Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 TaS
TaS
Park, P.*; Cho, W.*; Kim, C.*; An, Y.*; Avdeev, M.*; Iida, Kazuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Park, J.-G.*
Physical Review B, 109(6), p.L060403_1 - L060403_7, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.81(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Maurer, C.*; Galmarini, S.*; Solazzo, E.*; Ku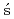 mierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Bar
mierczyk-Michulec, J.*; Bar , J.*; Kalinowski, M.*; Schoeppner, M.*; Bourgouin, P.*; Crawford, A.*; Stein, A.*; et al.
, J.*; Kalinowski, M.*; Schoeppner, M.*; Bourgouin, P.*; Crawford, A.*; Stein, A.*; et al.
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 255, p.106968_1 - 106968_27, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.52(Environmental Sciences)After performing multi-model exercises in 2015 and 2016, a comprehensive Xe-133 atmospheric transport modeling challenge was organized in 2019. For evaluation measured samples for the same time frame were gathered from four International Monitoring System stations located in Europe and North America with overall considerable influence of IRE and/or CNL emissions. As a lesion learnt from the 2nd ATM-Challenge participants were prompted to work with controlled and harmonized model set ups to make runs more comparable, but also to increase diversity. Effects of transport errors, not properly characterized remaining emitters and long IMS sampling times (12 to 24 hours) undoubtedly interfere with the effect of high-quality IRE and CNL stack data. An ensemble based on a few arbitrary submissions is good enough to forecast the Xe-133 background at the stations investigated. The effective ensemble size is below five.
Park, Y.-J.*; Sawada, Atsushi; Ozutsumi, Takenori*; Tanaka, Tatsuya*; Hashimoto, Shuji*; Morita, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Discrete Fracture Network Engineering (DFNE 2022) (Internet), 8 Pages, 2022/00
Safety analysis for underground disposal facilities for high-level radioactive waste requires thorough understanding of long-term groundwater flow and nuclide migration processes in geologic media. In the coastal subsurface systems, groundwater flow is defined by the complex interactions between freshwater of meteoric origin and denser saline water from the sea. In addition, sea levels are expected to fluctuate significantly due to a transgression and regression of the sea over the millions of years for safety analysis. This study presents long-term evolution of groundwater environment such as salinity concentration and flow velocity with focus of the interaction between fractures and matrix blocks in regional and near-field scale analysis framework for groundwater flow and nuclide migration for underground disposal facilities in hypothetical fractured crystalline coastal systems.

Park, J. S.*; Harada, Masahide; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sakai, Kenji; Suzuya, Kentaro; 55 of others*
Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (Internet), 2021(6), p.063C01_1 - 063C01_12, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.54(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kim, S. B.*; Zhang, Y.*; Won, S. M.*; Bandodkar, A. J.*; Sekine, Yurina; Xue, Y.*; Koo, J.*; Harshman, S. W.*; Martin, J. A.*; Park, J. M.*; et al.
