Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ozeki, Takahisa; Clement, L. S.*; Nakajima, Noriyoshi*
Fusion Engineering and Design, 89(5), p.529 - 531, 2014/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:53.95(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ozeki, Takahisa; Yonekawa, Izuru*
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 89(7), p.487 - 491, 2013/07
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P. T.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 51(10), p.103030_1 - 103030_8, 2011/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:29.29(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Hoshino, Kazuo; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Takizuka, Tomonori; Ozeki, Takahisa; Fukuyama, Atsushi*
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 6(Sp.1), p.2403065_1 - 2403065_8, 2011/08
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073015_1 - 073015_7, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.16(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Honda, Mitsuru; Takizuka, Tomonori; Tobita, Kenji; Matsunaga, Go; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Takizuka, Tomonori; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P.*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa; JET-EFDA Contributors*
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Ishii, Yasutomo; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Moriyama, Shinichi; Kamada, Yutaka; Ozeki, Takahisa; JT-60 Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 5, p.037_1 - 037_6, 2010/10
no abstracts in English
Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi*; Enoeda, Mikio; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Hayashi, Takumi; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Uto, Hiroyasu; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nishitani, Takeo; Isono, Takaaki; et al.
JAEA-Research 2010-019, 194 Pages, 2010/08
This report describes the results of the conceptual design study of the SlimCS fusion DEMO reactor aiming at demonstrating fusion power production in a plant scale and allowing to assess the economic prospects of a fusion power plant. The design study has focused on a compact and low aspect ratio tokamak reactor concept with a reduced-sized central solenoid, which is novel compared with previous tokamak reactor concept such as SSTR (Steady State Tokamak Reactor). The reactor has the main parameters of a major radius of 5.5 m, aspect ratio of 2.6, elongation of 2.0, normalized beta of 4.3, fusion out put of 2.95 GW and average neutron wall load of 3 MW/m . This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
. This report covers various aspects of design study including systemic design, physics design, torus configuration, blanket, superconducting magnet, maintenance and building, which were carried out increase the engineering feasibility of the concept.
Araki, Masanori; Hayashi, Kimio; Tobita, Kenji; Nishitani, Takeo; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nozawa, Takashi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Nakamichi, Masaru; Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Ozeki, Takahisa; et al.
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 86(4), p.231 - 239, 2010/04
The Broader Approach Activities, which support the ITER Project and implement activities to aim early realization of fusion energy, is an EU-Japan collaborative project to carry out various kinds of researches and developments during the period of the ITER construction phase. In this special topic, achievements and prospects of the projects on the International Fusion Energy Research Centre (IFERC) is described.
Matsunaga, Go; Takechi, Manabu; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Kurita, Genichi; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Koide, Yoshihiko; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Oyama, Naoyuki; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 4, p.051_1 - 051_7, 2009/11
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsuru; Takizuka, Tomonori; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Yoshida, Maiko; Ozeki, Takahisa
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.8, p.316 - 320, 2009/09
Characteristics of toroidal rotation profiles in tokamak plasmas are studied under the influence of fast-ion losses due to a toroidal field (TF) ripple by using a one-dimensional multi-fluid transport code, TASK/TX. When a neutral beam (NB) is injected into a plasma, a part of fast ions is lost due to the effect of the TF ripple. The radial current then flows inward in the bulk plasma to keep quasi-neutrality and it exerts a torque on the plasma in the direction opposite to the plasma current. A parametric survey of the toroidal rotation driven by this torque is conducted to quantify the sensitivity to various externally-controllable sources such as a co-tangential NBI power. In the case of a larger ripple amplitude, it is observed that the counter-toroidal rotation develops near the periphery of the plasma as an increase in the co-NBI input power while the co-toroidal rotation velocity on the magnetic axis reaches a maximum value at a certain NBI power. This torque can be mitigated by increasing a gas puff rate. An increase in the plasma current also leads to the reduction in the counter rotation induced by ripple.
