Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kubomi, Ko*; Nagata, Mitsuhiro; Ota, Hiroto*; Miyata, Kazunori*; Oto, Shigeru*
Chishitsugaku Zasshi (Internet), 129(1), p.453 - 460, 2023/09
The Hakobuchi Formation in Hokkaido, NE Japan, consists of marine to terrestrial clastic rocks of the uppermost part of the Yezo Group, was previously interpreted to range from Early Campanian to Late Paleocene age, with a hiatus near the K/Pg boundary. No definitive evidence of the depositional age indicating Lower Paleocene (Danian) has been reported from the formation so far. We reported the LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dates of a tuff layer of the Hakobuchi Formation in the Yubari area. The weighted average date of the youngest cluster was 64.1  1.1 Ma (2
1.1 Ma (2 ), suggesting the depositional age of the formation is Danian. The result is the first radiometric evidence indicating that the Hakobuchi Formation, at least partly, is correlated with the Danian, and is essential to discuss the depositional age of the Hakobuchi Formation and geochronology of the Yezo Group.
), suggesting the depositional age of the formation is Danian. The result is the first radiometric evidence indicating that the Hakobuchi Formation, at least partly, is correlated with the Danian, and is essential to discuss the depositional age of the Hakobuchi Formation and geochronology of the Yezo Group.
Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Morishita, Masaki*; Aizawa, Kosuke; Ando, Masanori; Ashida, Takashi; Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Doda, Norihiro; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Ezure, Toshiki; Fukano, Yoshitaka; et al.
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactors; JSME Series in Thermal and Nuclear Power Generation, Vol.3, 631 Pages, 2022/07
This book is a collection of the past experience of design, construction, and operation of two reactors, the latest knowledge and technology for SFR designs, and the future prospects of SFR development in Japan. It is intended to provide the perspective and the relevant knowledge to enable readers to become more familiar with SFR technology.
 Fe
Fe GeO
GeO with andalusite structure
with andalusite structureKakimoto, Kazuo*; Takada, Saki*; Ota, Hiroto*; Hayaguchi, Yuya*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Mitamura, Hiroyuki*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Hatakeyama, Atsushi*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054704_1 - 054704_7, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:15.88(Physics, Multidisciplinary) -xGeO
-xGeO with
with  = 0.09 and 0.15
= 0.09 and 0.15Kakimoto, Kazuo*; Ota, Hiroto*; Hayaguchi, Yuya*; Hagihara, Masato; Torii, Shuki*; Kamiyama, Takashi*; Katori, Hiroko*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 91(5), p.054707_1 - 054707_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sakai, Kenji; Oku, Takayuki; Okudaira, Takuya; Kai, Tetsuya; Harada, Masahide; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kakurai, Kazuhisa*; Shimizu, Hirohiko*; Hirota, Katsuya*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011116_1 - 011116_6, 2021/03
In neutron fundamental physics, study of correlation term  of a neutron spin
of a neutron spin 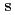 and a target nuclear spin
and a target nuclear spin 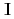 is important because
is important because  term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to
term interferes to parity non-conserving (PNC) and time reversal non-conserving terms. For this study, a xenon (Xe) is an interesting nucleus because it has been observed an enhancement of PNC effect around neutron resonance peaks, and polarizes up to 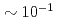 by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study
by using a spin exchange optical pumping (SEOP) method. We would plan to develop a polarized Xe gas target with a compact in-situ SEOP system, and to study  term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by
term by utilizing epithermal neutron beams supplied from a high intense pulsed spallation neutron source. As the first step, we attempted to measure neutron polarizing ability caused by  term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of
term at a 9.6 eV s-wave resonance peak of  Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change
Xe at BL10 in MLF, by detecting change  of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (
of ratio between neutron transmissions with the polarized and unpolarized Xe target. After demonstrating that our apparatus could detect small change (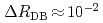 ) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of
) of neutron transmissions caused by Doppler broadening effect, a signified value of  has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained
has been obtained as preliminary results. For analyzing the obtained  in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
in detail, we are improving our nuclear magnetic resonance and electron paramagnetic resonance systems for evaluating Xe polarization independently of neutron beams.
Kitazato, Kohei*; Milliken, R. E.*; Iwata, Takahiro*; Abe, Masanao*; Otake, Makiko*; Matsuura, Shuji*; Takagi, Yasuhiko*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Hiroi, Takahiro*; Matsuoka, Moe*; et al.
Nature Astronomy (Internet), 5(3), p.246 - 250, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:58 Percentile:96.23(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Here we report observations of Ryugu's subsurface material by the Near-Infrared Spectrometer (NIRS3) on the Hayabusa2 spacecraft. Reflectance spectra of excavated material exhibit a hydroxyl (OH) absorption feature that is slightly stronger and peak-shifted compared with that observed for the surface, indicating that space weathering and/or radiative heating have caused subtle spectral changes in the uppermost surface. However, the strength and shape of the OH feature still suggests that the subsurface material experienced heating above 300  C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200
C, similar to the surface. In contrast, thermophysical modeling indicates that radiative heating does not increase the temperature above 200  C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
C at the estimated excavation depth of 1 m, even if the semimajor axis is reduced to 0.344 au. This supports the hypothesis that primary thermal alteration occurred due to radiogenic and/or impact heating on Ryugu's parent body.
 studied with high-pressure
studied with high-pressure  SR
SRSugiyama, Jun; Higemoto, Wataru; Andreica, D.*; Forslund, O. K.*; Nocerino, E.*; M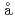 nsson, M.*; Sassa, Y.*; Gupta, R.*; Khasanov, R.*; Ota, Hiroto*; et al.
nsson, M.*; Sassa, Y.*; Gupta, R.*; Khasanov, R.*; Ota, Hiroto*; et al.
