Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Beerwerth, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Makii, Hiroyuki; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Osa, Akihiko; Toyoshima, Atsushi; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 140(44), p.14609 - 14613, 2018/11
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:69.46(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The first ionization potential (IP ) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP
) yields information on valence electronic structure of an atom. IP values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP
values of heavy actinides beyond einsteinium (Es, Z = 99), however, have not been determined experimentally so far due to the difficulty in obtaining these elements on scales of more than one atom at a time. Recently, we successfully measured IP of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP
of lawrencium (Lr, Z = 103) using a surface ionization method. The result suggests that Lr has a loosely-bound electron in the outermost orbital. In contrast to Lr, nobelium (No, Z = 102) is expected to have the highest IP among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP
among the actinide elements owing to its full-filled 5f and the 7s orbitals. In the present study, we have successfully determined IP values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP
values of No as well as fermium (Fm, Z = 100) and mendelevium (Md, Z = 101) using the surface ionization method. The obtained results indicate that the IP value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
value of heavy actinoids would increase monotonically with filling electrons up in the 5f orbital like heavy lanthanoids.
 SO
SO and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)
and HF/HCl solutions into toluene with Aliquat336; Sulfate and fluoride complex formation of Mo and W towards chemical studies of seaborgium (Sg)Toyoshima, Atsushi; Mitsukai, Akina; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Komori, Yukiko*; Murakami, Masashi; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Daisuke*; Asai, Masato; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 317(1), p.421 - 430, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.93(Chemistry, Analytical)We have studied extraction behavior of group-6 elements Mo and W to search for suitable conditions for an on-line extraction experiment of their heavier homolog, seaborgium (Sg). Batch-wise extraction of carrier-free radiotracers  Mo and
Mo and 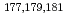 W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H
W were carried out from 0.10 - 8.6 M H SO
SO and 1.0
and 1.0 10
10 - 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H
- 5.0 M HF/1.0 M HCl into toluene with a quaternary ammonium compound, Aliquat336. Anionic sulfate complexes of Mo and W with charge - 2 were extracted with Aliquat336 from H SO
SO solutions with concentrations of [H
solutions with concentrations of [H SO
SO ]
]  2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
2 M. In HF/1.0 M HCl, oxyfluoro complexes of Mo and W with charge - 1 were interpreted to be formed and extracted with Aliquat336. From these results, favorable conditions for the extraction of Sg are discussed.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, C. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.05001_1 - 05001_6, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.9(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We measured ionization efficiencies of fermium, einsteinium, mendelevium, and lawrencium by using a newly developed gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of the elements have not been determined so far due to their low production rates and/or their short half-lives. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potentials of these actinide elements have been successfully determined.
Eichler, R.*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Chiera, N. M.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Dressler, R.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Even, J.*; Fangli, F.*; Goetz, M.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 131, p.07005_1 - 07005_7, 2016/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:72.98(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In recent years gas-phase chemical studies assisted by physical pre-separation allowed for the productions and investigations of fragile single molecular species of superheavy elements. The latest highlight is the formation of very volatile hexacarbonyl compound of element 106, Sg(CO) . Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO)
. Following this success, second-generation experiments were performed to measure the first bond dissociation energy between the central metal atom and the surrounding ligand. The method using a tubular decomposition reactor was developed and successfully applied to short-lived Mo(CO) , W(CO)
, W(CO) , and Sg(CO)
, and Sg(CO) .
.
Minoshima, Yusuke*; Seki, Yusuke*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics, 472, p.1 - 8, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:6.19(Chemistry, Physical)The dynamical process of electron attachment to a guanine-cytosine pair in the normal (h-GC) and deuterated (d-GC) forms has been studied theoretically by semiclassical ring-polymer molecular dynamics (RPMD) simulations using the empirical valence bond model. The initially formed dipole-bound anion is converted rapidly to the valence-bound anion within about 0.1 ps in both h-GC and d-GC. However, the subsequent proton transfer in h-GC occurs with a rate five times greater than the deuteron transfer in d-GC. The change of rates with isotopic substitution and temperature variation in the RPMD simulations are quantitatively and qualitatively different from those in the classical molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, demonstrating the importance of nuclear quantum effects on the dynamics of this system.