Ozeki, Takahisa; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Kawashima, Hisato; Hoshino, Kazuo; Takizuka, Tomonori; Tokuda, Shinji
Journal of Plasma and Fusion Research SERIES, Vol.8, p.1138 - 1142, 2009/09
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Takizuka, Tomonori; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa; Wiesen, S.*; Parail, V.*
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095015_1 - 095015_8, 2009/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:52.79(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Tobita, Kenji; Nishio, Satoshi; Enoeda, Mikio; Kawashima, Hisato; Kurita, Genichi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Honda, Mitsuru; Saito, Ai*; Sato, Satoshi; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(7), p.075029_1 - 075029_10, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:141 Percentile:97.50(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Recent design study on SlimCS focused mainly on the torus configuration including blanket, divertor, materials and maintenance scheme. For vertical stability of elongated plasma and high beta access, a sector-wide conducting shell is arranged in between replaceable and permanent blanket. The reactor adopts pressurized-water-cooled solid breeding blanket. Compared with the previous advanced concept with supercritical water, the design options satisfying tritium self-sufficiency are relatively scarce. Considered divertor technology and materials, an allowable heat load to the divertor plate should be 8 MW/m or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
or lower, which can be a critical constraint for determining a handling power of DEMO (a combination of alpha heating power and external input power for current drive).
 plasmas in the JT-60U tokamak
plasmas in the JT-60U tokamakMatsunaga, Go; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Shinohara, Koji; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Isayama, Akihiko; Takechi, Manabu; Suzuki, Takahiro; Oyama, Naoyuki; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Physical Review Letters, 103(4), p.045001_1 - 045001_4, 2009/07
Times Cited Count:48 Percentile:84.87(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji; Furukawa, Masaru*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 49(6), p.065015_1 - 065015_9, 2009/06
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:66.67(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Effects of a toroidal rotation are investigated numerically on the stability of the MHD modes in the tokamak edge pedestal, which relate to the type-I edge-localized mode (ELM). A linear MHD stability code MINERVA is newly developed for solving the Frieman-Rotenberg equation that is the linear ideal MHD equation with flow. Numerical stability analyses with this code reveal that the sheared toroidal rotation destabilizes edge localized MHD modes, and this rotation effect becomes stronger as the toroidal mode number of the unstable MHD mode increases in case that the toroidal mode number is smaller than 40. Since the toroidal mode number of the unstable MHD mode strongly depends on the safety factor profile, the destabilizing effect of the toroidal rotation is affected by the safety factor profile. The sheared toroidal rotation also has an impact on the mode structure of the edge localized MHD mode, and the mode structure can become narrower as the toroidal rotation increases.
Isayama, Akihiko; Matsunaga, Go; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Oyama, Naoyuki; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Urano, Hajime; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamada, Yutaka; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(5), p.055006_1 - 055006_9, 2009/05
Times Cited Count:74 Percentile:91.34(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsuru; Takizuka, Tomonori; Fukuyama, Atsushi*; Yoshida, Maiko; Ozeki, Takahisa
Nuclear Fusion, 49(3), p.035009_1 - 035009_10, 2009/03
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:50.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The generation of the toroidal rotation due to the radial current torque induced by the charge separation is studied by using one-dimensional multi-fluid transport code TASK/TX. Owing to the effect of the drift motion, the charge separation occurs as long as trapped ions are generated, typically by near-perpendicular NBI. Coupling the TASK/TX code with the OFMC code, we have reproduced that the toroidal rotation is driven due to the generation of the radial current 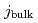 by the near-perpendicular NBI. The simulations has clarified that the NB on the equatorial plane drives the toroidal rotation most efficiently from the aspects of the collisional and
by the near-perpendicular NBI. The simulations has clarified that the NB on the equatorial plane drives the toroidal rotation most efficiently from the aspects of the collisional and 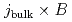 torques. The
torques. The 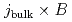 torque becomes a major driver of the rotation in a high density plasma. In a steady state, the toroidal rotation is determined by the balance among the torque, the viscosity, the friction with neutrals and the loss of momentum due to charge exchange.
torque becomes a major driver of the rotation in a high density plasma. In a steady state, the toroidal rotation is determined by the balance among the torque, the viscosity, the friction with neutrals and the loss of momentum due to charge exchange.
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji; Furukawa, Masaru*; Oyama, Naoyuki; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
Effects of a toroidal rotation are investigated numerically on the stability of the MHD modes in the edge pedestal, which relate to the type-I edge-localized mode (ELM). A new linear MHD stability code MINERVA is developed for solving the Frieman-Rotenberg equation, which is the linear ideal MHD equation with flow. As the result of the stability analysis, it is revealed that the sheared toroidal rotation destabilizes the edge localized MHD modes. The change of the safety factor profile affects this destabilizing effect. This is because the rotation effect on the edge MHD stability becomes stronger as the toroidal mode number of the unstable MHD mode increases, and this toroidal mode number strongly depends on the safety factor profile.