Small, 14(12), p.1703334_1 - 1703334_11, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:128 Percentile:96.23(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Luce, T. C.*; Challis, C. D.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Joffrin, E.*; Kamada, Yutaka; Politzer, P. A.*; Schweinzer, J.*; Sips, A. C. C.*; Stober, J.*; Giruzzi, G.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 54(1), p.013015_1 - 013015_15, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:45 Percentile:87.18(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Park, J.*; Takayama, Toshio*; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Kudo, Kazuaki*; Takayama, Toshio*
Polymer, 54(17), p.4570 - 4577, 2013/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:18.11(Polymer Science)Graft-type sulfonated polybenzimidazole was prepared through radiation-induced graft polymerization of styrenes into an alicyclic polybenzimidazole film and subsequent sulfonation. The alicyclic polybenzimidazole, ChPBI, was prepared from 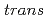 -1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid and 3,3'-diaminobenzidine using typical polycondensation. Anisotropic domains with a size of several tens of micrometers were found in the ChPBI films casted from LiCl-containing
-1,4-cyclohexanedicarboxylic acid and 3,3'-diaminobenzidine using typical polycondensation. Anisotropic domains with a size of several tens of micrometers were found in the ChPBI films casted from LiCl-containing  ,
, -dimethylacetamide. Irradiation of the ChPBI membranes with a 220 kGy dose of
-dimethylacetamide. Irradiation of the ChPBI membranes with a 220 kGy dose of  -rays created radical species with mean lifetimes of two days. The treatment of this membrane with a 50/50 (v/v) mixture of 1-propanol and styrene produced polystyrene graft chains. Sulfonation of the resulting grafted membrane with ClSOH
-rays created radical species with mean lifetimes of two days. The treatment of this membrane with a 50/50 (v/v) mixture of 1-propanol and styrene produced polystyrene graft chains. Sulfonation of the resulting grafted membrane with ClSOH OH occurred selectively on the polystyrene grafts. The sulfonated films showed proton conductivity on the order of 10
OH occurred selectively on the polystyrene grafts. The sulfonated films showed proton conductivity on the order of 10 to 10
to 10 S/cm with an ion exchange capacity between 2.1 and 2.9 mmol/g. SEM-EDX analysis of the membrane indicated the presence of macrophase separated domains up to 1
S/cm with an ion exchange capacity between 2.1 and 2.9 mmol/g. SEM-EDX analysis of the membrane indicated the presence of macrophase separated domains up to 1  m in diameter. The proton conductivity of the membrane did not decrease for 600 h at 120
m in diameter. The proton conductivity of the membrane did not decrease for 600 h at 120 C in liquid water.
C in liquid water.
Park, J.; Enomoto, Kazuyuki; Yamashita, Takashi*; Takagi, Yasuyuki*; Todaka, Katsunori*; Maekawa, Yasunari
Journal of Membrane Science, 438, p.1 - 7, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:42.96(Engineering, Chemical)Alicyclic polyimides (APIs) were successfully applied to radiation-induced graft polymerization for developing polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells. The grafting into fully aromatized polyimide barely proceeded (grafting degrees (GDs) of less than 5%), whereas that of styrene into the API films proceeded with styrene GDs of up to 70%. In combination of electron spin resonance measurements and ultraviolet-visible (UV-VIS) spectroscopy, the radical species was identified as a long-lived intermediate and 10% of the radicals were consumed as grafting initiators. The moderate reaction conditions allowed for selective sulfonation on the polystyrene grafts, and not on the API substrates, to give API-based polymer electrolyte membranes (PEMs) with ion exchange capacities (IEC) of 1.7-2.8 mmol/g. The PEMs exhibited appropriate proton conductivity and low water uptake, together with excellent mechanical properties, compared with conventional PEMs such as Nafion.
Pace, D. C.*; Austin, M. E.*; Bass, E. M.*; Budny, R.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hillesheim, J. C.*; Holcomb, C. T.*; Gorelenkova, M.*; Grierson, B. A.*; McCune, D. C.*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 20(5), p.056108_1 - 056108_18, 2013/05
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:81.13(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Energetic ion transport due to microturbulence is investigated in MHD-quiescent plasmas by way of neutral beam injection in the DIII-D tokamak. A range of on-axis and off-axis beam injection scenarios are employed to vary relevant parameters such as the character of the background microturbulence and the value of Eb/Te, where Eb is the energetic ion energy and Te the electron temperature. In all cases it is found that any transport enhancement due to microturbulence is too small to observe experimentally. These transport effects are modeled using numerical and analytic expectations that calculate the energetic ion diffusivity due to microturbulence. It is determined that energetic ion transport due to coherent modes, including possible reductions in neutral beam current drive, is a considerably larger effect and should therefore be considered more important for ITER.
