Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Luce, T. C.*; Challis, C. D.*; 井手 俊介; Joffrin, E.*; 鎌田 裕; Politzer, P. A.*; Schweinzer, J.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Stober, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013015_1 - 013015_15, 2013/12
被引用回数:44 パーセンタイル:86.54(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)The ITPA IOS group has coordinated experimental and modeling activity on the development of advanced inductive scenarios for applications in the ITER tokamak. This report documents the present status of the physics basis and the prospects for applications in ITER. The key findings are: (1) inductive scenarios capable of higher 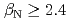 than the ITER baseline scenario (
than the ITER baseline scenario (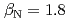 ) with normalized confinement at or above the standard H-mode scaling have been established under stationary conditions on the four largest diverted tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JET, JT-60U) in a broad range in
) with normalized confinement at or above the standard H-mode scaling have been established under stationary conditions on the four largest diverted tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JET, JT-60U) in a broad range in 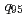 and density; (2) MHD modes can play a key role in reaching stationary high performance, but also define the stability and confinement limits; (3) the experiments have yielded clearer measurements of the normalized gyroradius scalin; and (4) coordinated modeling activity supports the present research by clarifying the most significant uncertainties in the projections to ITER.
and density; (2) MHD modes can play a key role in reaching stationary high performance, but also define the stability and confinement limits; (3) the experiments have yielded clearer measurements of the normalized gyroradius scalin; and (4) coordinated modeling activity supports the present research by clarifying the most significant uncertainties in the projections to ITER.
Wiesen, S.*; Brezinsek, S.*; J rvinen, A.*; Eich, T.*; Fundamenski, W.*; Huber, A.*; Parail, V.*; Corrigan, G.*; 林 伸彦; JET-EFDA Contributors*
rvinen, A.*; Eich, T.*; Fundamenski, W.*; Huber, A.*; Parail, V.*; Corrigan, G.*; 林 伸彦; JET-EFDA Contributors*
Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 53(12), p.124039_1 - 124039_12, 2011/12
被引用回数:26 パーセンタイル:69.31(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)A type-I ELMy H-mode discharge in JET has been analysed numerically using JINTRAC integrated code in order to obtain a self-consistent description of edge and core plasma. The time-dependent model consists of a self-consistent coupling of 1D core code JETTO/SANCO and 2D multi-fluid scrape-off-layer (SOL) code EDGE2D-EIRENE. The inter- and intra-ELM transport model has been adapted to match the experimental pre- and post ELM plasma profiles measured in JET and at the same time the observed ELM dynamics in terms of ELM frequency, ELM energy loss, ELM wetted area and heat flows towards target plates. It is found that the scaling for the free streaming approximations of ELM filamentary parallel SOL transport for the maximum heat flux, energy density and heat flux factor can be reproduced with the JINTRAC model. Results for the JET all-carbon reference case are then utilised to predict a type-I ELMy H-mode for ITER-like wall (ILW) assuming a full-tungsten divertor and beryllium main-chamber wall in the model. It is found that a moderate amount of seeded neon impurity (or other impurity species) is necessary to match a similar level of radiation when carbon is absent in the system. Finally, results of the ILW setup are used to estimate the total amount of tungsten particles eroded per ELM from the target plates and a rough estimate of the core radiative fraction due to W accumulation is given.