Physical Review B, 103(10), p.104418_1 - 104418_10, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:51.55(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The magnetic nature of a quasi-one-dimensional compound, BaVSe , has been investigated with positive muon spin rotation and relaxation measurements at ambient and high pressures. At ambient pressure, the spectrum recorded under zero external magnetic field exhibited a clear oscillation below the Curie temperature due to the formation of quasistatic ferromagnetic order. As pressure increased from ambient pressure,
, has been investigated with positive muon spin rotation and relaxation measurements at ambient and high pressures. At ambient pressure, the spectrum recorded under zero external magnetic field exhibited a clear oscillation below the Curie temperature due to the formation of quasistatic ferromagnetic order. As pressure increased from ambient pressure, 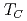 was found to decrease slightly up to about 1.5 GPa, at which point
was found to decrease slightly up to about 1.5 GPa, at which point 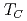 started to increase rapidly with the further increase of the pressure. Based on a strong ferromagnetic interaction along the
started to increase rapidly with the further increase of the pressure. Based on a strong ferromagnetic interaction along the  -axis, the result revealed that there are two magnetic interactions in the ab-plane.
-axis, the result revealed that there are two magnetic interactions in the ab-plane.
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCOkudaira, Takuya; Oku, Takayuki; Ino, Takashi*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Sakai, Kenji; Hiroi, Kosuke; Takahashi, Shingo*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Endo, Hitoshi*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 977, p.164301_1 - 164301_8, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:89.09(Instruments & Instrumentation) He
He
 excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron-
excimer cluster tracers in superfluid helium-4 via neutron- He absorption reaction
He absorption reactionSonnenschein, V.*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; Kokuryu, Shoma*; Kubo, Wataru*; Suzuki, So*; Tomita, Hideki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Matsushita, Taku*; Wada, Nobuo*; et al.
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(3), p.033318_1 - 033318_12, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation) He
He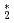 clusters via neutron-
clusters via neutron- He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulence
He absorption reaction toward visualization of full velocity field in quantum turbulenceMatsushita, Taku*; Sonnenschein, V.*; Guo, W.*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Hiroi, Kosuke; Hirota, Katsuya*; Iguchi, Tetsuo*; Ito, Daisuke*; Kitaguchi, Masaaki*; Kiyanagi, Yoshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, 196(1-2), p.275 - 282, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.92(Physics, Applied)Oikawa, Kenichi; Su, Y. H.; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Kawasaki, Takuro; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Harjo, S.; Parker, J. D.*; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; et al.
Physica B; Condensed Matter, 551, p.436 - 442, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.66(Physics, Condensed Matter)Su, Y. H.; Oikawa, Kenichi; Shinohara, Takenao; Kai, Tetsuya; Hiroi, Kosuke; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gong, W.; Zhang, S. Y.*; Parker, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Procedia, 88, p.42 - 49, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:87.16(Instruments & Instrumentation)Nishida, Akemi; Mukai, Yoichi*; Hamamoto, Takuji*; Kushibe, Atsumichi*; Komuro, Masato*; Ohashi, Yasuhiro*; Obi, Hirotoshi*; Tsubota, Haruji
Proceedings of 12th International Conference on Shock and Impact Loads on Structures (SI 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.379 - 388, 2017/06
Some design examples are presented to evaluate the shock-resistant performance of target buildings to confirm the applicability of the design criteria of AIJ guideline. Dynamic analyses are performed using SDOF model of an individual member on which an impulsive load is acting. Furthermore, analyses are performed using finite element model for the same member, and the results are compared to the results of the corresponding SDOF model for validation. Frame building structure model which is supposed to be located at the corner of a crossroad is investigated as an example. Dynamic responses and the corresponding damage states are illustrated for this building subjected to shock loads due to road vehicle crashes. As a non-structure member case, examples of window glass destruction subjected to internal and external gas explosions are presented.
 S
SGo, Shintaro*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Yokoyama, Rin*; Kobayashi, Motoki*; Kisamori, Keiichi*; Takaki, Motonobu*; Miya, Hiroyuki*; Ota, Shinsuke*; Michimasa, Shinichiro*; Shimoura, Susumu*; et al.