Sumita, Junya; Shibata, Taiju; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Fujita, Ichiro; Ohashi, Jun*; Takizawa, Kentaro*; Kim, W.*; Park, J.*
Ceramic Materials for Energy Applications; Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceedings, Vol.32, No.9, p.1 - 12, 2011/11
Since the temperature condition in Very High Temperature Reactor (VHTR), one of the Generation-IV reactor systems, is severe, the application of heat-resistant carbon fiber reinforced carbon matrix composite (C/C composite) for control rod elements is one of the important subjects for the VHTR development. JAEA focuses on the application of two-dimensional (2D-) C/C composites for control rod. The 2D-C/C composite has an anisotropy in properties for parallel and perpendicular to lamina directions. Irradiation effects of the 2D-C/C composite also show anisotropic behavior. It is hence important to consider the anisotropy in control rod design. To investigate the irradiation effects of the 2D-C/C composite on properties, irradiation test and post irradiation examination (PIE) were carried out and the irradiation effects were evaluated for the both directions. Since the C/C composite is composed of fibers and matrix, this geometry should be considered to evaluate the crack propagation in the composite. To assess the fracture behavior with crack propagation, bending test was carried out assuming a crack in the control rod and cracks in specimens were observed. This paper describes the irradiation effects of the 2D-C/C composite based on the PIE results considering the anisotropy. The evaluation results on equivalent fracture toughness and fracture mechanism are also discussed.
Sumita, Junya; Fujita, Ichiro; Shibata, Taiju; Makita, Taiyo*; Takagi, Takashi*; Kunimoto, Eiji*; Sawa, Kazuhiro; Kim, W. J.*; Park, J. Y.*
IOP Conference Series; Materials Science and Engineering, 18(16), p.162010_1 - 162010_4, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:50.35(Materials Science, Ceramics)For control rod element of Very High Temperature Reactor, carbon fiber reinforced carbon matrix composite (C/C composite) is one of the major candidate materials for its high strength and thermal stability. Since the crack propagation of the C/C composite is complicated, the fracture behavior is one of the most important subjects of the design methodology for the control rod with the C/C composite. In this study, in order to assess the Mode-II fracture behavior of the two-dimensional (2D-) C/C composite which has the layer structure of laminas composed of fibers and matrix, bending test with oxidized end notched flexure specimen was carried out. The interlaminar fracture toughness decreased with increasing the oxidation for the 2D-C/C composite. The oxidized matrix causes reduction of fracture toughness and the reduction ratio is dependent on the matrix type. The crack initiates at the boundary between fiber bundles and grows along them without breaking the fiber. It is thought that the cracks which were initiated at the interface between matrix and fiber were gathered into the voids in the boundary between fiber bundles, and then the crack grows up in the matrix.
Suzuki, Takahiro; Akers, R.*; Gates, D. A.*; G nter, S.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hobirk, J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Murakami, Masanori*; Park, J. M.*; Turnyanskiy, M.*; et al.
nter, S.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hobirk, J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Murakami, Masanori*; Park, J. M.*; Turnyanskiy, M.*; et al.