 at the single-atom level
at the single-atom levelSteinegger, P.*; Asai, Masato; Dressler, R.*; Eichler, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Piguet, D.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(13), p.7122 - 7132, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:60.73(Chemistry, Physical)A new experimental method "vacuum chromatography" has been developed to measure adsorption enthalpy of superheavy elements, and its feasibility has been examined using short-lived thallium isotopes. The short-lived thallium isotopes were produced at the JAEA tandem accelerator. The thallium ion beam prepared with an on-line isotope separator which ionized and mass-separated the thallium isotopes was injected into an isothermal vacuum chromatography apparatus. A temperature-dependent adsorption property of thallium atom on SiO surface were measured. The adsorption enthalpy of thallium was determined to be 158 kJ/mol. The thallium is a homolog of element 113. Thus, the vacuum chromatography developed in this study enables us to perform chemical experiments for short-lived superheavy elements with half-lives of a order of one second.
surface were measured. The adsorption enthalpy of thallium was determined to be 158 kJ/mol. The thallium is a homolog of element 113. Thus, the vacuum chromatography developed in this study enables us to perform chemical experiments for short-lived superheavy elements with half-lives of a order of one second.
 and W(CO)
and W(CO)
Usoltsev, I.*; Eichler, R.*; Wang, Y.*; Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 104(3), p.141 - 151, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:95.03(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Conditions of the production and decomposition of hexacarbonyl complexes of short-lived Mo and W isotopes were investigated to study thermal stability of the heaviest group 6 hexacarbonyl complex Sg(CO) . A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO)
. A tubular flow reactor was tested to decompose the hexacarbonyl complexes and to extract the first bond dissociation energies. A silver was found to be the most appropriate reaction surface to study the decomposition of the group 6 hexacarbonyl. It was found that the surface temperature at which the decomposition occurred was correlated to the first bond dissociation energy of Mo(CO) and W(CO)
and W(CO) , indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO)
, indicating that the first bond dissociation energy of Sg(CO) could be determined with this technique.
could be determined with this technique.
Iwai, Yasunori; Kubo, Hitoshi*; Oshima, Yusuke*; Noguchi, Hiroshi*; Edao, Yuki; Taniuchi, Junichi*
Fusion Science and Technology, 68(3), p.596 - 600, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.57(Nuclear Science & Technology)We have newly developed the hydrophobic platinum honeycomb catalysts applicable to tritium oxidation reactor since the honeycomb-shape catalyst can decrease the pressure drop. Two types of hydrophobic honeycomb catalyst have been test-manufactured. One is the hydrophobic platinum catalyst on a metal honeycomb. The other is the hydrophobic platinum catalyst on a ceramic honeycomb made of silicon carbide. The fine platinum particles around a few nanometers significantly improve the catalytic activity for the oxidation tritium at a tracer concentration. The hydrogen concentration in the gaseous feed slightly affects the overall reaction rate constant for hydrogen oxidation. Due to the competitive adsorption of hydrogen and water molecules on platinum surface, the overall reaction rate constant has the bottom value. The hydrogen concentration for the bottom value is 100 ppm under the dry feed gas. We have experimentally confirmed the activity of these honeycomb catalysts is as good as that of pellet-shape hydrophobic catalyst. The results support the hydrophobic honeycomb catalysts are applicable to tritium oxidation reactor.
Kubo, Hitoshi*; Oshima, Yusuke*; Iwai, Yasunori
JETI, 63(10), p.33 - 36, 2015/09
Tanaka Kikinzoku Kogyo provides a broad range of precious metals products and technologies. Tanaka Kikinzoku Kogyo and Japan Atomic Energy Agency have jointly developed a new method of manufacturing catalysts involving hydrophobic processing with an inorganic substance base. As a result, previous technological issues were able to be solved with the development of a catalyst that exhibited no performance degradation in response to radiation application of 530 kGy, a standard for radiation resistance, and maintenance of thermal stability at over 600 C, which is much higher than the 70
C, which is much higher than the 70 C temperature that is normally used. The application of this catalyst to the liquid phase catalytic exchange process is expected to overcome significant technological hurdles with regards to improving the reliability and efficiency of systems for collecting tritium from tritiated water. It is also anticipated that the hydrophobic platinum catalyst manufacturing technology used for this catalyst could be applied to a wide range of fields other than nuclear fusion research. It was verified that if applied to a hydro oxidation catalyst, hydrogen could be efficiently oxidized, even at room temperature. This catalyst can also contribute to improving safety at non-nuclear plants that use hydrogen in general by solving the aforementioned vulnerability issue.
