Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -decay properties of
-decay properties of 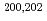 Fr
FrGhys, L.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Capponi, L.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; Cubiss, J.*; Derkx, X.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 100(5), p.054310_1 - 054310_13, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:75.29(Physics, Nuclear)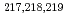 At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopy
At revealed by in-source laser spectroscopyBarzakh, A. E.*; Cubiss, J. G.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Seliverstov, M. D.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Ascher, P.*; Atanasov, D.*; Beck, D.*; Biero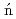 , J.*; et al.
, J.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 99(5), p.054317_1 - 054317_9, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:73.32(Physics, Nuclear)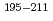 At
AtCubiss, J.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Mitsuoka, Shinichi*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ota, Shuya*; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; 60 of others*
Physical Review C, 97(5), p.054327_1 - 054327_19, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:93.44(Physics, Nuclear) Am at neutron energies below fission threshold
Am at neutron energies below fission thresholdHirose, Kentaro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro*; Ota, Shuya*; Nagayama, Tatsuro*; Tamura, Nobuyuki*; Goto, Shinichi*; Andreyev, A. N.; Vermeulen, M. J.; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 856, p.133 - 138, 2017/06
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:39.39(Instruments & Instrumentation) -delayed fission and
-delayed fission and  decay of
decay of 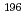 At
AtTruesdale, V. L.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Ghys, L.*; Huyse, M.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Sels, S.*; Andel, B.*; Antalic, S.*; Barzakh, A.*; Capponi, L.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 94(3), p.034308_1 - 034308_11, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.04(Physics, Nuclear) ) cross-sections using multi-nucleon transfer reactions
) cross-sections using multi-nucleon transfer reactionsMakii, Hiroyuki; Ota, Shuya*; Ishii, Tetsuro; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Chiba, Satoshi; Igashira, Masayuki*; Czeszumska, A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 797, p.83 - 93, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:30.26(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have installed new experimental apparatus to measure  rays from highly excited states populated by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions with heavy-ion projectiles to determine the (
rays from highly excited states populated by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions with heavy-ion projectiles to determine the ( ) cross sections by means of the surrogate reaction method. Apparatus consists of two anti-Compton LaBr
) cross sections by means of the surrogate reaction method. Apparatus consists of two anti-Compton LaBr (Ce) spectrometers to measure the
(Ce) spectrometers to measure the  rays and a Si
rays and a Si 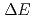 -
- detector system to detect outgoing projectile-like particles. Reactions of 153-MeV
detector system to detect outgoing projectile-like particles. Reactions of 153-MeV  O beams with
O beams with  Gd and
Gd and  Gd targets were used to study the performance of apparatus. By using the LaBr
Gd targets were used to study the performance of apparatus. By using the LaBr (Ce) scintillators with relatively large volume (101.6 mm in diameter and 127 mm in length), we have successfully measured
(Ce) scintillators with relatively large volume (101.6 mm in diameter and 127 mm in length), we have successfully measured  rays from the compound nuclei, which have excitation energy above neutron separation energy, populated by
rays from the compound nuclei, which have excitation energy above neutron separation energy, populated by  Gd(
Gd( O,
O,  O)
O) Gd and
Gd and  Gd(
Gd( O,
O,  O)
O)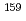 Gd two-neutron transfer reactions. The present study has demonstrated high capability of apparatus to measure the de-excitation
Gd two-neutron transfer reactions. The present study has demonstrated high capability of apparatus to measure the de-excitation  rays in the compound nuclei produced by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions for determination of the (
rays in the compound nuclei produced by the multi-nucleon transfer reactions for determination of the ( ) cross sections by using the surrogate reaction method.
) cross sections by using the surrogate reaction method.