Nuclear Fusion, 51(8), p.083020_1 - 083020_8, 2011/08
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:60.06(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)Joint experiments investigating the off-axis neutral beam current drive (NBCD) capability to be utilized for advanced operation scenario development in ITER was conducted in 5 tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JT-60U, MAST and NSTX) through the ITPA. We discuss results obtained in the joint experiments, where the toroidal field, 
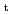 , covered 0.3-3.7 T, the plasma current,
, covered 0.3-3.7 T, the plasma current, 
 , 0.6-1.2 MA, and the beam energy, Eb, 67-350 keV. A current profile broadened by off-axis NBCD was observed in MAST. In DIII-D, good agreement between the measured and calculated NB driven current profile was observed. In JT-60U, agreement between measured and calculated NBCD location was obtained, when the NBCD location (0.3-0.6 in
, 0.6-1.2 MA, and the beam energy, Eb, 67-350 keV. A current profile broadened by off-axis NBCD was observed in MAST. In DIII-D, good agreement between the measured and calculated NB driven current profile was observed. In JT-60U, agreement between measured and calculated NBCD location was obtained, when the NBCD location (0.3-0.6 in  /
/ ), heating power (6-13 MW), triangularity
), heating power (6-13 MW), triangularity  (0.25-0.45), and
(0.25-0.45), and 
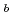 (85 and 350 keV) were widely scanned. In AUG (at low
(85 and 350 keV) were widely scanned. In AUG (at low 
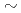 0.2) and DIII-D, introduction of a fast ion diffusion coefficient of
0.2) and DIII-D, introduction of a fast ion diffusion coefficient of 
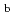 0.3-0.5 m
0.3-0.5 m /s in the calculation gave better agreement at high heating power (5 and 7.2 MW), suggesting anomalous transport of fast ions by turbulence. It was found through these ITPA joint experiments that NBCD related physics quantities reasonably agree with calculations (with
/s in the calculation gave better agreement at high heating power (5 and 7.2 MW), suggesting anomalous transport of fast ions by turbulence. It was found through these ITPA joint experiments that NBCD related physics quantities reasonably agree with calculations (with 
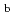 = 0-0.5 m
= 0-0.5 m /s) in all devices when there is no MHD activity except ELMs. Proximity of measured off-axis beam driven current to the corresponding calculation with
/s) in all devices when there is no MHD activity except ELMs. Proximity of measured off-axis beam driven current to the corresponding calculation with 
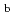 = 0 has been discussed for ITER in terms of a theoretically predicted scaling of fast-ion diffusion that depends on
= 0 has been discussed for ITER in terms of a theoretically predicted scaling of fast-ion diffusion that depends on 
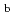 /
/
 for electrostatic turbulence or
for electrostatic turbulence or 
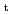 for electromagnetic turbulence.
for electromagnetic turbulence.
Suzuki, Takahiro; Akers, R.*; Gates, D. A.*; G nter, S.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hobirk, J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Murakami, Masanori*; Park, J. M.*; Turnyanskiy, M.*; et al.
nter, S.*; Heidbrink, W. W.*; Hobirk, J.*; Luce, T. C.*; Murakami, Masanori*; Park, J. M.*; Turnyanskiy, M.*; et al.
Proceedings of 23rd IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2010) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2010/10
Joint experiments investigating the off-axis neutral beam current drive (NBCD) capability to be utilized for advanced operation scenario development in ITER was conducted in 4 tokamaks (AUG, DIII-D, JT-60U and MAST) through the ITPA. We discuss results obtained in the joint experiments, where the toroidal field, Bt, covered 0.3-3.7 T, the plasma current, Ip, 0.6-1.2 MA, and the beam energy, Eb, 67-350 keV. A current profile broadened by off-axis NBCD was observed in MAST. In DIII-D, good agreement between the measured and calculated NB driven current profile was observed. In JT-60U, agreement between measured and calculated NBCD location was obtained, when the NBCD location (0.3-0.6 in r/a), heating power (6-13 MW), triangularity d (0.25-0.45), and Eb (85 and 350 keV) were widely scanned. In AUG (at low d 0.2) and DIII-D, introduction of a fast ion diffusion coefficient of Db 0.3-0.5 m /s in the calculation gave better agreement at high heating power (5 and 7.2 MW), suggesting anomalous transport of fast ions by turbulence. It was found through these ITPA joint experiments that NBCD related physics quantities reasonably agree with calculations (with Db=0-0.5 m
/s in the calculation gave better agreement at high heating power (5 and 7.2 MW), suggesting anomalous transport of fast ions by turbulence. It was found through these ITPA joint experiments that NBCD related physics quantities reasonably agree with calculations (with Db=0-0.5 m /s) in all devices when there is no MHD activity except ELMs.
/s) in all devices when there is no MHD activity except ELMs.
