Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
土屋 晴文; 藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 前田 亮; 米田 政夫
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(11), p.1301 - 1312, 2023/11
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:59.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)An integrated active neutron non-destructive analysis (NDA) system, Active-N, was developed to gain knowledge of active neutron NDA techniques that are applicable to measurements of nuclear materials in highly radioactive nuclear fuels. Active-N, equipped with a D-T neutron generator, combines three complementary active neutron NDA techniques: Differential Die-away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA), and Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA). In this paper, we provide an overview of Active-N and then demonstrate that the compact NRTA system in Active-N can quantify nuclear materials. Monte Carlo simulations were conducted to determine the design of the compact NRTA system including a moderator, flight tubes, and a detector shield. To investigate how accurately the compact NRTA system determines areal densities in a sample, measurements were performed with a Pu pellet-type sample as well as metallic plate samples of In and Ag. The experimental areal densities of  Pu,
Pu,  In and
In and  Ag were consistent with those calculated for the individual nuclei. These results show that it is feasible to develop a compact NRTA system capable of determining the contents of nuclear materials in nuclear fuels. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
Ag were consistent with those calculated for the individual nuclei. These results show that it is feasible to develop a compact NRTA system capable of determining the contents of nuclear materials in nuclear fuels. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
古高 和禎; 大図 章; 藤 暢輔
Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 55(11), p.4002 - 4018, 2023/11
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:23.64(Nuclear Science & Technology)An integrated neutron interrogation system has been developed for non-destructive assay of highly radioactive special nuclear materials, to accumulate knowledge of the method through developing and using it. The system combines a differential die-away (DDA) measurement system for the quantification of nuclear materials and a prompt gamma-ray analysis (PGA) system for the detection of neutron poisons which disturb the DDA measurements; a common D-T neutron generator is used. A special care has been taken for the selection of materials to reduce the background gamma rays produced by the interrogation neutrons. A series of measurements were performed to test the basic performance of the system. The results show that the DDA system can quantify plutonium of as small as 20~mg and it is not affected by intense neutron background up to 4.2~TBq and gamma ray of 2.2~TBq. As a result of the designing of the combined system as a whole, the gamma-ray background counting rate at the PGA detector was reduced down to 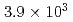 s
s even with the use of the D-T neutron generator. The test measurements show that the PGA system is capable of detecting less than 1~g of boron compound and about 100~g of gadolinium compound in~30 min. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
even with the use of the D-T neutron generator. The test measurements show that the PGA system is capable of detecting less than 1~g of boron compound and about 100~g of gadolinium compound in~30 min. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 小泉 光生
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/08
Since neutrons have exceptional ability to penetrate high-density materials and can induce fission, they are used in non-destructive analysis such as, Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA) and Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA). The different analytical methods give us complementary information, which are particularly useful for the quantification of Special Nuclear Materials in highly radioactive nuclear materials, including spent fuel. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission are collaborating to develop an active neutron NDA system for nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security. In the second phase of the project, an integrated active neutron NDA system: Active-N which enables the simultaneous measurements of DDA, PGA and NRTA has been developed. The DDA detects fission neutrons, and it can determine small amounts of the fissile mass. PGA is utilized for the quantification of neutron absorber and particularly useful for the detection of explosives. NRTA can be used to quantify almost all medium and high-Z elements and considered as one of the most accurate NDA. In this presentation, we will provide an overview of Active-N and report the recent experimental results. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion of MEXT: Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
古高 和禎; 大図 章; 藤 暢輔
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2021/08
We have been developing an integrated active neutron non-destructive analysis system for highly radioactive nuclear materials, "Active-N", using an intense D-T neutron source. The system is composed of the following mutually complementing different measurement systems: Differential Die-away Analysis (DDA), Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA), and Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA). The former two are for measurements of total amount of fissile material and of isotopic composition, respectively. The purpose of the last one, i.e. PGA measurement system is the detection of explosives contained in e.g., dirty bombs and of chemical warfare agents, as well as of neutron poisons which absorb neutrons and disturb DDA measurements. This report describes mainly the PGA measurement system. In the PGA measurement system, to resolve individual gamma-ray peaks, a Ge detector is utilized. It is well known that irradiation of fast neutrons (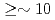 keV) to Ge detectors cause damages to the detectors and gradually worsen their resolution, and finally make them unusable without a laborious treatment. Therefore, it is essential to shield the PGA detector against the neutrons from the D-T neutron generator. In addition, to reduce background gamma rays from the materials used for the DDA system, they should also be carefully chosen. In order to design an appropriate neutron shield for the PGA measurement system and diminish the sources of the background gamma rays, simulation study was done using a particle transport code system PHITS. Based on the results, a shielding for the PGA measurement system has been designed which reduces the number of damaging neutrons by an order of magnitude. The Active-N system which incorporates the PGA measurement system equipped with the neutron shielding, has been installed at NUCEF facility in JAEA Tokai. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion from MEXT.
