Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Akagi, Hiroshi*; Kumada, Takayuki; Otobe, Tomohito*; Itakura, Ryuji*; Hasegawa, Hirokazu*; Oshima, Yasuhiro*
Chemistry Letters, 49(4), p.416 - 418, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.62(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Akagi, Hiroshi*; Kumada, Takayuki; Otobe, Tomohito*; Itakura, Ryuji*; Hasegawa, Hirokazu*; Oshima, Yasuhiro*
Applied Physics B, 124(1), p.14_1 - 14_8, 2018/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.98(Optics)We propose and numerically simulate a method of laser isotope separation based on field-free alignment of isotopologues, utilizing an intense switched nanosecond (ns) laser field which is slowly turned on and rapidly turned off at the peak with the falling time of 200 fs. The femtosecond (fs) laser induced alignment of molecules including a heavy atom is severely disturbed by ionization because of their small ionization potential. Our simulations for I Br and I
Br and I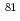 Br isotopologues demonstrate that the switched ns laser field can make isotopologues well-aligned with the reduced ionization probability at the laser intensity which is an order-of-magnitude lower than a typical intensity for field-free alignment induced by a fs laser field.
Br isotopologues demonstrate that the switched ns laser field can make isotopologues well-aligned with the reduced ionization probability at the laser intensity which is an order-of-magnitude lower than a typical intensity for field-free alignment induced by a fs laser field.
Kumada, Takayuki; Otobe, Tomohito; Nishikino, Masaharu; Hasegawa, Noboru; Hayashi, Terutake*
Applied Physics Letters, 108(1), p.011102_1 - 011102_4, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:48.97(Physics, Applied)The dynamics of photomechanical spallation during femtosecond laser ablation of fused silica was studied by time-resolved reflectivity with double pump pulses. Oscillation of reflectivity was caused by interference between the probe pulses reflected at the sample surface and the spallation layer, and was enhanced when the surface is irradiated with the second pump pulse within a time interval of several picoseconds after the first pump pulse. However, as the time-interval was increased, the oscillation amplitude decreased with an exponential decay time of 10 ps. The oscillation disappeared when the interval exceeded 20 ps. This result suggests that the formation time of the spallation layer is approximately 10 ps.
Otobe, Tomohito; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Physical Review B, 93(4), p.045124_1 - 045124_9, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:53 Percentile:86.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We theoretically investigate the dynamical Franz-Keldysh effect in femtosecond time resolution, that is, the time-dependent modulation of a dielectric function at around the band gap under an irradiation of an intense laser field. We develop a pump-probe formalism in two distinct approaches: first-principles simulation based on real-time time-dependent density functional theory and analytic consideration of a simple two-band model. We find that, while time-average modulation may be reasonably described by the static Franz-Keldysh theory, a remarkable phase shift is found to appear between the dielectric response and the applied electric field.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Lee, K.-M.*; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 92(20), p.205413_1 - 205413_6, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:84.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the energy deposition by very short laser pulses in SiO (
( -quartz) with a view to establishing systematics for predicting damage and nanoparticle production. The theoretical framework is time-dependent density functional theory, implemented by the real-time method in a multiscale representation. We find that the deposited energy in the medium can be accurately modeled as a function of the local electromagnetic pulse fluence. The energy deposition function can in turn be quite well fitted to the strong-field Keldysh formula. We find reasonable agreement between the damage threshold and the energy required to melt the substrate. The ablation threshold estimated by the energy to convert the substrate to an atomic fluid is higher than the measurement, indicating significance of nonthermal nature of the process. A fair agreement is found for the depth of the ablation.
-quartz) with a view to establishing systematics for predicting damage and nanoparticle production. The theoretical framework is time-dependent density functional theory, implemented by the real-time method in a multiscale representation. We find that the deposited energy in the medium can be accurately modeled as a function of the local electromagnetic pulse fluence. The energy deposition function can in turn be quite well fitted to the strong-field Keldysh formula. We find reasonable agreement between the damage threshold and the energy required to melt the substrate. The ablation threshold estimated by the energy to convert the substrate to an atomic fluid is higher than the measurement, indicating significance of nonthermal nature of the process. A fair agreement is found for the depth of the ablation.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akagi, Hiroshi; Itakura, Ryuji; Otobe, Tomohito; Nishikino, Masaharu; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Applied Physics Letters, 106(22), p.221605_1 - 221605_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:17.24(Physics, Applied)The dynamics of femtosecond laser ablation of transparent polymers were examined using time-resolved reflectivity. When these polymers were irradiated by a pump pulse with fluence above the ablation threshold of 0.8-2.0 J/cm , we observed the oscillation of the reflectivity caused by the interference between the reflected probe pulses from the sample surface and the thin layer due to the non-thermal photomechanical effects of spallation. As the fluence of the pump pulse increased, the separation velocity of the thin layer increased from 6 km/s to an asymptotic value of 11 km/s. It is suggested that the velocities are determined by shock-wave velocities of the photo-excited layer.