浦野 創; Saibene, G.*; 大山 直幸; Parail, V.*; de Vries, P.*; Sartori, R.*; 鎌田 裕; 神谷 健作; Loarte, A.*; L nnroth, J.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(11), p.113004_1 - 113004_10, 2011/11
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:39.40(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)JET及びJT-60Uにおいてトロイダル磁場リップルのスキャン実験を実施し、トロイダル磁場リップルによる周辺ペデスタル構造への影響を評価した。トロイダル磁場リップルは赤道面外側のセパラトリクス上で定義した。JT-60Uではフェライト鋼導入によってトロイダル磁場リップルは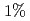 から
から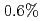 に低減し、一方JETではコイル電流の調整によって
に低減し、一方JETではコイル電流の調整によって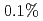 から
から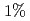 まで変化させた。JT-60Uではフェライト鋼導入によってペデスタル圧力に大きな差異は見られなかった。同様にJETでもペデスタル部の密度・温度に差異が見られなかった。しかし両装置ともに周辺トロイダル回転速度はリップルの増大とともに逆方向にシフトした。JT-60UではELM周波数がリップルとともに増大したが、JETでは変化が観測されなかった。この装置間比較実験の結果から、
まで変化させた。JT-60Uではフェライト鋼導入によってペデスタル圧力に大きな差異は見られなかった。同様にJETでもペデスタル部の密度・温度に差異が見られなかった。しかし両装置ともに周辺トロイダル回転速度はリップルの増大とともに逆方向にシフトした。JT-60UではELM周波数がリップルとともに増大したが、JETでは変化が観測されなかった。この装置間比較実験の結果から、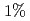 以下のトロイダル磁場リップルは周辺ペデスタル構造に大きな影響を与えないことが示された。しかし、ITERのような低衝突周波数領域での影響については今後の課題である。
以下のトロイダル磁場リップルは周辺ペデスタル構造に大きな影響を与えないことが示された。しかし、ITERのような低衝突周波数領域での影響については今後の課題である。
林 伸彦; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; 相羽 信行; 滝塚 知典; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P. T.*; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久
Nuclear Fusion, 51(10), p.103030_1 - 103030_8, 2011/10
被引用回数:7 パーセンタイル:26.07(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Two integrated core / scrape-off-layer / divertor transport codes TOPICS-IB and JINTRAC with links to MHD stability codes have been coupled with models of pellet injection to clarify effects of pellet on the behavior of edge localized modes (ELMs). Both codes predicted the following two triggering mechanisms. The energy absorption by the pellet and its further displacement due to the 

 drift, as well as transport enhancement by the pellet, were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes a radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent
drift, as well as transport enhancement by the pellet, were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes a radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent 

 drift. Further, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause the transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
drift. Further, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause the transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
Imbeaux, F.*; Citrin, J.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; K chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; 宮本 斉児; 中村 幸治*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
chl, F.*; Leonov, V. M.*; 宮本 斉児; 中村 幸治*; Parail, V.*; Pereverzev, G. V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083026_1 - 083026_11, 2011/08
被引用回数:38 パーセンタイル:80.80(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from various tokamaks have been analysed by means of integrated modelling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. A set of empirical heat transport models for L-mode has been validated on a multi-machine experimental dataset for predicting the 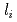 dynamics within
dynamics within  0.15 accuracy during current ramp-up and ramp-down phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of
0.15 accuracy during current ramp-up and ramp-down phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of 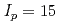 MA). These projections include a sensitivity study to various assumptions of the simulation. While the heat transport model is at the heart of such simulations, more comprehensive simulations are required to test all operational aspects of the current ramp-up and ramp-down phases of ITER scenarios. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free-boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are also described, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
MA). These projections include a sensitivity study to various assumptions of the simulation. While the heat transport model is at the heart of such simulations, more comprehensive simulations are required to test all operational aspects of the current ramp-up and ramp-down phases of ITER scenarios. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free-boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are also described, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
Litaudon, X.*; 坂本 宜照; de Vries, P. C.*; Salmi, A.*; Tala, T.*; Angioni, C.*; Benkadda, S.*; Beurskens, M. N. A.*; Bourdelle, C.*; Brix, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(7), p.073020_1 - 073020_13, 2011/07
被引用回数:11 パーセンタイル:42.10(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)内部輸送障壁の発生機構や構造形成は、装置や運転シナリオによって多様性があることが知られている。その多様性を理解するために、装置サイズがほぼ同じのJT-60と英国のJET装置において、同様の運転シナリオで形成した内部輸送障壁の輸送特性の比較を行った。特に、両装置のプラズマ形状,規格化衝突周波数,規格化ラーモア半径等の無次元変数を揃えた場合に着目した。その結果、内部輸送障壁の形成機構については、共通の形成条件があるが、定常状態での密度分布に大きな差異があることが明らかになった。この差異は、中心付近の磁気シアの違いに起因していると考えられる。
村上 和功*; Park, J. M.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Garcia, J.*; Bonoli, P.*; Budny, R. V.*; Doyle, E. J.*; 福山 淳*; 林 伸彦; 本多 充; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Recent progress on ITER steady-state scenario modeling by the ITPA-IOS group is reviewed. Code-to-code benchmarks as the IOS group's common activities for the two steady-state scenarios (weak shear scenario and internal transport barrier scenario) are reviewed. These are discussed in terms of transport and kinetic profiles, heating and CD sources using various transport codes.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; 福山 淳*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; 林 伸彦; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
In order to prepare adequate current ramp-up and ramp-down scenarios for ITER, present experiments from various tokamaks have been analysed by means of integrated modelling in view of determining relevant heat transport models for these operation phases. The most accurate heat transport models are then applied to projections to ITER current ramp-up, focusing on the baseline inductive scenario (main heating plateau current of Ip = 15 MA). These projections include a sensitivity studies to various assumptions of the simulation. Recent examples of such simulations, involving coupled core transport codes, free boundary equilibrium solvers and a poloidal field (PF) systems controller are described in the second part of the paper, focusing on ITER current ramp-down.