keV) to Ge detectors cause damages to the detectors and gradually worsen their resolution, and finally make them unusable without a laborious treatment. Therefore, it is essential to shield the PGA detector against the neutrons from the D-T neutron generator. In addition, to reduce background gamma rays from the materials used for the DDA system, they should also be carefully chosen. In order to design an appropriate neutron shield for the PGA measurement system and diminish the sources of the background gamma rays, simulation study was done using a particle transport code system PHITS. Based on the results, a shielding for the PGA measurement system has been designed which reduces the number of damaging neutrons by an order of magnitude. The Active-N system which incorporates the PGA measurement system equipped with the neutron shielding, has been installed at NUCEF facility in JAEA Tokai. This research was implemented under the subsidy for nuclear security promotion from MEXT.
大図 章; 前田 亮; 米田 政夫; 藤 暢輔
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.101 - 104, 2020/08
In the fields of safeguards, nuclear non-proliferation, and nuclear security, non-destructive analysis (NDA) techniques useful for highly radioactive nuclear materials (NMs) are not established yet because there are so many technical difficulties to measure the amount of the highly radioactive NMs. A novel NDA system with a pulsed neutron source as the method for determining the composition of mixed NMs has been developing in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. In the NDA system, a differential die-away analysis (DDA) technique is used to quantify the amount of fissile materials. The detection limit of fissile materials in DDA system is determined by the signal to noise ratio in fast neutron counting. A method to reduce the noise signal by using neutron absorber (B C rubber) sheets mounted on the inner entire surface in the sample cavity is proposed. The effect of the sheets on the reduction of noise signal in the fast neutron counting was investigated in both experimental test and simulation. The experimental results show that it is possible to detect a nuclear fissile material (
C rubber) sheets mounted on the inner entire surface in the sample cavity is proposed. The effect of the sheets on the reduction of noise signal in the fast neutron counting was investigated in both experimental test and simulation. The experimental results show that it is possible to detect a nuclear fissile material ( Pu) of as low as 1 mg in a vial bottle when the absorber sheets with a thickness of 3 mm is used. This paper also presents comparison between experimental data and simulation results.
Pu) of as low as 1 mg in a vial bottle when the absorber sheets with a thickness of 3 mm is used. This paper also presents comparison between experimental data and simulation results.
大図 章; 前田 亮; 米田 政夫; 藤 暢輔
Proceedings of 2018 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2018) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2019/10
A Differential Die-away Analysis (DDA) system using a compact pulsed neutron (DT: 14 MeV) generator has been successfully developed for nuclear non-proliferation and nuclear security in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. The DDA system employing the fast neutron direct interrogation method is designed to quantify fissile materials in samples which have different volume from a vial bottle (4 cc) to pail container (20 liter). It has been demonstrated experimentally that the DDA system is capable of quantifying a nuclear fissile material (Pu-239) less than 10 mg in a vial bottle. The performance of the DDA system with a large measurement sample such as a MOX can container (2 liter) was evaluated through the Monte Carlo simulation studies. The simulation results show that the Pu-239 mass of around 10 mg even in the MOX can container can be detected. The results of the simulation study are discussed and compared to those of the experimental test.
前田 亮; 古高 和禎; 呉田 昌俊; 大図 章; 米田 政夫; 藤 暢輔
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(7), p.617 - 628, 2019/07
被引用回数:3 パーセンタイル:25.69(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to measure the amount of nuclear materials in the fuel debris produced in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, we have designed a measurement system based on a Fast Neutron Direct Interrogation (FNDI) method. In particular, we have developed a fast response detector bank for fast neutron measurements by Monte Carlo simulations. The new bank has more than an order of magnitude faster response compared to the standard ones. We have also simulated the nondestructive measurements of the nuclear materials in homogeneously mixed fuel debris with various matrices which contain Stainless Steel (JIS SUS304), concrete, and various control-rod (CR) contents in the designed system. The results show that at least some types of the fissile materials in the debris can be measured by using the designed system.
