Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O/H
O/H O vapor generator for contrast-variation neutron scattering
O vapor generator for contrast-variation neutron scatteringArima-Osonoi, Hiroshi*; Takata, Shinichi; Kasai, Satoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Miyata, Noboru*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Iwase, Hiroki*; Hiroi, Kosuke; et al.
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(6), p.1802 - 1812, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:77.05(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 42(4), p.041503_1 - 041503_12, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:29.47(Environmental Sciences)Sheltering is one of the countermeasures against radiation exposure during nuclear accidents. The effectiveness of sheltering for inhalation exposure is often expressed by the reduction factor, which is defined as the ratio of the indoor to the outdoor cumulative radioactivity concentrations or doses. The indoor concentration is mainly controlled by the air exchange rate, penetration factor, and indoor deposition rate. Meanwhile, the air exchange rate depends on surrounding environmental conditions: the wind speed, leakage area normalized by the floor area of the house, and gross building coverage ratio. In this study, the ranges of the uncertainty of the reduction factors for particles and I were investigated under various environmental conditions, and sensitivity analyses were conducted to understand the parameter with the most influence on the uncertainty of the reduction factor. From the results of the uncertainty analyses, the calculated reduction factor was highly variable depending on the environmental condition and the airtightness of the houses. The uncertainty ranges of the reduction factor for particles and I
were investigated under various environmental conditions, and sensitivity analyses were conducted to understand the parameter with the most influence on the uncertainty of the reduction factor. From the results of the uncertainty analyses, the calculated reduction factor was highly variable depending on the environmental condition and the airtightness of the houses. The uncertainty ranges of the reduction factor for particles and I were up to 0.9 and 0.3, respectively, and were smaller for newer houses. From the results of the sensitivity analyses, the wind speed was the most influential parameter on the reduction factor. Additionally, the wind speed was less influential for the reduction factor in newer houses.
were up to 0.9 and 0.3, respectively, and were smaller for newer houses. From the results of the sensitivity analyses, the wind speed was the most influential parameter on the reduction factor. Additionally, the wind speed was less influential for the reduction factor in newer houses.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Kato, Nobuyuki*; Matsui, Yasuto*; Yoneda, Minoru*
Journal of Radiological Protection, 41(3), p.S139 - S149, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:31.52(Environmental Sciences)Sheltering is one of the countermeasures for protection against radiation exposures in nuclear accidents. The effectiveness of sheltering is often expressed by the reduction factor, that is the ratio of the indoor to the outdoor cumulative radioactivity concentrations or doses. The indoor concentration is mainly controlled by the air exchange rate, penetration factor, and indoor deposition rate. The penetration factor and indoor deposition rate depend on the surface and opening materials. We investigated experimentally these parameters of I and particles. The experiment was performed in two apartment houses, three single-family houses, and chambers. The obtained penetration factor ranged 0.3
and particles. The experiment was performed in two apartment houses, three single-family houses, and chambers. The obtained penetration factor ranged 0.3  1 for particles of 0.3
1 for particles of 0.3  1
1  m and 0.15
m and 0.15  0.7 for I
0.7 for I depending on the air exchange rate. The indoor deposition rate for a house room ranged 0.007
depending on the air exchange rate. The indoor deposition rate for a house room ranged 0.007  0.2 h
0.2 h for particles of 0.3
for particles of 0.3 1
1  m and 0.2
m and 0.2 1.5 h
1.5 h for I
for I depending on floor materials.
depending on floor materials.
Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Miyata, Noboru*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kasai, Satoshi*; Tsumura, Yoshihiro*; Aoki, Hiroyuki
Langmuir, 37(32), p.9873 - 9882, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.84(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Arima-Osonoi, Hiroshi*; Miyata, Noboru*; Yoshida, Tessei*; Kasai, Satoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Zhang, S.*; Miyazaki, Tsukasa*; Aoki, Hiroyuki
Review of Scientific Instruments, 91(10), p.104103_1 - 104103_7, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:55.99(Instruments & Instrumentation)Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*
High Pressure Research, 40(3), p.325 - 338, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:32.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary)To understand the practical effects of pressure-transmitting media (PTM) on neutron diffraction using Paris-Edinburgh presses, diffraction patterns of MgO were collected to approximately 20 GPa using PTMs of Pb, AgCl, 4:1 methano-ethanol (ME) mixture with and without heating, N , and Ar. Hydrostaticity in the sample chamber estimated from the MgO 220 peak width improves in the order of Pb, AgCl, Ar, ME mixture, N
, and Ar. Hydrostaticity in the sample chamber estimated from the MgO 220 peak width improves in the order of Pb, AgCl, Ar, ME mixture, N , and the heated ME mixture. Unlike previous results using a diamond anvil cell, the unheated ME mixture is superior to Ar even after freezing, probably due to the cup on the anvil face. Considering these results and the sizable coherent scattering of Ne, which would show good hydrostaticity, we conclude that the ME mixture (preferably the heated one) is the best PTM in neutron experiments up to 20 GPa, while Ar can be substituted when a sample is reactive to alcohols.
