Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wu, P.*; Zhang, B.*; Peng, K. L.*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kofu, Maiko; Lee, S. H.*; Kumigashira, Hiroshi*; Hu, C. S.*; Qi, Z. M.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 98(9), p.094305_1 - 094305_7, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:49.03(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Using angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and inelastic neutron scattering, we have studied how electronic structures and lattice dynamics evolve with temperature in Na-doped SnSe.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 84(1), p.012006_1 - 012006_18, 2011/07
Times Cited Count:33 Percentile:75.18(Astronomy & Astrophysics)We report on the event structure and double helicity asymmetry ( ) of jet production in longitudinally polarized
) of jet production in longitudinally polarized  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured
= 200 GeV. Photons and charged particles were measured by the PHENIX experiment. Event structure was compared with the results from PYTHIA event generator. The production rate of reconstructed jets is satisfactorily reproduced with the next-to-leading-order perturbative QCD calculation. We measured  = -0.0014
= -0.0014  0.0037 at the lowest
0.0037 at the lowest  bin and -0.0181
bin and -0.0181  0.0282 at the highest
0.0282 at the highest  bin. The measured
bin. The measured  is compared with the predictions that assume various
is compared with the predictions that assume various 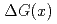 distributions.
distributions.
 collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV
= 200 and 62.4 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(6), p.064903_1 - 064903_29, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:193 Percentile:99.41(Physics, Nuclear)Transverse momentum distributions and yields for  , and
, and  in
in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different
= 200 and 62.4 GeV at midrapidity are measured by the PHENIX experiment at the RHIC. We present the inverse slope parameter, mean transverse momentum, and yield per unit rapidity at each energy, and compare them to other measurements at different  collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as
collisions. We also present the scaling properties such as  and
and  scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in
scaling and discuss the mechanism of the particle production in  collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
collisions. The measured spectra are compared to next-to-leading order perturbative QCD calculations.
 and Au+Au collisions at
and Au+Au collisions at  = 200 GeV
= 200 GeVAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Yasuyuki*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, Kazuya*; Aphecetche, L.*; Aramaki, Y.*; et al.
Physical Review C, 83(4), p.044912_1 - 044912_16, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:54.53(Physics, Nuclear)Measurements of electrons from the decay of open-heavy-flavor mesons have shown that the yields are suppressed in Au+Au collisions compared to expectations from binary-scaled  collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to
collisions. Here we extend these studies to two particle correlations where one particle is an electron from the decay of a heavy flavor meson and the other is a charged hadron from either the decay of the heavy meson or from jet fragmentation. These measurements provide more detailed information about the interaction between heavy quarks and the quark-gluon matter. We find the away-side-jet shape and yield to be modified in Au+Au collisions compared to  collisions.
collisions.
 +
+  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron production
= 200 GeV and scaling properties of hadron productionAdare, A.*; Afanasiev, S.*; Aidala, C.*; Ajitanand, N. N.*; Akiba, Y.*; Al-Bataineh, H.*; Alexander, J.*; Aoki, K.*; Aphecetche, L.*; Armendariz, R.*; et al.
Physical Review D, 83(5), p.052004_1 - 052004_26, 2011/03
Times Cited Count:181 Percentile:98.32(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The PHENIX experiment at RHIC has measured the invariant differential cross section for production of 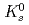 ,
,  ,
,  and
and  mesons in
mesons in  collisions at
collisions at  = 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,
= 200 GeV. The spectral shapes of all hadron transverse momentum distributions are well described by a Tsallis distribution functional form with only two parameters,  and
and  , determining the high
, determining the high  and characterizing the low
and characterizing the low  regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
regions for the spectra, respectively. The integrated invariant cross sections calculated from the fitted distributions are found to be consistent with existing measurements and with statistical model predictions.
Chen, L.-M.; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Hong, W.*; Hua, J. F.*; Kameshima, Takashi; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; Wen, X.*; Wu, Y.*; Tang, C.*; et al.
Chinese Optics Letters, 5(S1), p.S133 - S135, 2007/05
Chen, L.-M.; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Nakajima, Kazuhisa*; Koga, J. K.; Bulanov, S. V.; Tajima, Toshiki; Gu, Y. Q.*; Peng, H. S.*; Wang, X. X.*; Wen, T. S.*; et al.
Physics of Plasmas, 14(4), p.040703_1 - 040703_4, 2007/04
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:74.78(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)An experiment for the laser self-guiding studies has been carried out with 100 TW laser pulse interaction with the long underdense plasma. Formation of extremely long plasma channel with its length, about 10 mm, 20 times above the Rayleigh length is observed. The self-focusing channel features such as the laser pulse significant bending and the electron cavity formation are demonstrated experimentally for the first time.
Kameshima, Takashi; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru; Kawase, Keigo; Fukuda, Yuji; Chen, L. M.*; Homma, Takayuki; Kondo, Shuji; Esirkepov, T. Z.; et al.
no journal, ,
The acceleration method of laser plasma electron acceleration has very strong electric field, however, the acceleration length is veryshort. Hence, the energy gain of electron beams were confined to be approximately 100 MeV. Recently, this problem was solved by using discharge capillary. The feature of plasma was used that high dense plasma has low refractive index. Distributing plasma inside capillary as low dense plasma is in the center of capillary and high dense plasma is in the external side of capillary can make a laser pulse propaget inside capillary with initial focal spot size. Experiments with capillary were performed in China Academy of Engineering Physics (CAEP) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). We obtained the results of 4.4 J laser pulse optical guiding in 4 cm capillary and 0.56 GeV electron production in CAEP in 2006, and 1 J laser pulse optical guiding in 4 cm capillary and electron beams productions.
Koga, J. K.; Chen, L.-M.; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Bulanov, S. V.; Tajima, Toshiki; Gu, Y. Q.*; Peng, H. S.*; Hua, J. F.*; An, W. M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
First experiments for electron acceleration with the laser-gas plasma interaction have been carried out with 30 fs, 100 TW relativistic Ti:Sapphier laser pulse into a long slit (1.2  10 mm
10 mm ) gas plasma. The 10 mm length plasma channel formed that was longer than 20 times the Rayleigh length. Plasma density was the key factor for this long channel stimulation under 100 TW laser pulse irradiation that was much higher than critical power for relativistic self-focusing. For the first time, channel characteristics such as laser bending, hosing and cavity formation were demonstrated experimentally. In case of long channel guiding, accelerated electron bunch was tightly collimated with low emmitance
) gas plasma. The 10 mm length plasma channel formed that was longer than 20 times the Rayleigh length. Plasma density was the key factor for this long channel stimulation under 100 TW laser pulse irradiation that was much higher than critical power for relativistic self-focusing. For the first time, channel characteristics such as laser bending, hosing and cavity formation were demonstrated experimentally. In case of long channel guiding, accelerated electron bunch was tightly collimated with low emmitance 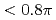 mm mrad and quasi-monoenergetic electron bunch (
mm mrad and quasi-monoenergetic electron bunch ( 70 MeV) was obtained as well. Accelerated electron charge current with electron energy
70 MeV) was obtained as well. Accelerated electron charge current with electron energy  1 MeV was
1 MeV was  10 nC/shot which was highest value in laser accelerator, to our knowledge, and ascribed to the contribution of long plasma channel. These well controlled laser-driven acceleration is an important cornerstone of relativistic engineering.
10 nC/shot which was highest value in laser accelerator, to our knowledge, and ascribed to the contribution of long plasma channel. These well controlled laser-driven acceleration is an important cornerstone of relativistic engineering.