antiferromagnetism in a prototypical quantum critical metal CeCoIn is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn
is known to be induced by slight substitutions of non-magnetic Zn atoms for In. In nominally 7% Zn substituted CeCoIn , an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn
, an antiferromagnetic (AFM) state coexists with heavy fermion superconductivity. Heterogeneity of the electronic states is investigated in Zn doped CeCoIn by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates
by means of nuclear quadrupole and magnetic resonances (NQR and NMR). Site-dependent NQR relaxation rates  indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature
indicate that the AFM state is locally nucleated around Zn substituents in the matrix of a heavy fermion state, and percolates through the bulk at the AFM transition temperature  . At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature
. At lower temperatures, an anisotropic superconducting (SC) gap below the SC transition temperature  , and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
, and the SC state permeates through the AFM regions via a SC proximity effect. Applying an external magnetic field induces a spin-flop transition near 5 T, reducing the volume of the AFM regions. Consequently, a short ranged inhomogeneous AFM state survives and coexists with a paramagnetic Fermi liquid state at high fields.
 acidic solutions
acidic solutionsYokoyama, Akihiko*; Kitayama, Yuta*; Fukuda, Yoshiki*; Kikunaga, Hidetoshi*; Murakami, Masashi*; Komori, Yukiko*; Yano, Shinya*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi*
Radiochimica Acta, 107(1), p.27 - 32, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.72(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Deki, Manato*; Oka, Tomoki*; Takayoshi, Shodai*; Naoi, Yoshiki*; Makino, Takahiro; Oshima, Takeshi; Tomita, Takuro*
Materials Science Forum, 778-780, p.661 - 664, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:70.05(Crystallography)no abstracts in English

Sakai, Hironori; Hattori, Taisuke; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Ronning, F.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; Yokoyama, Makoto*
no journal, ,
Dilute substitutions of non-magnetic dopants Zn can induce a long-ranged antiferromagnetic ordering to a heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn . We have microscopically investigated the Zn-doped CeCoIn
. We have microscopically investigated the Zn-doped CeCoIn by means of the nuclear quadrupole/magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques.
by means of the nuclear quadrupole/magnetic resonance (NQR/NMR) techniques.

Sakai, Hironori; Hattori, Taisuke; Higa, Nonoka; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Ronning, F.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; Yokoyama, Makoto*
no journal, ,
We have used Nuclear Quadrupole Resonance (NQR) to probe microscopically the response of prototypical quantum critical metal CeCoIn to substitutions of small amounts of Cd or Zn for In. Such non-magnetic Cd or Zn substitutions induce a long range antiferromagnetism. In the case of Cd substitutions, approximately half of the Cd substituents induce local Ce moments in their close proximity, as observed by site-dependent longitudinal nuclear spin relaxation rates
to substitutions of small amounts of Cd or Zn for In. Such non-magnetic Cd or Zn substitutions induce a long range antiferromagnetism. In the case of Cd substitutions, approximately half of the Cd substituents induce local Ce moments in their close proximity, as observed by site-dependent longitudinal nuclear spin relaxation rates  . In the paramagnetic state, the values of
. In the paramagnetic state, the values of  at the main peak position are similar to those in the pure CeCoIn
at the main peak position are similar to those in the pure CeCoIn , while those are enhanced at the skirt position of spectrum. We will discuss about the heterogeneous electronic state realized in such a Zn substituted system and discuss about the coexistence of superconductivity with the antiferromagnetism, as well.
, while those are enhanced at the skirt position of spectrum. We will discuss about the heterogeneous electronic state realized in such a Zn substituted system and discuss about the coexistence of superconductivity with the antiferromagnetism, as well.
 SR studies of CeCo(In
SR studies of CeCo(In Zn
Zn )
) , 3
, 3Higemoto, Wataru; Miyazaki, Itsuki*; Oda, Yuto; Ito, Takashi; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; Yokoyama, Makoto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The Ni-substitutions of Co in the heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn are reported to suppress the superconductivity by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki Univ. To microscopically investigate the Ni doping effect, we have performed NMR study in the alloy system of Ce(Co, Ni)In
are reported to suppress the superconductivity by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki Univ. To microscopically investigate the Ni doping effect, we have performed NMR study in the alloy system of Ce(Co, Ni)In . We would like to discuss the spin fluctuations and the electronic state near the critical composition for the superconductivity in this system.
. We would like to discuss the spin fluctuations and the electronic state near the critical composition for the superconductivity in this system.
 SR study on CeCo(In
SR study on CeCo(In Zn
Zn )
) , 2
, 2Higemoto, Wataru; Oda, Yuto; Miyazaki, Itsuki*; Ito, Takashi; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; Yokoyama, Makoto*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Suzuki, Kohei*; Oshima, Yoshiki*; et al.
no journal, ,
Substitutions of In sites by Zn atoms in heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn is reported to induce an antiferromagnetic order by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki University. Near the critical region, non-Fermi-liquid behavior has been observed in magnetization and specific heat. We have performed NMR measurements to reveal the spin fluctuations near the critical region.
is reported to induce an antiferromagnetic order by Yokoyama et al. in Ibaraki University. Near the critical region, non-Fermi-liquid behavior has been observed in magnetization and specific heat. We have performed NMR measurements to reveal the spin fluctuations near the critical region.

Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Ronning, F.*; Zhu, J.-X.*; Thompson, J. D.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; Suzuki, Kohei*; et al.
no journal, ,
Heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn is considered as a quantum critical antiferromagnetic material. When the In elements are slightly substituted by Zn elements, a long-range antiferromagnetism is induced. On the other hand, slight Sn substitutions make the system step away from the quantum critical point. In the case of Zn substitutions, heterogeneity of antiferromagnetic area in the matrix of heavy fermion state has been microscopically confirmed by NQR measurements. In the case of Ni substitutions for the Co elements, the NQR result appears to be the same as in Sn substituted system.
is considered as a quantum critical antiferromagnetic material. When the In elements are slightly substituted by Zn elements, a long-range antiferromagnetism is induced. On the other hand, slight Sn substitutions make the system step away from the quantum critical point. In the case of Zn substitutions, heterogeneity of antiferromagnetic area in the matrix of heavy fermion state has been microscopically confirmed by NQR measurements. In the case of Ni substitutions for the Co elements, the NQR result appears to be the same as in Sn substituted system.
Oka, Tomoki*; Deki, Manato; Naoi, Yoshiki*; Makino, Takahiro; Oshima, Takeshi; Tomita, Takuro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yanagita, Eizo*; Kondo, Kenta*; Bando, Yota*; Deki, Manato*; Makino, Takahiro; Oshima, Takeshi; Onoda, Shinobu; Naoi, Yoshiki*; Tomita, Takuro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Haga, Yoshinori; Kambe, Shinsaku; Zhu, J.-X.*; Ronning, F.*; Ramakrishna, S. K.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Kotegawa, Hisashi*; To, Hideki*; et al.
no journal, ,
In heavy fermion superconductor CeCoIn , slight Zn substitutions for In atoms induce antiferromagnetism, while slight Ni substitutions for Co atoms suppress superconductivity. The both substituted CeCoIn
, slight Zn substitutions for In atoms induce antiferromagnetism, while slight Ni substitutions for Co atoms suppress superconductivity. The both substituted CeCoIn exhibit non- fermi-liquid behaviors near the phase boundaries which have been detected by magnetization and specific heat measurements. We have performed NMR experiments in these systems to investigate the microscopic effects by substituents. We will discuss about the spin fluctuations near the boundaries by NMR relaxation rates.
exhibit non- fermi-liquid behaviors near the phase boundaries which have been detected by magnetization and specific heat measurements. We have performed NMR experiments in these systems to investigate the microscopic effects by substituents. We will discuss about the spin fluctuations near the boundaries by NMR relaxation rates.