, and the heated ME mixture. Unlike previous results using a diamond anvil cell, the unheated ME mixture is superior to Ar even after freezing, probably due to the cup on the anvil face. Considering these results and the sizable coherent scattering of Ne, which would show good hydrostaticity, we conclude that the ME mixture (preferably the heated one) is the best PTM in neutron experiments up to 20 GPa, while Ar can be substituted when a sample is reactive to alcohols.
Yokouchi, Hiroshi*; Inagaki, Atsushi*; Kanda, Manabu*; Onodera, Naoyuki
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, B1 (Suikogaku) (Internet), 76(2), p.I_253 - I_258, 2020/00
Hight-resolution pollutant model embedded into Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) is constructed. We focuses on Particle pollutants. Flow field is calculated using D3Q27 model of LBM and particle is calculated by Lagrangian method. Using this model, we discuss the change in concentration distribution when there is a huge building (GARUDA) in Jakarta as a application. As a result, we can find the relation of differences in particle density and differences in flow velocity due to GARUDA. When the velocity in the case w/o GARUDA is faster than the other, particle velocity in the case w/o GARUDA is reduced. And also, we can find the velocity near the solid boundary is underestimated and the particle density is higher than theoretical value. However, this model is valid far away from the solid boundary.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2019 (ASRAM 2019) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2019/09
no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Seiko; Takahashi, Ryuta*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Yamauchi, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Masatoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kira, Hiroshi*; Kambara, Wataru*; Aoyama, Kazuhiro*; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; et al.
Journal of Neutron Research, 21(1-2), p.17 - 22, 2019/05
The Cryogenics and Magnets group in the Sample Environment team is responsible for operation of cryostats and magnets for user's experiments at the MLF in J-PARC. We have introduced a top-loading  He cryostat, a bottom-loading
He cryostat, a bottom-loading  He cryostat, a dilution refrigerator insert and a superconducting magnet. The frequency of use of them dramatically becomes higher in these two years, as the beam power and the number of proposal increase. To respond such situation, we have made efforts to enhance performance of these equipment as follows. The
He cryostat, a dilution refrigerator insert and a superconducting magnet. The frequency of use of them dramatically becomes higher in these two years, as the beam power and the number of proposal increase. To respond such situation, we have made efforts to enhance performance of these equipment as follows. The  He cryostat originally involves an operation software for automatic initial cooling down to the base temperature and automatic re-charge of
He cryostat originally involves an operation software for automatic initial cooling down to the base temperature and automatic re-charge of  He. Recently we made an additional program for automatic temperature control with only the sorb heater. Last year, a new outer vacuum chamber of the magnet with an oscillating radial collimator (ORC) was fabricated. The data quality was drastically improved by introducing this ORC so that the magnet can be used even for the inelastic neutron scattering experiments.
He. Recently we made an additional program for automatic temperature control with only the sorb heater. Last year, a new outer vacuum chamber of the magnet with an oscillating radial collimator (ORC) was fabricated. The data quality was drastically improved by introducing this ORC so that the magnet can be used even for the inelastic neutron scattering experiments.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2018 (ASRAM 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 8 Pages, 2018/10
no abstracts in English
Kawamura, Seiko; Oku, Takayuki; Watanabe, Masao; Takahashi, Ryuta; Munakata, Koji*; Takata, Shinichi; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Hattori, Takanori; et al.
Journal of Neutron Research, 19(1-2), p.15 - 22, 2017/11
Sample environment (SE) team at the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC has worked on development and operation of SE equipment and devices. All the members belong to one sub-team at least, such as Cryogenic and magnet, High temperature, High pressure, Soft matter and special environment including Pulse magnet, Hydrogen environment, Light irradiation and  He spin filter. Cryostats, a magnet, furnaces, a VX-6-type Paris-Edinburgh press and a prototype of a Spin-Exchange Optical Pumping (SEOP) based
He spin filter. Cryostats, a magnet, furnaces, a VX-6-type Paris-Edinburgh press and a prototype of a Spin-Exchange Optical Pumping (SEOP) based  He spin filter for polarized neutron beam experiments are in operation. Furthermore, a prototype of compact power supply for a pulsed magnet system is currently developed. In the J-PARC Research Building, several pieces of equipment for softmatter research such as a rheometer and a gas and vapor adsorption measurement instrument have been prepared.