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 6, p.030005_1 - 030005_4, 2015/06
Nishida, Akemi; Ohashi, Yasuhiro*; Obi, Hirotoshi*; Takeuchi, Yoshitaka*; Kano, Toshiya*; Ryuzaki, Hibiki*; Ota, Toshiro*; Kishi, Tokumitsu*; Komuro, Masato*; Nakamura, Naohiro*
Kenchikubutsu No Taishogeki Sekkei No Kangaekata, p.161 - 202, 2015/01
Though design guidelines for earthquake and wind loads are specified for buildings, the guideline for impulsive load as explosion and impact is not specified yet in architectural field. This document corresponds to Chapter 8 of the book titled "Introduction to Shock-Resistant Design of Buildings" which made towards the impact design guideline. Some design examples are presented to illustrate the applicability of the tentative guideline for impulsive loads. Two buildings - a steel frame and a reinforced concrete frame building structures - located at the corner of a crossroads are selected. Dynamic responses and the corresponding damage states are illustrated for the cases of two buildings subjected to impact loads due to road vehicle crashes, internal and external explosions. The idea has been shown in this document are those that can be applied to nuclear facilities.

Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Matsuda, Yasuhiro*; Her, J.-L.*; Kindo, Koichi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Chen, B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(11), p.114702_1 - 114702_11, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.34(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The X-ray absorption and magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectra at the Yb L edge were measured in the mixed-valent heavy fermion compound YbAgCu
edge were measured in the mixed-valent heavy fermion compound YbAgCu at high magnetic fields and low temperatures. The magnetic-field-temperature (H-T) phase boundary determined by the valence state is in very good agreement with that determined by the magnetization. It is clearly found that the metamagnetism of this compound is due to the field induced valence transition. A distinctive positive peak of the XMCD spectra appears in the vicinity of the white line of the absorption due to Yb
at high magnetic fields and low temperatures. The magnetic-field-temperature (H-T) phase boundary determined by the valence state is in very good agreement with that determined by the magnetization. It is clearly found that the metamagnetism of this compound is due to the field induced valence transition. A distinctive positive peak of the XMCD spectra appears in the vicinity of the white line of the absorption due to Yb state, while no feature is observed in the XMCD spectra corresponding to the Yb
state, while no feature is observed in the XMCD spectra corresponding to the Yb state. A small negative XMCD peak was observed at a lower energy and was attributed to the quadrupole trasition from theoretical calcuration, which explains its peculicar magnetic field dependence.
state. A small negative XMCD peak was observed at a lower energy and was attributed to the quadrupole trasition from theoretical calcuration, which explains its peculicar magnetic field dependence.
Uchida, Kenichi*; Ota, Takeru*; Adachi, Hiroto; Xiao, J.*; Nonaka, Tatsumi*; Kajiwara, Yosuke*; Bauer, G. E. W.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 111(10), p.103903_1 - 103903_11, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:127 Percentile:95.86(Physics, Applied)Takeda, Masayasu; Yamazaki, Dai; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Maruyama, Ryuji; Hayashida, Hirotoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito; Yamazaki, Tatsuya; Kubota, Masato; Aizawa, Kazuya; Arai, Masatoshi; et al.
Chinese Journal of Physics, 50(2), p.161 - 170, 2012/04
 at high Magnetic fields
at high Magnetic fieldsMatsuda, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Toshiyuki*; Her, J.-L.*; Kindo, Koichi*; Michimura, Shinji*; Inami, Toshiya; Mizumaki, Masaichiro*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Suzuki, Motohiro*; Chen, B.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(1), p.015002_1 - 015002_2, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:56.34(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The valence change of Yb ion in YbAgCu was measured by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy under high magnetic fields up to 35T. The valence state of Yb in YbAgCu
was measured by means of X-ray absorption spectroscopy under high magnetic fields up to 35T. The valence state of Yb in YbAgCu at 4.8K significantly increases at the metamagnetic transition. The saturation value of
at 4.8K significantly increases at the metamagnetic transition. The saturation value of  at 55T is evaluated as 2.97 using the relation
at 55T is evaluated as 2.97 using the relation 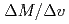 at 35T. This value is in good agreement with
at 35T. This value is in good agreement with  for the related compound YbInCu
for the related compound YbInCu at high temperatures and the Yb valence in the localized high-field phase. We conclude that the metamagnetic transition in YbAgCu
at high temperatures and the Yb valence in the localized high-field phase. We conclude that the metamagnetic transition in YbAgCu arises from the valence transition, as theoretically predicted.
arises from the valence transition, as theoretically predicted.
Uchida, Kenichi*; Adachi, Hiroto; An, Toshu*; Ota, Takeru*; Toda, Masaya*; Hillebrands, B.*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Nature Materials, 10(10), p.737 - 741, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:241 Percentile:98.45(Chemistry, Physical)We show that, using a NiFe/Pt bilayer wire on an insulating sapphire plate, electrons in the wire recognize their position on the sapphire. Under a temperature gradient in the sapphire, surprisingly, the voltage generated in the Pt layer is shown to reflect the wire position, although the wire is isolated both electrically and magnetically. This non-local voltage due to the coupling of spins and phonons: the only possible carrier of information in this system. We demonstrate this coupling by directly injecting sound waves, which realizes the acoustic spin pumping. Our finding provides a persuasive answer to the long-range nature of the spin Seebeck effect, and it opens the door to "acoustic spintronics" in which sound waves are exploited for constructing spin-based devices.