 (Ce) spectrometer for measurement of surrogate reactions
(Ce) spectrometer for measurement of surrogate reactionsMakii, Hiroyuki; Ota, Shuya*; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Wakabayashi, Yasuo*; Chiba, Satoshi*; Igashira, Masayuki*
Nuclear Data Sheets, 119, p.361 - 364, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:18.04(Physics, Nuclear)Anti-Compton LaBr (Ce) spectrometers have been installed at JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility in order to measure the
(Ce) spectrometers have been installed at JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility in order to measure the  rays from the highly excited states produced by surrogate reactions. Each spectrometer consists of a central LaBr
rays from the highly excited states produced by surrogate reactions. Each spectrometer consists of a central LaBr (Ce) detector with a diameter of 10.2 cm and a length of 12.7 cm, and an annular BGO detector with a thickness of 2.5 cm and a length of 25.4 cm. In this contribution, we will present the results of performance test using the standard
(Ce) detector with a diameter of 10.2 cm and a length of 12.7 cm, and an annular BGO detector with a thickness of 2.5 cm and a length of 25.4 cm. In this contribution, we will present the results of performance test using the standard  ray source and high-energy
ray source and high-energy  rays from the
rays from the  Al(p,
Al(p, )
) Si reaction, and a measurement plan for (n,
Si reaction, and a measurement plan for (n, ) cross sections using a surrogate reaction at JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility.
) cross sections using a surrogate reaction at JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator facility.
Tamura, Nobuyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Kimura, Atsushi; Ota, Shuya*; Andreyev, A. N.; Vermeulen, M.*; Gillespire, S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ota, Shuya*; Yasuda, Nakahiro*; Sihver, L.*; Kodaira, Satoshi*; Ideguchi, Yusuke*; Hasebe, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
Projectile charge-changing cross sections for nuclei in galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) on hydrogen play essentially important roles for the study of origin and source composition of GCRs. Previous experimental and theoretical works done so far made much progress on those cross sections. However, there are still uncertainties in much of the cross section data, and therefore the present knowledge of cross sections has not led to successful determination of the GCR source composition. To improve the uncertainties, a novel measurement system of projectile charge-changing cross section using CR-39 plastic nuclear track detectors with excellent position and nuclear charge resolutions has been developed. We carried out measurements of total and partial charge-changing cross sections for Fe and Mg on 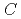 and
and 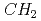 targets at 0.1 to 1 GeV/n using the method.
targets at 0.1 to 1 GeV/n using the method.
 Li and
Li and  Li
LiMakii, Hiroyuki; Segawa, Mariko; Ota, Shuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nishinaka, Ichiro*; Nishio, Katsuhisa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Iwase, Hiroshi*; Namito, Yoshihito*; Hirayama, Hideo*; Niita, Koji*; Hashimoto, Shintaro; Matsuda, Norihiro; Noda, Shusaku; Ota, Shuya*; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sato, Tatsuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
The Electron Gamma Shower (EGS), which has been developed by Univ. of Michigan, SLAC, Canadian government, KEK etc., is one of the electrons and  -ray shower transport Monte Carlo code. The EGS5 code is used in various fields of radiation shielding of accelerator facilities, design of radiation detectors, dose estimation in medical application, and so on. The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System PHITS, the multi-purpose and multi-particle Monte Carlo code, has a lot of useful user-interfaces and output functions. It would be of great benefit to EGS users if EGS5 can be operated in the PHITS system, and to PHITS users too, if the EGS5 physics can be used in the PHITS code. The EGS5 models are divided into some parts and implemented in the PHITS code in a manner that the calculation procedure is identical to the original EGS5 so that users can obtain same results.
-ray shower transport Monte Carlo code. The EGS5 code is used in various fields of radiation shielding of accelerator facilities, design of radiation detectors, dose estimation in medical application, and so on. The Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System PHITS, the multi-purpose and multi-particle Monte Carlo code, has a lot of useful user-interfaces and output functions. It would be of great benefit to EGS users if EGS5 can be operated in the PHITS system, and to PHITS users too, if the EGS5 physics can be used in the PHITS code. The EGS5 models are divided into some parts and implemented in the PHITS code in a manner that the calculation procedure is identical to the original EGS5 so that users can obtain same results.