林 伸彦; Parail, V.*; Koechl, F.*; 相羽 信行; 滝塚 知典; Wiesen, S.*; Lang, P.*; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久; JET-EFDA Contributors*
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/03
Two integrated core / scrape-off-layer (SOL) / divertor transport codes TOPICS-IB and JINTRAC with links to MHD stability codes have been coupled with models of pellet injection to clarify effects of pellet on the behavior of edge localized modes (ELMs). The energy absorption by pellet and its further displacement due to E B drift as well as transport enhancement by the pellet were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes the radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent E
B drift as well as transport enhancement by the pellet were found to be able to trigger the ELM. The ablated cloud of pellet absorbs the background plasma energy and causes the radial redistribution of pressure due to the subsequent E B drift. On the other hand, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of an increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
B drift. On the other hand, the sharp increase in local density and temperature gradients in the vicinity of ablated cloud could cause transient enhancement of heat and particle transport. Both mechanisms produce a region of an increased pressure gradient in the background plasma profile within the pedestal, which triggers the ELM. The mechanisms have the potential to explain a wide range of experimental observations.
Imbeaux, F.*; Basiuk, V.*; Budny, R.*; Casper, T.*; Citrin, J.*; Fereira, J.*; 福山 淳*; Garcia, J.*; Gribov, Y. V.*; 林 伸彦; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
ITERでの電流立ち上げ・立ち下げシナリオの準備に向けて、これら運転状態においてどの熱輸送モデルが適切であるかを決定するために、代表的なトカマクでの現在の実験結果を統合モデルシミュレーションにより解析した。本研究では、トカマク実験の解析結果をもとに、ITER標準誘導運転(プラズマ電流15MA)の電流立ち上げ・立ち下げシナリオでの予測を行った。統合モデルシミュレーション結果を、ASDEX Upgrade, C-Mod, DIII-D, JET, Tore Supraのオーミック加熱プラズマ及び外部加熱・電流駆動プラズマ実験データと比較することにより、さまざまな輸送モデルの検証を行った。最も実験結果の再現性の良かった幾つかのモデルを用いて、ITERの電流立ち上げ・立ち下げ段階での電子密度・電流密度プロファイルの予測を行った。電子温度プロファイルには輸送モデルによって大きな差が見られたが、最終的な電流密度プロファイルはモデル間でよく一致することがわかった。
林 伸彦; 滝塚 知典; 相羽 信行; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久; Wiesen, S.*; Parail, V.*
Nuclear Fusion, 49(9), p.095015_1 - 095015_8, 2009/09
被引用回数:17 パーセンタイル:50.64(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Energy loss due to an edge localized mode (ELM) crash and its cycle have been studied by using an integrated core transport code with a stability code for peeling-ballooning modes and a transport model of scrape-off-layer (SOL) and divertor plasmas. The integrated code reproduces a series of ELMs in which the ELM energy loss increases with decreasing collisionality and the ELM frequency increases linearly with the input power, as seen in experiments of type-I ELMs. A transport model with the neoclassical transport in the pedestal connected to the SOL parallel transport reproduces a lowered inter-ELM transport in the case of low collisionality so that the ELM loss power is enhanced as observed in experiments. The inter-ELM energy confinement time evaluated from simulation results agrees with the JT-60U scaling. The steep pressure gradient in the core just beyond the pedestal top, desirable for improved H-mode plasmas with the 
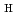 factor above unity, is found to enhance the ELM energy loss and reduce the ELM frequency so that the ELM loss power remains constant. The steep pressure gradient in the core beyond the pedestal top broadens eigenfunction profiles of unstable modes and possibly induces subsequent instabilities. In the subsequent instabilities, when a large energy is transported to the vicinity of the separatrix by the instabilities, a subsequent instability arises near the separatrix and makes an additional loss.
