Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(5), p.133 - 137, 2022/05
The effect of the corrosion inhibitor on the corrosion of steel under a thin solution layer was investigated. As a result of forming a thin solution layer with a thickness of 1.0-0.2 mm on the specimen, adding a mixed solution of sodium molybdate and aluminum lactate as a corrosion inhibitor, and performing electrochemical measurement, the corrosion inhibitor suppresses the anodic reaction. And in the thin solution layer, it was suggested that the morphology of the protective layer structure by the corrosion inhibitor changed according to the amount of liquid as compared with the bulk immersion.
Momma, Yuichiro*; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Otani, Kyohei
Zairyo To Kankyo, 71(4), p.121 - 125, 2022/04
The effect of solution layer thickness on the atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel was investigated using novel devices fabricated by a 3D printer. These novel devices allowed us to control the solution layer thickness precisely. Potentiodynamic polarization measurements were performed under thickness-controlled solution layer, and oxygen diffusion limiting current density ( ) and anodic current density (
) and anodic current density ( ) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,
) were measured. As the solution layer become thinner,  increased and
increased and  decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20
decreased. This result indicates that corrosion accelerates when the solution layer becomes thinner. The diffusion coefficient of oxygen was calculated as 3.20 10
10 cm
cm s
s from the relationship between
from the relationship between  and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
and solution layer thickness, and the critical diffusion thickness was estimated to be 0.87 mm.
Kudo, Hideyuki*; Otani, Yuichi*; Hara, Masahide*; Kato, Atsushi; Otaka, Masahiko; Ide, Akihiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(4), p.408 - 420, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)In a fuel handling system of sodium-cooled fast reactors (SFRs), it is necessary to remove the sodium remaining on spent fuel assemblies (FAs) before storing them in a spent fuel water pool (SFP) in order to minimize plant operating loads. A next-generation SFR in Japan has adopted an advanced dry cleaning process which consists of the following steps, argon gas blowing to remove the metallic residual sodium on the FA, moist argon gas blowing to deactivate the residual sodium, and direct storage in the SFP. This three-step process increases economic competitiveness and reduces waste products thanks to a waterless process. In this R&D work, performance of the dry cleaning process has been investigated.
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hirano, Koichiro; Ito, Takashi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Kitamura, Ryo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Oguri, Hidetomo; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Shinto, Katsuhiro; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 1350, p.012077_1 - 012077_7, 2019/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.67(Physics, Particles & Fields)We have upgraded a 3-MeV linac at J-PARC. The ion source is same as the J-PARC linac's, and the old 30-mA RFQ is replaced by a spare 50-mA RFQ, therefore, the beam energy is 3 MeV and the nominal beam current is 50 mA. The main purpose of this system is to test the spare RFQ, but also used for testing of various components required in order to keep the stable operation of the J-PARC accelerator. The accelerator has been already commissioned, and measurement programs have been started. In this paper, present status of this 3-MeV linac is presented.
Kudo, Hideyuki*; Otani, Yuichi*; Hara, Masahide*; Kato, Atsushi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Otaka, Masahiko; Nagai, Keiichi; Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Ide, Akihiro*
Proceedings of 2019 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2019) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2019/05
A next generation SFR in Japan has adopted an advanced dry cleaning system which consists of the argon gas blowing process to reduce the amount of metallic residual sodium remaining on spent fuel assemblies. This paper describes experimental and analytical work focusing on the amount of residual sodium remaining on a fuel pin bundle before and after the argon gas blowing process. The experiments were conducted using a sodium test loop and a short specimen consisting of a 7 pin bundle. The effects of the blowing gas velocity and the blowing time were quantitatively analyzed in the experiments. On the basis of these experimental results, evaluation models predicting the amount of the residual sodium were constructed.
Kato, Atsushi; Nagai, Keiichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Otaka, Masahiko; Oka, Nobuki*; Tanaka, Masako*; Otani, Yuichi*; Ide, Akihiro*
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2017/04
In a fuel handling system (FHS) of a sodium-cooled fast reactor, it is necessary to reduce residual sodium on a spent fuel subassembly before storing at a spent fuel water-pool (SFP) in order to minimize design loads. Although the wet cleaning process adopted on MONJU could eliminate almost all of residual sodium, a large amount of radioactive liquid waste occurs and it needs long duration of cleaning treatment and large plant commodities. On the other hand, Japan sodium-cooled fast reactor adopted an advanced dry cleaning system which consists of roughly blowing massive sodium on the fuel subassembly out by 300 C argon gas, inactivation of residual sodium to NaOH by moist argon gas and directly immersion into the SFP to achieve economic competitiveness and waste reduction. This paper reports current status of recent R&D activities to demonstrate a performance of the dry cleaning process in Japan which are for improvement of the cleaning performance and optimizing the FHS design.