He spin filter for polarized neutron beam experiments are in operation. Furthermore, a prototype of compact power supply for a pulsed magnet system is currently developed. In the J-PARC Research Building, several pieces of equipment for softmatter research such as a rheometer and a gas and vapor adsorption measurement instrument have been prepared.
Hirouchi, Jun; Takahara, Shogo; Komagamine, Hiroshi*; Watanabe, Masatoshi*; Munakata, Masahiro
Proceedings of Asian Symposium on Risk Assessment and Management 2017 (ASRAM 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 11 Pages, 2017/11
no abstracts in English
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Abe, Jun*; Machida, Shinichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Inamura, Yasuhiro
Koatsuryoku No Kagaku To Gijutsu, 26(2), p.89 - 98, 2016/06
PLANET is a high-pressure neutron beamline constructed at pulsed-neutron source in Materials and Life Science Facility (MLF) in J-PARC. The six-axis multi-anvil press designed for time of flight (TOF) neutron diffraction experiments enables routine data collection at high pressures and high temperatures up to 10 GPa and 2000 K, respectively. To obtain clean data, the beamline is equipped with the incident slits and receiving collimators that eliminate parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell. The high performance of the diffractometer for the resolution (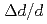
 0.6%) and the accessible d-spacing range (0.2 - 8.4
0.6%) and the accessible d-spacing range (0.2 - 8.4  ) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Ikeda, Hiroshi; Kato, Yuko; Ouchi, Nobuo; Yoshii, Akinobu*
Proceedings of 10th International Workshop on Personal Computers and Particle Accelerator Controls (PCaPAC 2014) (Internet), p.193 - 195, 2015/02
J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex) consists of much equipment. In Linac and 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron ring (RCS), the data of over the 64,000 EPICS records for these equipment has been collected. The Data volume is about 2 TB in every year, and the stored total data volume is about 10 TB. The data have been being stored by a Relational Data Base (RDB) system using PostgreSQL, but it is not enough in availability, performance, and capability to increase of data volume flexibility. Hadoop/HBase, which is known as a distributed, scalable and big data store, has been proposed for our next-generation archive system to solve these problems. The test system was built and verified about data transition or database utilization. This report shows the current status of the new archive system, and its advantages and problems which have been obtained through our verification.
 -ray emitting radioactive nuclides from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accident
-ray emitting radioactive nuclides from the Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant accidentSaito, Kimiaki; Tanihata, Isao*; Fujiwara, Mamoru; Saito, Takashi*; Shimoura, Susumu*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Onda, Yuichi*; Hoshi, Masaharu*; Ikeuchi, Yoshihiro*; Takahashi, Fumiaki; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 139, p.308 - 319, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:237 Percentile:98.59(Environmental Sciences)Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Ikeda, Hiroshi; Yoshii, Akinobu*; Kato, Yuko; Ouchi, Nobuo
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.794 - 798, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Oguri, Hidetomo; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Ito, Takashi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirano, Koichiro; Morishita, Takatoshi; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Ao, Hiroyuki; Okoshi, Kiyonori; Kondo, Yasuhiro; et al.
Proceedings of 11th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.389 - 393, 2014/10
no abstracts in English
Ikuta, Tomoya*; Hosaka, Koichi*; Akagi, Hiroshi; Yokoyama, Atsushi; Yamanouchi, Kaoru*; Kannari, Fumihiko*; Itakura, Ryuji
Journal of Physics B; Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics, 44(19), p.191002_1 - 191002_5, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:45.81(Optics)Ionization and subsequent electronic excitation occurring within the same laser pulse (400 nm, 96 fs, 1.3 18 TW/cm
18 TW/cm ) are separately investigated by measuring in coincidence an electron and a product ion produced from C
) are separately investigated by measuring in coincidence an electron and a product ion produced from C H
H OH. We reveal that the nascent population in the electronically excited C
OH. We reveal that the nascent population in the electronically excited C H
H OH
OH prepared by the ionization decreases as the laser intensity increases, while the subsequent electronic excitation is enhanced through the resonant electronic transitions. Ionization and electronic excitation mechanisms are described based on the electronic state distributions of C
prepared by the ionization decreases as the laser intensity increases, while the subsequent electronic excitation is enhanced through the resonant electronic transitions. Ionization and electronic excitation mechanisms are described based on the electronic state distributions of C H
H OH
OH .
.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:192 Percentile:99.39(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
Akagi, Hiroshi; Itakura, Ryuji; Otobe, Tomohito; Kumada, Takayuki; Tsubouchi, Masaaki; Yokoyama, Atsushi
JAEA-Conf 2011-001, p.40 - 43, 2011/03
no abstracts in English