factor above unity, is found to enhance the ELM energy loss and reduce the ELM frequency so that the ELM loss power remains constant. The steep pressure gradient in the core beyond the pedestal top broadens eigenfunction profiles of unstable modes and possibly induces subsequent instabilities. In the subsequent instabilities, when a large energy is transported to the vicinity of the separatrix by the instabilities, a subsequent instability arises near the separatrix and makes an additional loss.
Sips, A. C. C.*; Casper, T.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hutchinson, I.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 49(8), p.085015_1 - 085015_11, 2009/08
被引用回数:58 パーセンタイル:87.44(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)ITERにおける放電の時間発展に関して、実験的に検証した。すなわち、着火から電流立ち上げ,電流フラットトップ,電流立ち下げである。着火に関しては、JETのような大型トカマクではECRFによる補助なしで、またECRFによる補助が有る場合にはすべての装置でITERの要求である一周電界 0.35V/mでの着火を確認できた。立ち上げ時には、早期にダイバータ移行し大きなプラズマ断面を早くに形成することによりインダクタンスをよく制御できることがわかった。フラットトップでの種々の特性、特にH-mode遷移後と逆遷移後のインダクタンスの変化についてデータが得られた。
0.35V/mでの着火を確認できた。立ち上げ時には、早期にダイバータ移行し大きなプラズマ断面を早くに形成することによりインダクタンスをよく制御できることがわかった。フラットトップでの種々の特性、特にH-mode遷移後と逆遷移後のインダクタンスの変化についてデータが得られた。
篠原 孝司; 及川 聡洋; 浦野 創; 大山 直幸; L nnroth, J.*; Saibene, G.*; Parail, V.*; 鎌田 裕
nnroth, J.*; Saibene, G.*; Parail, V.*; 鎌田 裕
Fusion Engineering and Design, 84(1), p.24 - 32, 2009/01
被引用回数:27 パーセンタイル:83.84(Nuclear Science & Technology)By using a fully three dimensional magnetic field orbit-following Monte-Carlo code, the energetic ion confinement was investigated for the current conceptual design of the ferromagnetic components in ITER which will be employed for reducing the toroidal magnetic field (TF) ripple. The ferromagnetic insert is effective in the reference Scenario No. 2 and Scenario No. 4 to improve the energetic ion confinement. Over-compensation appears at half of the full toroidal magnetic field and its effect becomes stronger when the amount of the ferromagnetic insert is increased. Whether to increase the ferromagnetic insert to achieve lower TF ripple amplitude at the full field operation depends on how prospected are possibilities of lower field operations. Planned test blanket modules do not induce large loss at the full field in Scenario No. 4. At the half field, however, the loss reaches 10% for the alpha particles due to localized large TF ripple.
Roach, C. M.*; Walters, M.*; Budny, R. V.*; Imbeaux, F.*; Fredian, T. W.*; Greenwald, M.*; Stillerman, J. A.*; Alexander, D. A.*; Carlsson, J.*; Cary, J. R.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 48(12), p.125001_1 - 125001_19, 2008/12
被引用回数:35 パーセンタイル:25.40(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)本論文では、国際トカマク物理活動において構築し2008年に一般公開した分布データベースについて述べる。分布データベースは、プラズマ輸送特性を記述するモデルの検証に活用される。1998年に一般公開した分布データベースに加えて、世界のトカマク装置(11台)で得られた代表的な分布データ(約100放電)を新たに登録している。例えば、JETとTFTRで実施されたDT放電、各装置で得られた内部輸送障壁を持つ放電やハイブリッド運転シナリオの放電などが含まれており、新規登録されたすべての放電の目的や特徴を装置ごとに記述している。また、分布データベースはftp, http, MDSplusを通して読み出しが可能である。
Sips, A. C. C.*; Casper, T. A.*; Doyle, E. J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; Gribov, Y.*; Hobirk, J.*; Hogeweij, G. M. D.*; Horton, L. D.*; Hubbard, A. E.*; Hutchinson, I.*; et al.