C argon gas, inactivation of residual sodium to NaOH by moist argon gas and directly immersion into the SFP to achieve economic competitiveness and waste reduction. This paper reports current status of recent R&D activities to demonstrate a performance of the dry cleaning process in Japan which are for improvement of the cleaning performance and optimizing the FHS design.
Otani, Hiroshi; Mizui, Hiroyuki; Higashiura, Norikazu; Bando, Fumio*; Endo, Nobuyuki*; Yamagishi, Ryuichiro*; Kume, Kyo*
Heisei-25-Nendo Koeki Zaidan Hojin Wakasawan Enerugi Kenkyu Senta kenkyu Nempo, 16, P. 66, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Tsujita, Yuichi; Yamagishi, Nobuhiro*; Kimura, Kazuyuki*; Otani, Takayuki; Tsuruoka, Nobuhiko*; Fujita, Naoyuki*
Joho Shori Gakkai Kenkyu Hokoku 2002-HPC-92, p.7 - 12, 2002/10
SCore system has been developed to provide flat computing infrastructure for parallel computing without awareness of each compute host in a PC cluster system. An SCore cluster system can be handled as a single computer. MPICH-SCore, which is an MPI library in SCore, is not available across multiple SCore cluster systems as well as multiple platforms. We have implemented an MPI communication library, Stampi in SCore cluster system to enable MPI communication between SCore cluster systems and measured communication performance of the library using SCore cluster systems.
 SiO
SiO
Kubo, Tomoaki*; Otani, Eiji*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Kambe, Yuichi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru; Kikegawa, Takumi*; Fujino, Kiyoshi*
Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 129(1-2), p.153 - 171, 2002/01
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:66.19(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
 SiO
SiO
Kubo, Tomoaki*; Otani, Eiji*; Kato, Takumi*; Urakawa, Satoru*; Suzuki, Akio*; Kambe, Yuichi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Wataru; Fujino, Kiyoshi*
Geophysical Research Letters, 27(6), p.807 - 810, 2000/03
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:61.89(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Natori, Hina; Sato, Tetsuya; Asai, Masato; Ito, Yuta; Uchibaba, Yuta; Gong, G.; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Miyachi, Yuta; Nagame, Yuichiro*; Otani, Ryo; et al.
no journal, ,
We have conducted gas-phase chemical experiments to investigate the volatilities of group-6 compounds as a model experiment for element 106, seaborgium (Sg). In this study, an isothermal gas chromatographic (IGC) technique was employed for off-line and on-line gas phase studies of volatile oxychlorides of group-6 elements, molybdenum (Mo) and tungsten (W). The volatile oxychloride formation of Mo and W was examined under various conditions using their short-lived isotopes. Moreover, several isothermal gas chromatograms were obtained for the compounds. The evaluated -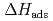 values were in good agreement with the estimated value for MoO
values were in good agreement with the estimated value for MoO Cl
Cl and WO
and WO Cl
Cl , respectively. We concluded that only MO
, respectively. We concluded that only MO Cl
Cl (M=Mo, W) would be formed under the studied condition, and that adsorption enthalpies of MoO
(M=Mo, W) would be formed under the studied condition, and that adsorption enthalpies of MoO Cl
Cl and WO
and WO Cl
Cl were successfully obtained.
were successfully obtained.
Kato, Atsushi; Nagai, Keiichi; Oka, Nobuki*; Ide, Akihiro*; Tanaka, Masako*; Otani, Yuichi*
no journal, ,
JAEA, MFBR and MHI have been studying the dry cleaning system of residual sodium on core components with blowing argon gas. This reports the master planning of the glove box test and sodium loop test to investigate and demonstrate the dry cleaning performances.