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 小泉 光生
Proceedings of INMM 60th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/07
Nuclear material accountancy plays a key role in nuclear safeguards and security. The collaboration between the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission aims to develop an active neutron NDA system for Special Nuclear Materials (SNM) and Minor Actinides (MA) in highly radioactive nuclear materials. Several active neutron NDA techniques, namely Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA), Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA), Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Delayed Gamma-ray Analysis (DGA) have been developed. The different methods can provide complementary information. In the first phase of the project, we developed a combined NDA system, which enables the simultaneous measurements of DDA and PGA. The DDA technique can determine very small amounts of the fissile mass. PGA is valuable for the measurement of light elements. In the second phase, we will continue to conduct additional research to improve the methodology and develop a new integrated NDA system which can use for NRTA as well as DDA and PGA. In this presentation, we will provide an overview of the project and report the recent results, especially the design of new integrated NDA system. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
大図 章; 前田 亮; 米田 政夫; 藤 暢輔; 小泉 光生; 瀬谷 道夫
Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2017) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2018/11
A Differential Die-away Analysis (DDA) system using a compact pulsed neutron (14 MeV) generator has been newly developed for non-nuclear proliferation and nuclear security in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The DDA system was designed to be able to detect a nuclear fissile material (Pu-239) of as low as 10 mg and to handle samples of a different volume: a vial bottle (20 mL), a pail container (20 L), through a Monte Carlo simulation. In the DDA system, the Fast Neutron Direct Interrogation (FNDI) technique, which utilizes fast neutrons for interrogation, was applied to measure the amount of fissile mass contained in the sample. The fundamental performance of the DDA system was investigated in the demonstration experiment. The simulation results show that the Pu-239 masses of less than 10 mg can be detected in the DDA system. The results of the experiment are discussed and compared with those of the simulation.
米田 政夫; 大図 章; 森 貴正; 中塚 嘉明; 前田 亮; 呉田 昌俊; 藤 暢輔
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(8), P. 962, 2018/08
被引用回数:0 パーセンタイル:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)以前に発表した論文(アクティブ中性子法における中性子増倍効果に関する研究(J Nucl Sci Technol. 2017;54(11):1233-1239)における式の導出法を訂正する。式の導出法に間違いがあったが、最終的に導出される式は正しい。そのため、論文の結論及び議論に変更は無い。
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 小泉 光生; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
Nuclear material accountancy is of fundamental importance for nuclear safeguards and security. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is no established technique that enables us to accurately determine the amount of Special Nuclear Materials (SNM) and Minor Actinides (MA) in high radioactive nuclear materials. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission Collaboration Action Sheet-7 started in 2015. The purpose of this project is to develop an innovative non-destructive analysis (NDA) system using a D-T pulsed neutron source. Active neutron NDA techniques, namely Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA), Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA), Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Delayed Gamma-ray Analysis (DGA) have been studied and developed. The different methods can provide complementary information which is particularly useful for quantification of SNM and MA in high radioactive nuclear materials. The second phase of the project has started. In the second phase, we will continue to conduct additional research to improve the methodology and develop an integrated NDA system. This presentation gives an overview of the project and the NDA system and reports the recent results. This research was implemented under the subsidiary for nuclear security promotion of MEXT.
 U
U迫田 晃弘; 中塚 嘉明; 石森 有; 中島 伸一; 米田 政夫; 大図 章; 藤 暢輔
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 55(6), p.605 - 613, 2018/06
被引用回数:1 パーセンタイル:9.77(Nuclear Science & Technology)核物質の計量管理の向上のため、我々は以前、ドラム缶に充填されたウラン廃棄物を対象にした非破壊検査装置(JAWAS-N: JAEA Waste Assay System at Ningyo-toge)を開発した。これは高速中性子直接問いかけ(FNDI)法に基づいている。FNDI法の特性やJAWAS-Nの性能をより明らかにするために、既知量の天然ウランを含む様々な乾燥物質を用いて、実験と計算によるモックアップ試験を行った。その結果、 U核分裂に由来した高速中性子の消滅時間(
U核分裂に由来した高速中性子の消滅時間(
 )とカウントの間に直線性があることを実験と計算で確認した。また、MCNPによる計算から、
)とカウントの間に直線性があることを実験と計算で確認した。また、MCNPによる計算から、 U核分裂確率、中性子の検出効率、および感度に対するドラム缶内のウラン分布の影響を議論した。計算結果は既報の実験結果とも一致しており、FNDI法に基づくウラン定量に関して実践的な情報を得た。さらに、JAWAS-Nの名目の検出効率を評価したところ、
U核分裂確率、中性子の検出効率、および感度に対するドラム缶内のウラン分布の影響を議論した。計算結果は既報の実験結果とも一致しており、FNDI法に基づくウラン定量に関して実践的な情報を得た。さらに、JAWAS-Nの名目の検出効率を評価したところ、
 =0.2, 0.3, 0.4msecの物質でそれぞれ15, 4, 2g(天然ウラン量)であった。本研究で得られた知見は、FNDI法による実ウラン廃棄物の
=0.2, 0.3, 0.4msecの物質でそれぞれ15, 4, 2g(天然ウラン量)であった。本研究で得られた知見は、FNDI法による実ウラン廃棄物の U量評価に貢献する。
U量評価に貢献する。
大図 章; 前田 亮; 米田 政夫; 古高 和禎; 藤 暢輔
日本核物質管理学会第38回年次大会論文集(インターネット), 9 Pages, 2018/04
原子力機構では、欧州委員会共同研究センターと共同で核不拡散、核セキュリティ用非破壊測定技術の開発に取り組んでおり、従来の技術では測定が難しい核変換用MA-Pu燃料等の高線量核物質や共存物質が多い難測定核物質を測定する技術の確立を目指している。その技術開発において、核分裂性核物質の定量が可能な次世代型アクティブ中性子ダイアウェイ時間差分析(DDA)部と元素分析が可能な即発 線分析(PGA)部を組み合わせた、小型DT中性子源を用いるアクティブ中性子統合非破壊測定試験装置"Active-N"を新たに設計、開発した。現在、製作したDDA部の基本性能を評価するために微量のPu酸化物試料を封入したバイアル瓶を用いて測定試験を実施している。本報では、その試験結果をモンテカルロシミュレーション(MCNP)結果と比較して報告する。
線分析(PGA)部を組み合わせた、小型DT中性子源を用いるアクティブ中性子統合非破壊測定試験装置"Active-N"を新たに設計、開発した。現在、製作したDDA部の基本性能を評価するために微量のPu酸化物試料を封入したバイアル瓶を用いて測定試験を実施している。本報では、その試験結果をモンテカルロシミュレーション(MCNP)結果と比較して報告する。
大図 章; 米田 政夫; 呉田 昌俊; 中塚 嘉明; 中島 伸一
日本原子力学会誌ATOMO , 59(12), p.700 - 704, 2017/12
, 59(12), p.700 - 704, 2017/12
ウラン廃棄物ドラム缶内のウラン量を定量する従来の非破壊測定法では、内容物の種類やウランの偏在に起因する測定誤差の大きさが問題となるケースや、さらに長時間の測定時間が必要となる測定上の問題がある。このような問題を解決する高速中性子直接問いかけ法というアクティブ中性子非破壊測定法を開発し、実廃棄物ドラム缶のウラン定量に実用化することができた。本報では、本測定法を概説するとともに今後の展望について解説する。
米田 政夫; 大図 章; 森 貴正; 中塚 嘉明; 前田 亮; 呉田 昌俊; 藤 暢輔
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(11), p.1233 - 1239, 2017/11
被引用回数:9 パーセンタイル:60.26(Nuclear Science & Technology)アクティブ中性子法における中性子増倍効果に関して、解析及び実験による研究を実施した。アクティブ中性子法を用いた核物質の測定では、第2世代以降の中性子による中性子増倍の影響を受ける。しかしながら、そのような中性子増倍効果による影響について、これまで十分に調べられてこなかった。本研究では、第3世代中性子による中性子増倍が無視できる場合において、測定データから第2世代中性子による中性子増倍効果の影響を補正する手法について調べ、測定データから中性子増倍の影響を除外する補正方法を提案した。更に、本手法を利用した深い未臨界度の評価手法についても示した。
米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 大図 章; 呉田 昌俊; 藤 暢輔
Proceedings of International Nuclear Fuel Cycle Conference (GLOBAL 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 3 Pages, 2017/09
アクティブ中性子法の一つであるFNDI法を用いた核物質の計量管理技術の開発を行っている。FNDI法は、対象物にパルス中性子を照射し、そこで発生する核分裂中性子の総数及び消滅時間を用いて核分裂性物質量を求める測定法である。FNDI法を用いたデブリ計測システムの設計解析に取り組んでおり、次のような計算モデルを作成してシミュレーションを実施した。装置高さ: 140cm、装置外径: 80cm、He-3検出器(長さ100cm、直径2.5cm)本数: 16本。デブリの状態として湿式と乾式の2種類を考え、乾式デブリでは中性子の減速効果を補うために収納管周りにポリエチレンを取り付けている。シミュレーションは計算コードMVPを用いた。本発表では燃焼組成や均質度を変えた様々なデブリに対する計算結果及びFNDI法を用いたデブリ測定の適用範囲に関する検討結果を示す。
大図 章; 前田 亮; 米田 政夫; 飛田 浩; 呉田 昌俊
第37回核物質管理学会日本支部年次大会論文集(CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2017/02