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
ITERにおける放電の時間発展に関して、実験的に検証した。すなわち、着火から電流立ち上げ,電流フラットトップ,電流たち下げである。着火に関しては、JETのような大型トカマクではECRFによる補助なしで、またECRFによる補助が有る場合にはすべての装置でITERの要求である一周電界 0.35V/mでの着火を確認できた。立ち上げ時には、早期にダイバータ移行し大きなプラズマ断面を早くに形成することによりインダクタンスをよく制御できることがわかった。フラットトップでの種々の特性、特にH-mode遷移後と逆遷移後のインダクタンスの変化についてデータが得られた。
0.35V/mでの着火を確認できた。立ち上げ時には、早期にダイバータ移行し大きなプラズマ断面を早くに形成することによりインダクタンスをよく制御できることがわかった。フラットトップでの種々の特性、特にH-mode遷移後と逆遷移後のインダクタンスの変化についてデータが得られた。
林 伸彦; 滝塚 知典; 相羽 信行; 大山 直幸; 小関 隆久; Wiesen, S.*; Parail, V.*
Proceedings of 22nd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2008) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/10
The energy loss due to an edge localized mode (ELM) crash and its cycle have been studied by using an integrated transport code with a stability code for peeling-ballooning modes and a transport model of scrape-off-layer (SOL) and divertor plasmas. The integrated code reproduces a series of ELMs with the following characteristics. The ELM energy loss increases with decreasing the collisionality and the ELM frequency increases linearly with the input power, as the same as experiments of type-I ELMs. A transport model with the pedestal neoclassical transport connected to the SOL parallel transport reproduces the inter-ELM transport, which decreases in the low collisionality so that the ELM loss power is enhanced as observed in experiments. The inter-ELM energy confinement time agrees with the scaling based on the JT-60U data. The steep pressure gradient inside the pedestal top, required for improved H-mode plasmas with the 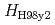 factor above unity, is found to enhance the ELM energy loss and reduce the ELM frequency so that the ELM loss power remains constant. The steep pressure gradient inside the pedestal top broadens the region of the ELM enhanced transport and induces subsequent instabilities. When the large energy is transported near to the separatrix by the instabilities, a subsequent instability arises near the separatrix and makes an additional loss.
factor above unity, is found to enhance the ELM energy loss and reduce the ELM frequency so that the ELM loss power remains constant. The steep pressure gradient inside the pedestal top broadens the region of the ELM enhanced transport and induces subsequent instabilities. When the large energy is transported near to the separatrix by the instabilities, a subsequent instability arises near the separatrix and makes an additional loss.
de Vries, P. C.*; Salmi, A.*; Parail, V.*; Giroud, C.*; Andrew, Y.*; Biewer, T. M.*; Cromb , K.*; Jenkins, I.*; Johnson, T.*; Kiptily, V.*; et al.