Nozawa, Takashi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Park, J.-S.*; Koyama, Akira*
Proceedings of 33rd International Conference on Advanced Ceramics and Composites (CD-ROM), p.65 - 76, 2009/09
SiC/SiC composites are promising candidate materials for various energy industries. One of key issues for their practical application is to develop design basis of quasi-ductile composites. Understanding the crack propagation behavior is therefore essential. For this purpose, determining a fracture resistances undoubtedly important and this paper aims to evaluate this using various types of notched specimens. With the preliminary analysis by the authors, a new methodology to determine the fracture resistance has been developed based on the non-linear fracture mechanics, separately discussing the effect of irreversible energies. By adopting this method for nano-infiltration transient-eutectic-phase sintered (NITE) SiC/SiC composites, several key findings were obtained: (1) notch insensitivity, (2) no significant size effect, and (3) superior crack tolerance.
Park, J.*; Enomoto, Kazuyuki; Yamashita, Takashi*; Takagi, Yasuyuki*; Todaka, Katsunori*; Maekawa, Yasunari
Journal of Photopolymer Science and Technology, 22(3), p.285 - 287, 2009/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Polymer Science)Alicyclic Polyimide (A-PI) films were utilized as a substrate of radiation-induced polymerization to prepare PEM for fuel cells. We successfully prepared the A-PI- PEM by radiation-induced grafting of styrene into A-PI films and subsequent sulfonation. The obtained A-PI-PEM has higher ion conductivity and mechanical and thermal properties, compared with conventional PEM (Nafion). Furthermore, the long-lived intermediates in irradiated A-PI films were observed in the UV-VIS spectra. In comparison with the decay profile of ESR spectra of irradiated A-PI films, the initiation radicals (600, 420 nm) and radical anion (720 nm) can be characterized in terms of the graft polymerization mechanism of A-PI films.
Sakakibara, Tetsuro; Aoyama, Yoshio; Yamaguchi, Hiromi; Sasaki, Naoto*; Nishikawa, Takeshi*; Murata, Minoru*; Park, J.*; Taniguchi, Shoji*; Fujita, Michiru*; Fukuda, Tomoyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of International Waste Management Symposium 2009 (WM '09) (CD-ROM), 15 Pages, 2009/03
The volume reduction treatment of solid waste system by ultra-high frequency induction furnace (UHFIF) was developed from FY2005 to FY2007. Basic data for melting performance were collected by non-radioactive experiments using the bench scale UHFIF with a crucible capacity of 10 liters. Based on the obtained data, engineering specifications were evaluated for a demonstration scale UHFIF with a crucible capacity of 30 liters. A new demonstration scale UHFIF was constructed and melting experiments of surrogate wastes were carried out by this furnace. It was confirmed that the demonstration scale UHFIF can melt ferrous metal, ceramics and aluminum all together and stabilize aluminum by oxidation to alumina. Density, chemical composition, and surface condition of the solidified substances were analyzed, and homogeneity of the solidified substances was confirmed. Melting behavior in the demonstration scale UHFIF was analyzed by computer simulation and simulation results agreed well with the experimental ones. From the design study for a full scale UHFIF with a crucible capacity of 100 liters, basic specifications were evaluated for the full scale UHFIF. Based on the obtained specification, melting behavior in the full scale UHFIF was analyzed by computer simulation.
Kim, K. Y.*; Hwang, Y. S.*; Park, J.-G.*; Torikai, Naoya*; Takeda, Masayasu; Han, S. W.*; Shin, S. C.*
Physica Status Solidi (B), 244(12), p.4499 - 4502, 2007/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:6.30(Physics, Condensed Matter)We have investigated the effect of the field cooling on the exchange bias and the coercivity in an exchange-biased Fe/Cr(100) bilayer using SQUID magnetometer. After the field cooling, magnetization shifted upwards, indicative of surplus magnetic moments, which could be interpreted as an evidence of pinned and uncompensated Cr magnetic moments induced by the cooling field. Interestingly enough, we also discovered that not all the pinned and uncompensated spins seem to be involved in producing the exchange bias, although they contribute to increasing the coercivity and inducing the surplus magnetization.