原子力機構では、2015年より欧州委員会共同研究センターと共同で核不拡散、核セキュリティ用非破壊測定技術の開発に取り組んでおり、従来の技術では測定が難しい高線量核燃料や共存物質が多い難測定核物質を測定する技術の確立を目指している。現在、その非破壊測定技術の一つとして核分裂性核種の総質量を測定する小型中性子源を用いた次世代型アクティブ中性子ダイアウェイ時間差分析(DDA)装置を開発している。DDA装置の測定性能は装置内部の壁の材料の種類、測定サンプルの周囲に配置するポリエチレン製の中性子モデレータの厚さに大きく依存する。本報では、MOX粉末試料をサンプルとした場合のモンテカルロシミュレーション(MCNP)により得られた検出下限値、検出性能の壁材の種類及びモデレータ厚さの依存性に関して報告する。
前田 亮; 米田 政夫; 飛田 浩; 大図 章; 呉田 昌俊; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J. M.*; Varasano, G.*; Pedersen, B.*
第37回核物質管理学会日本支部年次大会論文集(CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2017/02
原子力機構(JAEA)と欧州共同研究センター(JRC)は、使用済み燃料や次世代型MA燃料などの高線量核物質に適用可能な非破壊測定技術の研究開発を共同で実施している。本研究では、次世代型ダイアウェイ時間差分析法(DDA)の実証装置の設計・開発に用いる中性子輸送コードの信頼性が重要となる。そこで中性子輸送コードの信頼性を評価するために、JRC型DDAを用いたPulsed Neutron Interrogation Test Assembly (PUNITA)とJAEA型DDAを用いたJAEA Active Waste Assay System-Tokai (JAWAS-T)の2つの装置の測定空間内の中性子束分布を測定し、さらにPUNITAでは測定試料のマトリクス内の中性子束分布を測定し、中性子輸送コードによるシミュレーション結果と比較した。本報では、それら試験及びシミュレーション結果と信頼性の評価結果について報告する。
藤 暢輔; 大図 章; 土屋 晴文; 古高 和禎; 北谷 文人; 米田 政夫; 前田 亮; 呉田 昌俊; 小泉 光生; 瀬谷 道夫; et al.
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.684 - 693, 2017/00
In 2015, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) and the Joint Research Centre (JRC) of the European Commission collaboration started to develop an active neutron non-destructive assay system for nuclear nonproliferation and nuclear security. To the best of our knowledge, no adequate technique exists that allows us to determine the amount of special nuclear materials and minor actinides in high radioactive nuclear materials, such as spent fuel, transuranic waste, etc. The collaboration aims at contributing to the establishment of an innovative NDA system using a D-T pulsed neutron source for various applications. We utilize several active neutron NDA techniques, namely Differential Die-Away Analysis (DDA), Prompt Gamma-ray Analysis (PGA), Neutron Resonance Capture Analysis (NRCA), Neutron Resonance Transmission Analysis (NRTA) and Delayed Gamma Spectroscopy (DGS). All of these techniques have advantages and disadvantages. The different methods can provide complementary information which is particularly useful for nuclear nonproliferation and nuclear security. In this project, we have developed a combined NDA system, which enables the measurements of DDA and PGA, at NUclear fuel Cycle safety Engineering research Facility (NUCEF) in JAEA. In this presentation, we will introduce our project and report the recent progress of developments, especially in NRTA, DDA and PGA.
前田 亮; 米田 政夫; 大図 章; 呉田 昌俊; 藤 暢輔; Bogucarska, T.*; Crochemore, J. M.*; Varasano, G.*; Pedersen, B.*
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.694 - 701, 2017/00
JAEA and EC/JRC have been carrying out collaborative research for developing new non-destructive assay techniques that can be utilized for quantifying high radioactive special nuclear materials such as spent fuel and next generation minor actinide fuels. In the research, accuracy of Monte Carlo simulation is important since it is utilized for design and development of a demonstration system of next-generation Differential Die-away (DDA) technique in JAEA. In order to evaluate the accuracy, neutron flux in the sample cavity of the PUNITA device which utilizes JRC type DDA technique and one of JAWAS-T device which utilizes JAEA type DDA technique were measured. The neutron flux in the target sample placed in the PUNITA sample cavity was also measured. The measurement results were compared with the simulation results. In this presentation, we report on comparison results for the neutron flux obtained by experiment and simulation.