Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kojima, Satoru*; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kariya, Yoshihiko*; Katayama, Yoshikazu*; Nishio, Gaku*
Proceedings of 5th International Workshop on Rock Mechanics and Engineering Geology in Volcanic Fields (RMEGV 2021) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2021/09
A local tephra embedded in a hand-auger boring core drilled at near-shore of Kinugasanoike Pond about 4.6 km NE of Mt.Yakedake, one of the most active volcanoes in central Japan, is composed mainly of several kinds of volcanic glass shards (microlite-bearing, blocky, fluted and micro-vesicular types) with minor amounts of crystal minerals including quartz, plagioclase, hornblende, biotite, and pyroxene. Plant remains recovered from the horizon 10 cm below the tephra layer yield  C ages of 2,331-2,295 (19.2% probability distribution) and 2,270-2,155 (76.2% probability distribution) cal yrs BP. We measured major element compositions of 241 individual glass shards using Electron Probe Micro Analyzer. They are plotted on the SiO
C ages of 2,331-2,295 (19.2% probability distribution) and 2,270-2,155 (76.2% probability distribution) cal yrs BP. We measured major element compositions of 241 individual glass shards using Electron Probe Micro Analyzer. They are plotted on the SiO -K
-K O, SiO
O, SiO -Na
-Na O+K
O+K O, and FeO
O, and FeO -K
-K O diagrams in a region different from those of major regional tephras distributed in central Japan. The clast and chemical compositions coincide with those of a tephra embedded in the Nakao pyroclastic flow deposits distributed about 2 km NNW of Mt. Yakedake dated as around 2,300 cal yrs BP. The tephra could be used as a local marker of 2,300 cal yrs BP in the southern part of Northern Japan Alps.
O diagrams in a region different from those of major regional tephras distributed in central Japan. The clast and chemical compositions coincide with those of a tephra embedded in the Nakao pyroclastic flow deposits distributed about 2 km NNW of Mt. Yakedake dated as around 2,300 cal yrs BP. The tephra could be used as a local marker of 2,300 cal yrs BP in the southern part of Northern Japan Alps.
 TiBi
TiBi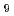
Motoyama, Gaku*; Haga, Yoshinori; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Kawasaki, Ikuto*; Sumiyama, Akihiko*; Yamamura, Tomoo*
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.157 - 160, 2018/11

Gochi, Jun*; Sumiyama, Akihiko*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Motoyama, Gaku*; Kimura, Noriaki*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika
Physical Review B, 93(17), p.174514_1 - 174514_5, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.71(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Saigusa, Mikio*; Oyama, Gaku*; Matsubara, Fumiaki*; Takii, Keita*; Sai, Takuma*; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 96-97, p.577 - 582, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:42.34(Nuclear Science & Technology)A wideband polarizer has been developed for an ECCD system in JT-60SA. The groove depth of the mirrors installed in miter bends were optimized for two frequencies (110 GHz and 138 GHz) by numerical simulations. All surfaces of Poincare spheres were covered at both of the frequencies in low power test. The thermal stress of polarizer were estimated by the numerical simulations. The twister polarizer has been tested up to 0.24 MW during 3 s at 110 GHz.

Gochi, Jun; Sumiyama, Akihiko*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Motoyama, Gaku*; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 84(9), p.094714_1 - 094714_5, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:19.19(Physics, Multidisciplinary) and conventional superconductors under pressure
and conventional superconductors under pressureGochi, Jun*; Sumiyama, Akihiko*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Motoyama, Gaku*; Kimura, Noriaki*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 3, p.011067_1 - 011067_6, 2014/06
 as a test of the odd-parity order parameter
as a test of the odd-parity order parameterGochi, Jun*; Sumiyama, Akihiko*; Motoyama, Gaku*; Yamaguchi, Akira*; Kimura, Noriaki*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Haga, Yoshinori; Onuki, Yoshichika
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 81(11), p.113701_1 - 113701_4, 2012/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:41.58(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Sai, Takuma*; Matsubara, Fumiaki*; Takii, Keita*; Oyama, Gaku*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishio, Gaku*; Kagami, Saya; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Kariya, Yoshihiko*; Kojima, Satoru*
no journal, ,
We attempt to use local tephra derived from nearby volcanoes as an age marker. The Kamikochi area in the southern part of the Northern Alps is strongly affected by the Yakedake volcano. We prepared distinctive tephras, (1) one sample of glassy volcanic ash in hand auger boring cores drilled at the near-shore Kinugasanoike Pond, about 4.7 km northeast of Mt. Yakedake and (2) two samples of glassy volcanic ash in the Nakao pyroclastic flow deposites, which is considered to be a product of the last magmatic eruption about 2,300 years ago, distributed about 1.5 km north-northwest of Mt. Yakedake. We investigated the clast composition of these tephras and the chemical composition and refractive index of volcanic glass. Approximately 70% of the clasts were volcanic glasses, and most of them were vesicular and blocky types. These glasses were characterized by high SiO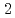 , K
, K O, Na
O, Na O and low Al
O and low Al O
O , FeO, which were clearly distinguishable from the volcanic glasses in Quaternary widespread tephras. The refractive indices of 30 volcanic glasses for each tephra were 1.4958-1.5011 with a peak in the range of 1.497 to 1.499. The results of this study indicate the tephra from Kinugasanoike Pond were erupted from Mt. Yakedake about 2,300 years ago. Therefore, the tephra with the above characteristics can be used as a useful age marker for the southern part of the Northern Alps about 2,300 years ago.
, FeO, which were clearly distinguishable from the volcanic glasses in Quaternary widespread tephras. The refractive indices of 30 volcanic glasses for each tephra were 1.4958-1.5011 with a peak in the range of 1.497 to 1.499. The results of this study indicate the tephra from Kinugasanoike Pond were erupted from Mt. Yakedake about 2,300 years ago. Therefore, the tephra with the above characteristics can be used as a useful age marker for the southern part of the Northern Alps about 2,300 years ago.
Sugiyama, Naoya*; Oyama, Gaku*; Matsubara, Fumiaki*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Isayama, Akihiko; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi
no journal, ,
The development status of a wide-band polarizer for ECCD system in JT-60SA is reported. The polarizer was designed at the frequency bands of 110, 130 and 140 GHz based on the simulation results with the finite differential time domain (FDTD) method. The properties of polarizer have been measured with low power test at both of the frequency bands of 110 GHz and 138 GHz. In future work, it is necessary to draw the Poincare sphere based on an experimental result, and to optimize the depth of the grooved mirrors. After that, the wide-band polarizer with a cooling system will be designed, fabricated and tested at high power up to 1 MW.
Sugiyama, Naoya*; Oyama, Gaku*; Matsubara, Fumiaki*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Moriyama, Shinichi
no journal, ,
Electron Cyclotron Current Drive (ECCD) is one of the most promising methods of heating and driving current in fusion plasmas. Incident wave into fusion plasmas should be converted from the linear polarization of a gyrotron output mode to the specific elliptical polarization in order to generate suitable plasma wave at high mode purity. The polarizer was designed at the frequency bands of 110,130 and 140 GHz based on the simulation results with the finite differential time domain method. The mock-up polarizer has been tested with low power at the both frequency bands of 110 GHz and 138 GHz. The high power model of wide-band polarizer was designed considering the results of low power test.
Oyama, Gaku*; Sugiyama, Naoya*; Matsubara, Fumiaki*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Moriyama, Shinichi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English