Kato, Atsushi; Nagai, Keiichi; Oka, Nobuki*; Ide, Akihiro*; Otani, Yuichi*; Tanaka, Masako*
no journal, ,
JAEA, MFBR and MHI have been studying the dry cleaning system of residual sodium on core components with blowing argon gas. This reports the results of the glove box test to conduct for investigating the sodium test conditions of demonstration test by sodium loop.
Kudo, Hideyuki*; Otani, Yuichi*; Hara, Masahide*; Otaka, Masahiko; Nagai, Keiichi; Saito, Junichi; Ishikawa, Nobuyuki; Ara, Kuniaki; Ide, Akihiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kimura, Daisuke; Hikinuma, Yuichi; Tanabe, Masanori; Makino, Tatsuya; Maegawa, Yoshiharu; Hayata, Kenichi*; Shiotani, Junya*; Nohara, Naofumi; Hoshi, Katsuya; Tsujimura, Norio; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tetsuya; Gong, G.*; Honda, Maki; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Miyachi, Yuta; Natori, Hina; Uchibaba, Yuta; Aoki, Ryota; Otani, Ryo; Tsukada, Kazuaki; et al.
no journal, ,
To elucidate the chemical properties of superheavy elements (Z  103) in the liquid phase, we have been developing a flow-type liquid-phase chemical separation system. In this work, we have developed an ion exchange surface that can be applied to
103) in the liquid phase, we have been developing a flow-type liquid-phase chemical separation system. In this work, we have developed an ion exchange surface that can be applied to  -particle detectors in the system. To form the functional surface, Self-Assembled Monolayers (SAMs) onto the Au surface using functionalized thiol was employed. We confirmed the formed SAMs surface has sufficient durability in nitric acid for long hours, and an ion exchange function using a short-lived Hf isotope,
-particle detectors in the system. To form the functional surface, Self-Assembled Monolayers (SAMs) onto the Au surface using functionalized thiol was employed. We confirmed the formed SAMs surface has sufficient durability in nitric acid for long hours, and an ion exchange function using a short-lived Hf isotope, 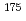 Hf, a homolog of rutherfordium (Rf, Z=104).
Hf, a homolog of rutherfordium (Rf, Z=104).
Otani, Ryo; Sato, Tetsuya; Aoki, Ryota*; Shirai, Kaori*; Suzuki, Hayato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Ito, Yuta; Nagame, Yuichiro*; Sakama, Minoru*
no journal, ,
The adsorption enthalpy of the Sg dioxydichloride on a quartz surface (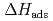 (SgO
(SgO Cl
Cl )) has been reported to be -98 kJ/mol. The result, however, is still ambiguous because the value was evaluated based on a few experimental points with large statistics errors. To obtain a reliable
)) has been reported to be -98 kJ/mol. The result, however, is still ambiguous because the value was evaluated based on a few experimental points with large statistics errors. To obtain a reliable 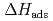 (SgO
(SgO Cl
Cl )) for a discussion of an influence of relativistic effects, a stable gas chemistry apparatus with good reproducibility is mandatory. In this study, we have conducted offline experiments of an isothermal gas chromatography) with short-lived Mo isotopes originated from a
)) for a discussion of an influence of relativistic effects, a stable gas chemistry apparatus with good reproducibility is mandatory. In this study, we have conducted offline experiments of an isothermal gas chromatography) with short-lived Mo isotopes originated from a  Cf fission source. We searched for experimental parameters for an on-line experiment. At the presentation, we will present the obtained optimum conditions for gas chromatographic separation of group-6 elements and determined
Cf fission source. We searched for experimental parameters for an on-line experiment. At the presentation, we will present the obtained optimum conditions for gas chromatographic separation of group-6 elements and determined 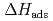 (MoO
(MoO Cl
Cl )).
)).
Aoki, Ryota*; Sato, Tetsuya; Otani, Ryo; Suzuki, Hayato; Ito, Yuta; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro*
no journal, ,
To apply a SHEs ion-beam to physical and chemical investigations, we have been developing ion sources that apply to a short-lived single atom. We employed the Electron Beam Generated Plasma (EBGP) method to ionize an element with high ionization energy. The EBGP ion source can ionize an element or a molecule of nuclear reaction products by bombarding an electron beam that accelerated between the cathode and the anode electrode. In this work, we built the EBGP ion source and searched for an optimum condition ionization of a single atom.