C temperature that is normally used. The application of this catalyst to the liquid phase catalytic exchange process is expected to overcome significant technological hurdles with regards to improving the reliability and efficiency of systems for collecting tritium from tritiated water. It is also anticipated that the hydrophobic platinum catalyst manufacturing technology used for this catalyst could be applied to a wide range of fields other than nuclear fusion research. It was verified that if applied to a hydro oxidation catalyst, hydrogen could be efficiently oxidized, even at room temperature. This catalyst can also contribute to improving safety at non-nuclear plants that use hydrogen in general by solving the aforementioned vulnerability issue.
Iwai, Yasunori; Kubo, Hitoshi*; Oshima, Yusuke*
Isotope News, (736), p.12 - 17, 2015/08
We have successfully developed a new hydrophobic platinum catalyst for collecting tritium at nuclear fusion reactors. Catalysts used to collect tritium are called hydrophobic precious metal catalysts. In Japan, hydrophobic precious metal catalysts manufactured from polymers have been used for heavy water refinement.However, this catalyst has issues related to embrittlement to radiation and thermal stability. These technological issues needed to be solved to allow for its application to nuclear fusion reactors requiring further enrichment from highly-concentrated tritiated water. We developed a new method of manufacturing catalysts involving hydrophobic processing with an inorganic substance base. As a result, previous technological issues were able to be solved with the development of a catalyst that exhibited no performance degradation in response to radiation application of 530kGy, a standard for radiation resistance, and maintenance of thermal stability at over 600 C, which is much higher than the 70
C, which is much higher than the 70 C temperature that is normally used. The catalyst created with this method was also confirmed to have achieved the world's highest exchange efficiency, equivalent to 1.3 times the previously most powerful efficiency. The application of this catalyst to the liquid phase catalytic exchange process is expected to overcome significant technological hurdles with regards to improving the reliability and efficiency of systems for collecting tritium from tritiated water.
C temperature that is normally used. The catalyst created with this method was also confirmed to have achieved the world's highest exchange efficiency, equivalent to 1.3 times the previously most powerful efficiency. The application of this catalyst to the liquid phase catalytic exchange process is expected to overcome significant technological hurdles with regards to improving the reliability and efficiency of systems for collecting tritium from tritiated water.
Abe, Hiroshi; Shimomura, Takuya; Tokuhira, Shinnosuke*; Shimada, Yukihiro*; Takenaka, Yusuke*; Furuyama, Yuta*; Nishimura, Akihiko; Uchida, Hirohisa*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Oshima, Takeshi
Proceedings of 7th International Congress on Laser Advanced Materials Processing (LAMP 2015) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2015/08
A short pulse laser (the nanosecond and femtosecond) was applied to hydrogen absorbing alloys surface layer, and a surface modification experiment was put into effective to aim at improvement of hydrogen adsorption functionally. It was investigated about correlation between an initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate of hydrogen alloys and a laser irradiation in this research. The laser irradiation condition was done with pulse width 100 fsec and energy 0.2 - 3.4 mJ/pulse. It blazed down on hydrogen absorbing alloys (LaNi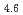 Al
Al ) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
) and changed local order in the surface. As a result, the initial hydrogen absorption reaction rate was 1.5 - 3.0 times as fast as a irradiated sample, and the result and laser irradiated sample found out that a hydrogen absorption function improves. A laser irradiation can conclude to be effective in surface modification of the hydrogen storage materials.
Iwai, Yasunori; Kubo, Hitoshi*; Oshima, Yusuke*
Kagaku, 70(5), p.35 - 40, 2015/05
We have successfully developed a new hydrophobic platinum catalyst for collecting tritium at nuclear fusion reactors. Catalysts used to collect tritium are called hydrophobic precious metal catalysts. In Japan, hydrophobic precious metal catalysts manufactured from polymers have been used for heavy water refinement. However, this catalyst has issues related to embrittlement to radiation and thermal stability. These technological issues needed to be solved to allow for its application to nuclear fusion reactors requiring further enrichment from highly-concentrated tritiated water. We developed a new method of manufacturing catalysts involving hydrophobic processing with an inorganic substance base. As a result, previous technological issues were able to be solved with the development of a catalyst that exhibited no performance degradation in response to radiation application of 530 kGy, a standard for radiation resistance, and maintenance of thermal stability at over 600 C, which is much higher than the 70
C, which is much higher than the 70 C temperature that is normally used. The catalyst created with this method was also confirmed to have achieved the world's highest exchange efficiency, equivalent to 1.3 times the previously most powerful efficiency. The application of this catalyst to the liquid phase catalytic exchange process is expected to overcome significant technological hurdles with regards to improving the reliability and efficiency of systems for collecting tritium from tritiated water.