, we observed the oscillation of the reflectivity caused by the interference between the reflected probe pulses from the sample surface and the thin layer due to the non-thermal photomechanical effects of spallation. As the fluence of the pump pulse increased, the separation velocity of the thin layer increased from 6 km/s to an asymptotic value of 11 km/s. It is suggested that the velocities are determined by shock-wave velocities of the photo-excited layer.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Physical Review B, 90(17), p.174303_1 - 174303_8, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:83.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the dielectric response of excited crystalline silicon in electron thermal equilibrium by adiabatic time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) to model the response to irradiation by high-intensity laser pulses. We find that the extracted effective mass are in the range of 0.22-0.36 and lifetimes are in the range of 1-14 fs depending on the temperature.
Kumada, Takayuki; Akagi, Hiroshi; Itakura, Ryuji; Otobe, Tomohito; Yokoyama, Atsushi
Journal of Applied Physics, 115(10), p.103504_1 - 103504_9, 2014/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:54.10(Physics, Applied)Femtosecond laser ablation dynamics of fused silica is examined via time-resolved reflectivity measurements. After optical breakdown was caused by irradiation of a pump pulse, the reflectivity oscillated with a period of 63 ps for a wavelength 795 nm. The period was reduced by half for 398 nm. We ascribe the oscillation to the interference between the probe pulses reflected from the front and rear surfaces of the photo-excited molten fused silica layer.
 -quartz irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulse
-quartz irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulseLee, K.-M.*; Kim, C. M.*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Otobe, Tomohito; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro; Jeong, T. M.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 115(5), p.053519_1 - 053519_8, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:70.35(Physics, Applied)A computational method based on a first-principles multiscale simulation has been used for calculating the optical response and the ablation threshold of an optical material irradiated with an ultrashort intense laser pulse. The method was applied to investigate the changes in the optical reflectance of quartz bulk, half-wavelength thin-film and quarter-wavelength thin-film and to estimate their ablation thresholds. Despite the adiabatic local density approximation used in calculating the exchange-correlation potential, the reflectance and the ablation threshold obtained from our method agree well with the previous theoretical and experimental results. The method can be applied to estimate the ablation thresholds for optical materials in general.
Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 89(6), p.064304_1 - 064304_8, 2014/02
Times Cited Count:68 Percentile:90.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We calculate the dielectric response of crystalline silicon following irradiation by a high-intensity laser pulse, modeling the dynamics by the time-dependent Kohn-Sham equations in the presence of the laser field. As expected, the excited silicon shows features of an electron-hole plasma of nonequilibrium phase in its response, characterized by a negative divergence in the real part of the dielectric function at small frequencies. We also find that the imaginary part of the dielectric function can be negative, particularly for the parallel polarization of pump and probe fields.
 /SiO
/SiO multilayer
multilayerTateno, Ryo*; Okada, Hajime; Otobe, Tomohito; Kawase, Keigo*; Koga, J. K.; Kosuge, Atsushi; Nagashima, Keisuke; Sugiyama, Akira; Kashiwagi, Kunihiro*
Journal of Applied Physics, 112(12), p.123103_1 - 123103_3, 2012/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:12.93(Physics, Applied)Elucidation of the mechanisms of laser damage is indispensable in realizing high resistance mirrors for the next generation of ultra-short pulse high intensity lasers. In this study, the surface and a section of the laser-damaged area of a laser mirror were observed with a laser microscope and a transmission electron microscope (cross-sectional TEM), respectively. A grain boundary of HfO microcrystal was observed in the damaged area. This observation, and an evaluation of the mirror's damage resistance showed that the formation of crystals in the multilayer mirror is one of the major determinants of damage resistance.
microcrystal was observed in the damaged area. This observation, and an evaluation of the mirror's damage resistance showed that the formation of crystals in the multilayer mirror is one of the major determinants of damage resistance.
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Iwata, Junichi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*
Nihon Butsuri Gakkai-Shi, 67(10), p.685 - 689, 2012/10
Coherent phonon is the macroscopic coherent oscillation of atoms in a solid state generating under the ultrafast laser pulse which is shorter than the frequency of the phonon. Some physical processes for the coherent phonon have been proposed. We are studying the computational method describing the dynamics of the electron and atom employing the time-dependent density functional theory. Our computational results show the origine of the coherent phonon in Si quantitatively.
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Sato, Shunsuke*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Iwata, Junichi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 137(22), p.22A527_1 - 22A527_8, 2012/08
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:68.61(Chemistry, Physical)The time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) is the leading computationally feasible theory to treat excitations by strong electromagnetic fields. Here the theory is applied to coherent optical phonon generation. We examine the process in the crystalline semimetal antimony (Sb), where nonadiabatic coupling and optical phonon of different symmetries can be observed. The TDDFT is able to account for a number of qualitative features of the observed coherent phonon.