, K.*; Jenkins, I.*; Johnson, T.*; Kiptily, V.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 48(3), p.035007_1 - 035007_6, 2008/03
被引用回数:50 パーセンタイル:85.50(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)JETにおいてトロイダル磁場リップルがトカマクプラズマの性能に与える影響を調べた結果、トロイダル磁場リップルがプラズマの回転に大きな影響を及ぼすことがわかった。回転速度を熱速度で規格化したマッハ数(M)は、トロイダル磁場リップル強度の関数として減少する。プラズマ中心部のMは、JETの通常の運転におけるリップル率0.08%におけるM=0.4-0.55に対し、0.5%ではM=0.25-0.40、1%ではM=0.1-0.3と減少する。プラズマ電流と同じ方向の中性粒子ビーム入射を用いる通常の実験では、プラズマ電流と同じ方向にプラズマが回転する。しかし、トロイダル磁場リップルが大きい場合( 1%)、プラズマ中心部ではプラズマ電流と同じ方向に回転するものの、プラズマ周辺部ではプラズマ電流と逆方向に回転することがわかった。
1%)、プラズマ中心部ではプラズマ電流と同じ方向に回転するものの、プラズマ周辺部ではプラズマ電流と逆方向に回転することがわかった。
大山 直幸; Saibene, G.*; 鎌田 裕; 神谷 健作; Loarte, A.*; L nnroth, J.*; Parail, V.*; 坂本 宜照; Salmi, A.*; Sartori, R.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; Parail, V.*; 坂本 宜照; Salmi, A.*; Sartori, R.*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 123, p.012015_1 - 012015_13, 2008/00
被引用回数:10 パーセンタイル:91.01(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)JETとJT-60Uにおいてトロイダル磁場リップルと周辺トロイダル回転がHモード・ペデスタル性能やELM特性に与える影響を調べた。JT-60Uでは、フェライト鋼の設置により平均磁場リップルを約1.2%から約0.5%に低減することができた。一方、JETでは、コイル電流を変えることでリップル率を能動的に変化できる。どちらの装置も、リップル率を増やすとプラズマ電流方向(co方向)のトロイダル回転が減少する。しかし、同じリップル率0.5%で比較しても、JETの回転よりJT-60Uの回転は小さい。一連のパワースキャン,密度スキャンの結果、小さいリップル率か大きなco方向回転が高いペデスタル性能と閉じ込め性能には適していることがわかった。ELM特性に関しては、大きなco方向回転がELMによるエネルギー損失を増加させると考えられる。
Saibene, G.*; 大山 直幸; L nnroth, J.*; Andrew, Y.*; la Luna, E. de.*; Giroud, C.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; 鎌田 裕; Kempenaars, M. A. H.*; Loarte, A.*; et al.
nnroth, J.*; Andrew, Y.*; la Luna, E. de.*; Giroud, C.*; Huysmans, G. T. A.*; 鎌田 裕; Kempenaars, M. A. H.*; Loarte, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(8), p.969 - 983, 2007/08
被引用回数:37 パーセンタイル:74.86(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)JETとJT-60Uにおいて、プラズマ形状を一致させてプラズマの比較を行う実験を行った。この配位は、安全係数,非円形度,三角度,小半径が両装置でほぼ等しく、大半径はJT-60Uの方が15%大きい。このとき、無次元パラメータが両装置で一致するためには、同じペデスタル密度のプラズマに対してJT-60Uのペデスタル温度が約20%高いことが要求されるがJT-60Uのペデスタル圧力はJETより低い値に留まった。両装置で大きく異なっているものがトロイダル磁場リップルとトロイダル回転速度であることに着目し、JETでは接線方向のNBIの代わりに垂直入射NBIもしくはICRHを使用した実験を、JT-60Uでは垂直NBIの代わりに負イオン源を用いたCO方向NBIを用いた実験を行った。その結果、JETではペデスタル圧力が低下し、JT-60Uではペデスタル圧力の上昇が観測された。JT-60Uではペデスタル圧力の上昇と同時にELMの周波数や振幅,圧力勾配も変わっている。ペデスタル圧力の改善は見られたが、プラズマ全体の閉じ込めは依然としてJETよりも低く、コアプラズマの性能は別の機構により制限されていると思われる。
Doyle, E. J.*; Houlberg, W. A.*; 鎌田 裕; Mukhovatov, V.*; Osborne, T. H.*; Polevoi, A.*; Bateman, G.*; Connor, J. W.*; Cordey, J. G.*; 藤田 隆明; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 47(6), p.S18 - S127, 2007/06
本稿は、国際熱核融合実験炉(ITER)の物理基盤に関し、プラズマ閉じ込めと輸送に関する最近7年間(1999年に発刊されたITER Physics Basis後)の世界の研究の進展をまとめたものである。輸送物理一般、プラズマ中心部での閉じ込めと輸送,Hモード周辺ペデスタル部の輸送とダイナミクス及び周辺局在化モード(ELM)、そして、これらに基づいたITERの予測について、実験及び理論・モデリングの両面から体系的に取りまとめる。