C temperature that is normally used. The catalyst created with this method was also confirmed to have achieved the world's highest exchange efficiency, equivalent to 1.3 times the previously most powerful efficiency. The application of this catalyst to the liquid phase catalytic exchange process is expected to overcome significant technological hurdles with regards to improving the reliability and efficiency of systems for collecting tritium from tritiated water.
Honda, Tomohiro*; Minoshima, Yusuke*; Yokoi, Yuki*; Takayanagi, Toshiyuki*; Shiga, Motoyuki
Chemical Physics Letters, 625, p.174 - 178, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:19.29(Chemistry, Physical)Electron attachment dynamics to the guanine-cytosine (G-C) base pair in the gas phase isstudied using DFT and molecular dynamics. The potential energy surface of the G-C anion isconstructed with the empirical-valence-bond method using force-field information obtained from long-range corrected DFT calculations. Ring-polymer molecular dynamics simulations predict that theinitial dipole-bound anion readily converts into the valence-bound anion within 0.1 ps and proton-transfer occurs subsequently within 10 ps. The same process was found in classical simulations, buton a much slower time scale. This result suggests that nuclear quantum effects are important inunderstanding DNA damage by low-energy electrons.
Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Borschevsky, A.*; Stora, T.*; Sato, Nozomi; Kaneya, Yusuke; Tsukada, Kazuaki; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eberhardt, K.*; Eliav, E.*; et al.
Nature, 520(7546), p.209 - 211, 2015/04
Times Cited Count:107 Percentile:97.49(Multidisciplinary Sciences)Ionization efficiency in a surface ionization process depends on the first ionization potential of the atom. Based on the dependence, the ionization potential of the atom can be determined. We successfully measured ionization efficiencies of lawrencium (Lr,  =103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
=103) using a gas-jet coupled surface ion-source. The ionization potential of Lr has not been determined owing to its low production rate and its short half-life. Based on a relationship between the ionization efficiency and the ionization potential obtained via measurements of short-lived lanthanide isotopes, the ionization potential of Lr was determined.
Even, J.*; Ackermann, D.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(3), p.2457 - 2466, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:77.56(Chemistry, Analytical)Rapid In situ synthesis of metal carbonyl complexes has been demonstrated using short-lived isotopes produced in nuclear fission and fusion reactions. The short-lived isotopes with high recoil energy directly react with carbon-monoxides and form carbonyl complexes. Only highly volatile complexes were fast transported in a gas stream to counting and chemistry devices. Short-lived Mo, Tc, Ru, Rh, W, Re, Os, and Ir were found to form volatile carbonyl complexes, while no volataile complex of Hf and Ta were detected. This technique has been applied to a chemical investigation of the superheavy element Sg (atomic number 106), and will be applicable to various fields of nuclear science with short-lived transition metal isotopes.
 gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)
gas-jet system coupled to a surface-ionization type ion-source in JAEA-ISOL; towards determination of the first ionization potential of Lr (Z = 103)Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Oe, Kazuhiro*; Miyashita, Sunao*; Kaneya, Yusuke; Osa, Akihiko; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1253 - 1257, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.13(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a surface-ionization ion-source coupled to the He/CdI gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr,
gas-jet transport system for the Isotope Separator On-Line (ISOL) at the JAEA tandem accelerator for experimental determination of the first ionization potential of lawrencium (Lr, 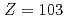 ). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of
). We performed to ionize a short-lived Lr isotope and various lanthanide isotopes. We successfully observed mass-separated ions of  Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Lr by using our present system at the first time. The first ionization potential of Lr was evaluated based on a correlation between of effective ionization potential and ionization efficiency of short-lived lanthanide isotopes in our system.