Otobe, Tomohito
Journal of Applied Physics, 111(9), p.093112_1 - 093112_7, 2012/05
Times Cited Count:34 Percentile:76.47(Physics, Applied)We present a first-principles description for the electron excitation and the high-harmonic generation (HHG) in a diamond by intense laser pulse irradiation and their laser parameter dependence. The pulse of the HHG above band gap are generated after the peak intensity and are shorter than the incident laser pulse. The intensity of HHG spectra increases as laser intensity increase nonlinearly, and we find the blue shift of the HHG spectrum when the optical breakdown occurs.
Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Sugiyama, Takeshi*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 85(4), p.045134_1 - 045134_11, 2012/01
Times Cited Count:207 Percentile:98.02(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We apply the coupled dynamics of time-dependent density functional theory and Maxwell equations to the interaction of intense laser pulses with crystalline silicon. As a function of electromagnetic field intensity, we see several regions in the response. At the lowest intensities, the pulse is reflected and transmitted in accord with the dielectric response, and the characteristics of the energy deposition is consistent with two-photon absorption. The absorption process begins to deviate from that at laser intensities  10
10 W/cm
W/cm , where the energy deposited is of the order of 1 eV per atom. Changes in the reflectivity are seen as a function of intensity. When it passes a threshold of about
, where the energy deposited is of the order of 1 eV per atom. Changes in the reflectivity are seen as a function of intensity. When it passes a threshold of about 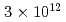 W/cm
W/cm , there is a small decrease. At higher intensities, above 2
, there is a small decrease. At higher intensities, above 2 10
10 W/cm
W/cm , the reflectivity increases strongly. This behavior can be understood qualitatively in a model treating the excited electron-hole pairs as a plasma.
, the reflectivity increases strongly. This behavior can be understood qualitatively in a model treating the excited electron-hole pairs as a plasma.
Akagi, Hiroshi; Itakura, Ryuji; Otobe, Tomohito; Kumada, Takayuki; Tsubouchi, Masaaki; Yokoyama, Atsushi
JAEA-Conf 2011-001, p.40 - 43, 2011/03
no abstracts in English
Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Shinohara, Yasushi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Iwata, Junichi*; Bertsch, G. F.*
Procedia Computer Science, 4, p.852 - 859, 2011/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:59.74(Computer Science, Theory & Methods)We report a first-principle computational method to describe many-electron dynamics in crystalline solid. The method is based on the time-dependent density functional theory, solving time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation in real-time and real-space. The calculation is efficiently parallelized by distributing computations of different  -point among processors. To illustrate usefulness of the method and efficiency of the parallel computation, we show calculations of electron dynamics in bulk Si induced by intense and ultrafast laser pulse.
-point among processors. To illustrate usefulness of the method and efficiency of the parallel computation, we show calculations of electron dynamics in bulk Si induced by intense and ultrafast laser pulse.
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Kawashita, Yosuke*; Iwata, Junichi*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Physical Review B, 82(15), p.155110_1 - 155110_10, 2010/10
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:88.53(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We apply the adiabatic time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) to the generation of coherent optical phonons in Si crystals by intense laser pulses. The theory reproduces the main phenomena observed experimentally: dependence on polarization, strong growth at the direct band gap, and the change in phase from below to above the band gap. Both show that two mechanisms invoked in phenomenological theory, namely, impulsively stimulated Raman scattering and displacive excitation, are present in the TDDFT. The calculated phase of the coherent phonon is in qualitative agreement with experiment and with phenomenological modeling in the vicinity of the direct band gap. At higher laser frequencies, the TDDFT predicts additional structure not present in the modeling.
Shinohara, Yasushi*; Kawashita, Yosuke*; Iwata, Junichi*; Yabana, Kazuhiro*; Otobe, Tomohito; Bertsch, G. F.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 22(38), p.384212_1 - 384212_4, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:49.38(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report a first-principle description for coherent phonon generation in diamond based on the time-dependent density functional theory. The time-dependent Kohn-Sham equation is solved in real-time to calculate the electron dynamics in periodic solid under an ultrashort laser pulse. We find the calculated forces acting on ions are consistent with measurements in selection rule and in dependence on laser intensity.
 -quartz under intense short laser irradiation
-quartz under intense short laser irradiationOtobe, Tomohito
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 22(38), p.384204_1 - 384204_4, 2010/09
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:58.76(Physics, Condensed Matter)We simulated the electron excitation process in  -quartz under intense laser field by solving time-dependent Khon-Sham equation with real-time and -space method. We found that the extra photo-absorption above the band gap. This results is similar to the above-threshold ionization (ATI) in atoms and molecules and indicates absorption of many photon at once or after electron excitation from valence band to conduction band.
-quartz under intense laser field by solving time-dependent Khon-Sham equation with real-time and -space method. We found that the extra photo-absorption above the band gap. This results is similar to the above-threshold ionization (ATI) in atoms and molecules and indicates absorption of many photon at once or after electron excitation from valence band to conduction band.