Ota, Shuya; Sihver, L.*; Kobayashi, Shingo*; Hasebe, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
Neutron production by galactic cosmic rays (GCR) in the lunar subsurface plays an important role in the radiation environment on the surface and subsurface of the Moon and to make its accurate estimation is therefore very important for lunar and planetary nuclear spectroscopy and space dosimetry. In this work, the depth dependency of neutron production from protons and alpha particles in galactic cosmic ray (GCR) was estimated using the three-dimensional particle and heavy ion transport simulation code PHITS incorporating the latest high energy nuclear data, JENDL-HE. Our estimation of equilibrium neutron density profiles in the lunar subsurface was compared with the experimental data obtained by Apollo 17 Lunar Neutron Probe Experiment (LNPE). As the results, our calculation successfully reproduced the LNPE data within experimental errors of 15% (measurement) + 30% (systematic).
 Ne (
Ne ( ,
, )
)  Mg using
Mg using  Ne +
Ne +  Li reaction
Li reactionOta, Shuya; Makii, Hiroyuki; Ishii, Tetsuro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Chiba, Satoshi
no journal, ,
While the reaction  Ne (
Ne ( ,n)
,n)  Mg in stellar helium burning is considered to be the dominant neutron source for s-process in massive stars with M
Mg in stellar helium burning is considered to be the dominant neutron source for s-process in massive stars with M  8 solar mass, the competing
8 solar mass, the competing  Ne (
Ne ( ,
, )
)  Mg reaction may be considerable strength and significantly reduce the neutron production. A branching ratio of the two reactions and resonance parameters such as levels and strengths in
Mg reaction may be considerable strength and significantly reduce the neutron production. A branching ratio of the two reactions and resonance parameters such as levels and strengths in  Mg produced by
Mg produced by  +
+  Ne should be experimentally determined with good accuracy. Presently, uncertainty in the observed resonance levels at E
Ne should be experimentally determined with good accuracy. Presently, uncertainty in the observed resonance levels at E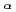 (830 keV) have not been cleared up despite their important roles in the neutron production. In this work, we set our goal to investigate this low energy resonance. Experiments were performed using
(830 keV) have not been cleared up despite their important roles in the neutron production. In this work, we set our goal to investigate this low energy resonance. Experiments were performed using  Ne beam at Tokai Tandem accelerator in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In this symposium, we will present our experimental scheme and future prospective.
Ne beam at Tokai Tandem accelerator in Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In this symposium, we will present our experimental scheme and future prospective.
Chiba, Satoshi; Ota, Shuya*; Yasuda, Nakahiro*; Sihver, L.*; Kodaira, Satoshi*; Ideguchi, Yusuke*; Hasebe, Nobuyuki*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nagayama, Tatsuro*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Mitsuoka, Shinichi; Makii, Hiroyuki; Ota, Shuya*; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Ishii, Tetsuro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Makii, Hiroyuki; Segawa, Mariko; Ota, Shuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Harada, Hideo
no journal, ,
The neutron capture cross section of light elements, such as Li, Be, and B, plays an important role in inhomogeneous Big-Bang nucleosynthesis scenarios or in explosive nucleosynthesis, like r-process. However, data for neutron capture reaction of light elements sparse and / or disagree in the astrophysical relevant energy region, since the cross section of light elements is quite small even at the thermal energy. Intense pulsed neutron beam provided by the Material and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC and high performance Ge spectrometer, which is the main detector of the Accurate Neutron-Nucleus Reaction Measurement Instrument (ANNRI) installed at Beam Line No. 04 of MLF in the J-PARC, will allow us to study neutron capture reaction of light elements. At first we have measured the neutron capture cross section of Li-7 at the MLF in the J-PARC. In this contribution, we will present the results of the measurement.
Hirose, Kentaro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; L guillon, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Orlandi, R.; Smallcombe, J.; Ishii, Tetsuro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; et al.
guillon, R.; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Orlandi, R.; Smallcombe, J.; Ishii, Tetsuro; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; et al.
no journal, ,
Makii, Hiroyuki; Ishii, Tetsuro; Ota, Shuya*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Nagayama, Tatsuro*; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Mitsuoka, Shinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishio, Katsuhisa; Hirose, Kentaro; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Ota, Shuya; Nagayama, Tatsuro*; Chiba, Satoshi; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Ishii, Tetsuro; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Makii, Hiroyuki; Segawa, Mariko; Ota, Shuya*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nishinaka, Ichiro; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Harada, Hideo
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English