Oe, Kazuhiro*; Attallah, M. F.*; Asai, Masato; Goto, Naoya*; Gupta, N. S.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Huang, M.*; Kanaya, Jumpei*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Kasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; et al.
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 303(2), p.1317 - 1320, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:64.63(Chemistry, Analytical)A new technique for continuous dissolution of nuclear reaction products transported by a gas-jet system was developed for superheavy element (SHE) chemistry. In this technique, a hydrophobic membrane is utilized to separate an aqueous phase from the gas phase. With this technique, the dissolution efficiencies of short-lived radionuclides of 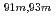 Mo and
Mo and  W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
W were measured. Yields of more than 80% were observed for short-lived radionuclides at aqueous-phase flow rates of 0.1-0.4 mL/s. The gas flow-rate had no influence on the dissolution efficiency within the studied flow range of 1.0-2.0 L/min. These results show that this technique is applicable for on-line chemical studies of SHEs in the liquid phase.
Even, J.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F. L.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Tetsuya; Brand, H.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eichler, R.*; Fan, F. L.*; et al.
Science, 345(6203), p.1491 - 1493, 2014/09
Times Cited Count:63 Percentile:83.28(Multidisciplinary Sciences)A new superheavy element complex, a seaborgium carbonyl, has been successfully synthesized, and its adsorption property has been studied using a cryo-thermochromatography and  -detection apparatus COMPACT. Nuclear reaction products of short-lived
-detection apparatus COMPACT. Nuclear reaction products of short-lived  Sg preseparated with a gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS at RIKEN were directly injected into a gas cell filled with He/CO mixture gas, and chemical reaction products of volatile carbonyl complexes were trasported to COMPACT. The Sg carbonyl complex detected with COMPACT was found to be very volatile with adsorption enthalpy of
Sg preseparated with a gas-filled recoil ion separator GARIS at RIKEN were directly injected into a gas cell filled with He/CO mixture gas, and chemical reaction products of volatile carbonyl complexes were trasported to COMPACT. The Sg carbonyl complex detected with COMPACT was found to be very volatile with adsorption enthalpy of  50 kJ/mol, from which we have concluded that this complex should be a Sg hexacarbonyl Sg(CO)
50 kJ/mol, from which we have concluded that this complex should be a Sg hexacarbonyl Sg(CO) . This is the first synthesis of organometallic compounds of transactinide elements for which only simple inorganic comounds have been synthesized so far.
. This is the first synthesis of organometallic compounds of transactinide elements for which only simple inorganic comounds have been synthesized so far.
Iwai, Yasunori; Kubo, Hitoshi*; Sato, Katsumi; Oshima, Yusuke*; Noguchi, Hiroshi*; Taniuchi, Junichi*
Proceedings of 7th Tokyo Conference on Advanced Catalytic Science and Technology (TOCAT-7) (USB Flash Drive), 2 Pages, 2014/06
Hydrophobic platinum catalysts have been developed especially for combustion of hydrogen isotopes released in a nuclear facility. A new type of hydrophobic hydrogen combustion catalyst commercially named TKK-KNOITS catalyst is hardly susceptible to water mist and water vapor in the atmosphere and water produced by hydrogen combustion. It is capable of maintaining the activity even at relatively low temperatures. The TKK-KNOITS catalyst is superior to other previous hydrophobic catalysts in applicability to wide range of hydrogen concentration from very thin to dense. The catalyst which carrier is composed of inorganic oxide has thermal stability up to 873 K.
 /Md
/Md reduction potential studied with flow electrolytic chromatography
reduction potential studied with flow electrolytic chromatographyToyoshima, Atsushi; Li, Z.*; Asai, Masato; Sato, Nozomi; Sato, Tetsuya; Kikuchi, Takahiro; Kaneya, Yusuke; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 52(21), p.12311 - 12313, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:23.58(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The reduction behavior of mendelevium (Md) was studied using a flow electrolytic chromatography apparatus. By applying appropriate potentials on the chromatography column, the more stable Md is reduced to Md
is reduced to Md . The reduction potential of the Md
. The reduction potential of the Md + e
+ e
 Md
Md couple was determined to be -0.16
couple was determined to be -0.16 0.05 V vs. a normal hydrogen electrode.
0.05 V vs. a normal hydrogen electrode.