 Ru
Ru O
O and the possible formation of Haldane chains in three-dimensional crystals
and the possible formation of Haldane chains in three-dimensional crystalsLee, S.*; Park, J.-G.*; Adroja, D. T.*; Khomskii, D.*; Streltsov, S.*; McEwen, K. A.*; Sakai, Hironori; Yoshimura, Kazuyoshi*; Anisimov, V. I.*; Mori, Daisuke*; et al.
Nature Materials, 5(6), p.471 - 476, 2006/06
Times Cited Count:116 Percentile:94.44(Chemistry, Physical)Here we show that the three-dimensional cubic system of Tl Ru
Ru O
O most probably evolves into a one-dimensional spin-one Haldane system with a spin gap below 120 K, accompanied by anomalies in the structure, resistivity, and susceptibility. We argue that these anomalies are due to an orbital ordering of Ru
most probably evolves into a one-dimensional spin-one Haldane system with a spin gap below 120 K, accompanied by anomalies in the structure, resistivity, and susceptibility. We argue that these anomalies are due to an orbital ordering of Ru 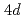 electrons, with a strong coupling among three degrees of freedom: orbital, spin, and lattice. Our work provides a unique example of the spontaneous formation of Haldane system with an insight into the intriguing interplay of different degrees of freedom.
electrons, with a strong coupling among three degrees of freedom: orbital, spin, and lattice. Our work provides a unique example of the spontaneous formation of Haldane system with an insight into the intriguing interplay of different degrees of freedom.
Lee, J.-K.; Naganuma, Masayuki; Park, J.-S.*; Koyama, Akira*
Proceedings of International Conference on Nuclear Energy System for Future Generation and Global Sustainability (GLOBAL 2005) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2005/10
The possibility of SiC/SiC (Silicon carbide fiber reinforced Silicon carbide) composites application for fuel sub-assembly of Fast Breeder Reactor was investigated. To select a raw material of SiC/SiC composites, a few kinds of SiC nano powder was estimated by SEM observation and XRD analysis. Furthermore, SiC monolithic was sintered from them and estimated by flexural test. SiC nano-powder which showed good sinterability, it was used for fabrication of SiC/SiC composites by Hot Pressing method. From the sintering condition of 1800, 1820 C temperature and 15, 20MPa pressure, SiC/SiC composite was fabricated and then estimated by tensile test. SiC/SiC composite, which made by 1820
C temperature and 15, 20MPa pressure, SiC/SiC composite was fabricated and then estimated by tensile test. SiC/SiC composite, which made by 1820 C and 20MPa condition, showed the highest mechanical strength by the monotonic tensile test. SiC/SiC composite, which made by 1800
C and 20MPa condition, showed the highest mechanical strength by the monotonic tensile test. SiC/SiC composite, which made by 1800 C and 15MPa condition, showed a stable fracture behavior at the monotonic and cyclic tensile test. And then, the hoop stress of ideal model of SiC/SiC composites was discussed. It was confirmed that applicability of SiC/SiC composites by Hot Pressing method for fuel sub-assembly structural material. To make it real attractive one, to maintain the reliability and safety as a high temperature structural material, the design and process study on SiC/SiC composites material will be continued.
C and 15MPa condition, showed a stable fracture behavior at the monotonic and cyclic tensile test. And then, the hoop stress of ideal model of SiC/SiC composites was discussed. It was confirmed that applicability of SiC/SiC composites by Hot Pressing method for fuel sub-assembly structural material. To make it real attractive one, to maintain the reliability and safety as a high temperature structural material, the design and process study on SiC/SiC composites material will be continued.
Park, S.*; Kono, Hidetoshi; Wang, W.*; Boder, E. T.*; Saven, J. G.*
Computers & Chemical Engineering, 29(3), p.407 - 421, 2005/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:61.22(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)no abstracts in English